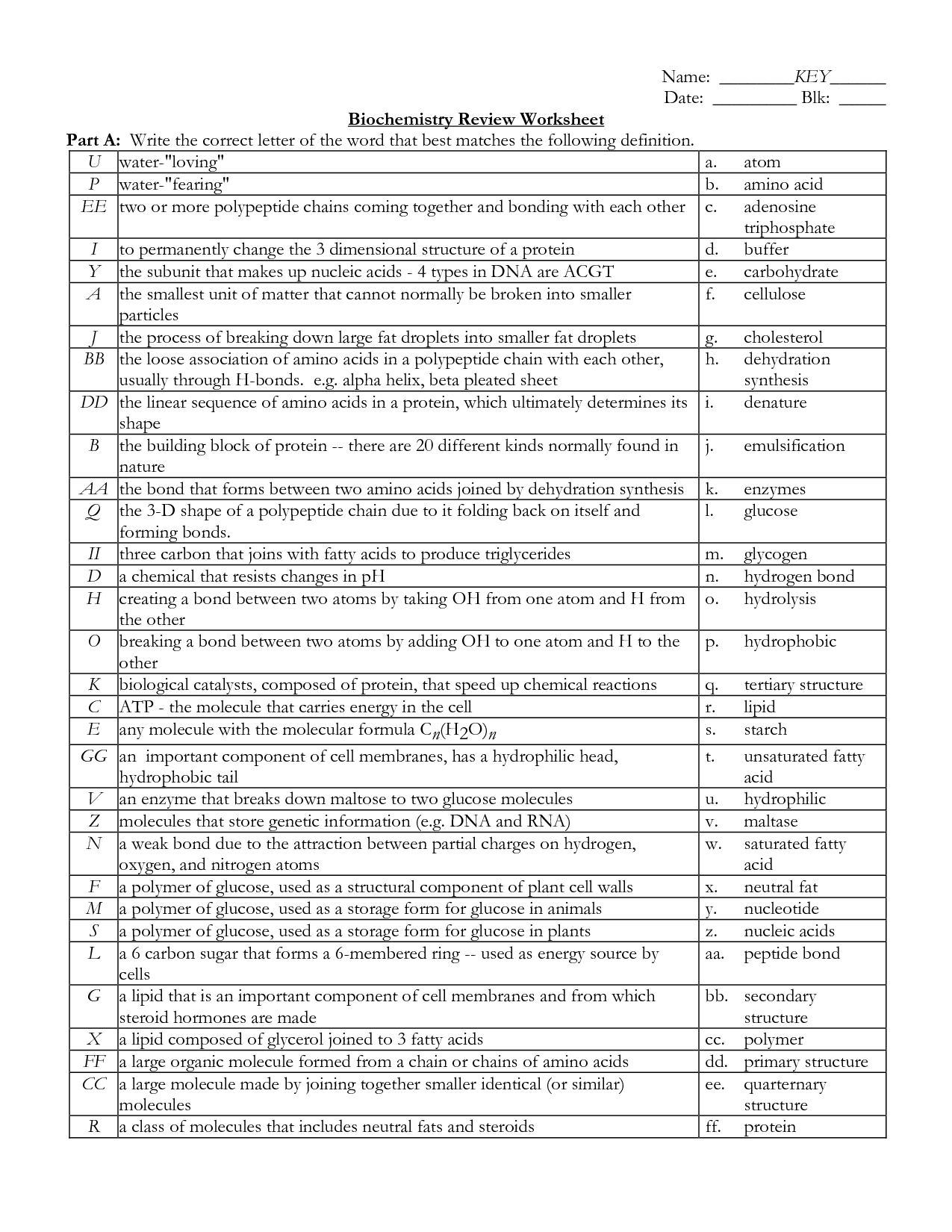
Carbohydrate Structure Worksheet
Understanding the structure of carbohydrates is essential for students studying biology or chemistry. Whether you're a high school student learning the basics or a college student diving deeper into the subject, a carbohydrate structure worksheet can be a helpful tool to enhance your understanding. These worksheets provide a clear and concise way to practice identifying and labeling the different components of carbohydrates, allowing you to reinforce your knowledge and solidify your understanding of this important topic.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
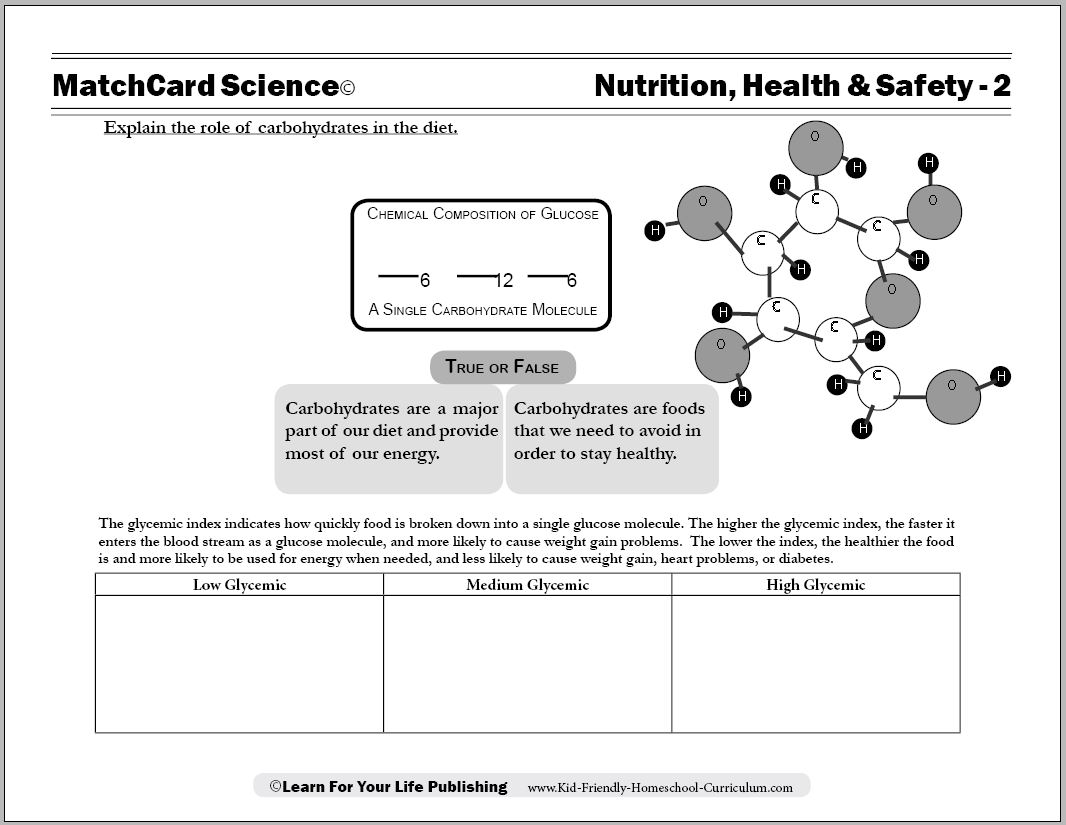
What are carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are macronutrients that serve as a primary energy source for the body. They are found in foods like grains, fruits, vegetables, and dairy products, and are broken down into glucose to fuel various bodily functions, including providing energy for cells, tissues, and organs.
How are carbohydrates classified?
Carbohydrates are classified based on their structure and complexity. They can be categorized as either simple carbohydrates, such as sugars, or complex carbohydrates, such as starches and fibers. Simple carbohydrates consist of one or two sugar molecules, while complex carbohydrates are made up of long chains of sugar molecules. Additionally, carbohydrates can be classified as either monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharides depending on the number of sugar units they contain.
What is the general formula for carbohydrates?
The general formula for carbohydrates is (CH2O)n, where n represents the number of carbon atoms in the molecule. This formula reflects the basic structure of carbohydrates, which are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in the ratio of 1:2:1.
