Bonding Basics Worksheet Practice
Are you a student or a teacher in search of a helpful resource to reinforce your understanding of bonding basics? Look no further as we introduce the Bonding Basics Worksheet Practice. Designed to cater to both students and teachers, this worksheet provides a comprehensive practice on the fundamentals of bonding in chemistry. Whether you are learning about ionic, covalent, or metallic bonds, this worksheet is the perfect tool to solidify your knowledge and enhance your subject comprehension.
Table of Images 👆
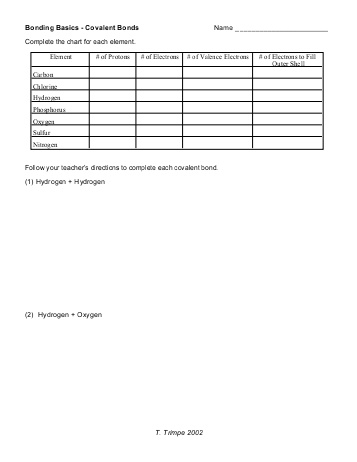
- Bonding Basics Covalent Bonds Worksheet Answers
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding Worksheet
- Drawing Ionic and Covalent Bonds Worksheet
- Chemical Bonding Worksheet Answers
- Ionic vs Covalent Worksheet
- Practice Ionic Covalent Compound Worksheet