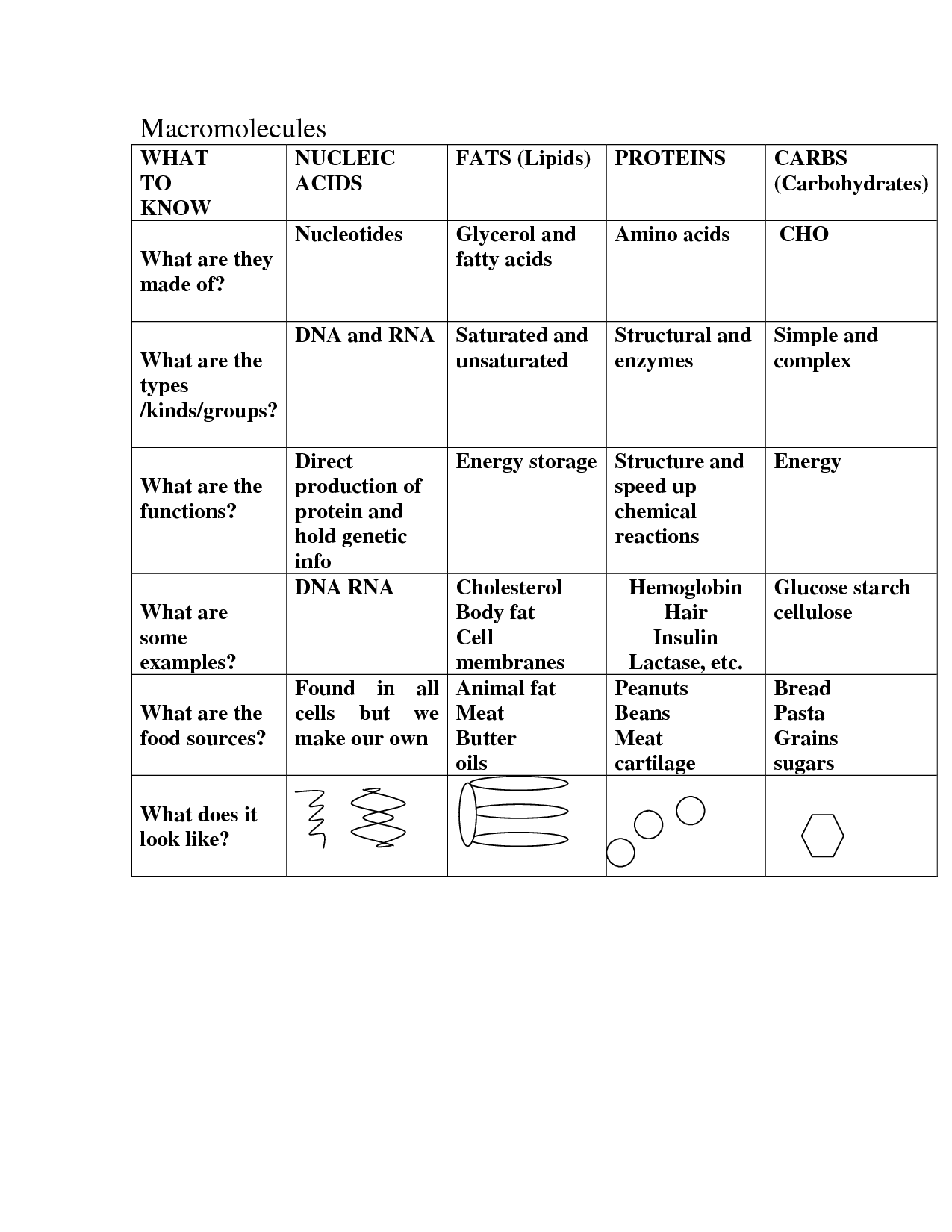
What are monosaccharides?
Monosaccharides are simple sugars that consist of a single sugar unit, making them the most basic form of carbohydrates. They are often referred to as the building blocks of more complex carbohydrates and are easily absorbed and utilized by the body for energy production. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose.
Give examples of monosaccharides.
Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose.
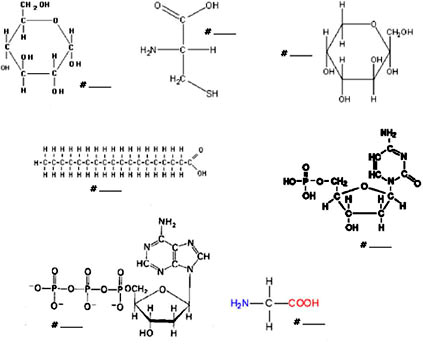
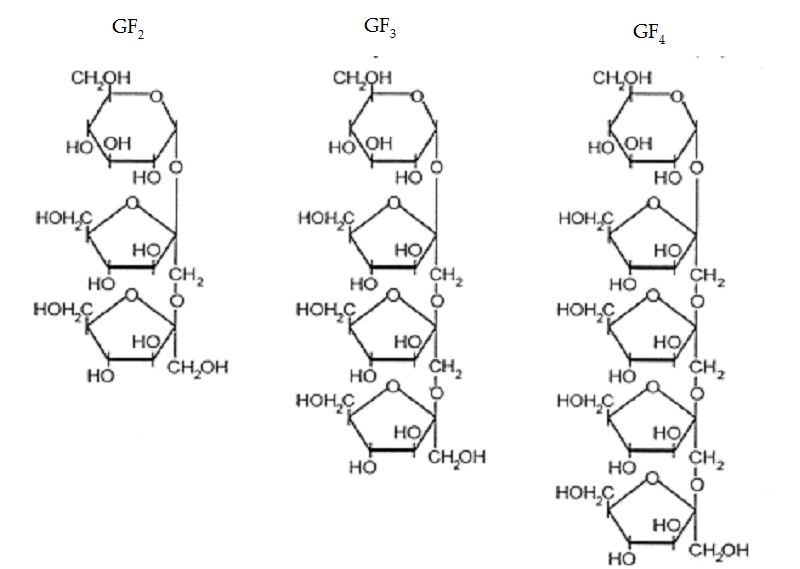
How are monosaccharides linked together to form disaccharides and polysaccharides?
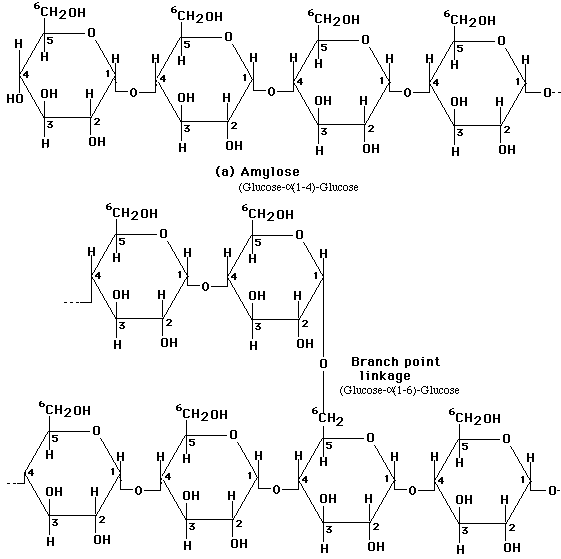
Monosaccharides are linked together through a dehydration reaction, where a molecule of water is removed to form a glycosidic bond between the two monosaccharides. In the case of disaccharides, two monosaccharides are linked together while polysaccharides are formed by multiple monosaccharide units being joined together through glycosidic bonds, creating complex carbohydrates such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen.
What are disaccharides?
Disaccharides are a type of carbohydrate composed of two sugar molecules joined together. They are formed through a condensation reaction that links the carbon atoms of two sugar molecules, resulting in a molecule with a glycosidic bond. Common examples of disaccharides include sucrose (table sugar), lactose (milk sugar), and maltose. These molecules are broken down by digestive enzymes in the body into their constituent sugars for energy usage.
Give examples of disaccharides.
Some examples of disaccharides include sucrose (table sugar), lactose (found in milk), and maltose (found in malted beverages and some foods).
What are polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates made up of multiple monosaccharide (sugar) units linked together. They are found in many foods such as grains, vegetables, and fruits, and play important roles in energy storage, structural support, and cell communication in living organisms. Examples of polysaccharides include starch, glycogen, and cellulose.
Give examples of polysaccharides.
Some examples of polysaccharides include starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin. Starch is found in plants and serves as a storage molecule for energy. Glycogen is the animal equivalent of starch and is stored in the liver and muscles. Cellulose is the structural component of plant cell walls, providing rigidity and support. Chitin is found in the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans, as well as in the cell walls of fungi.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments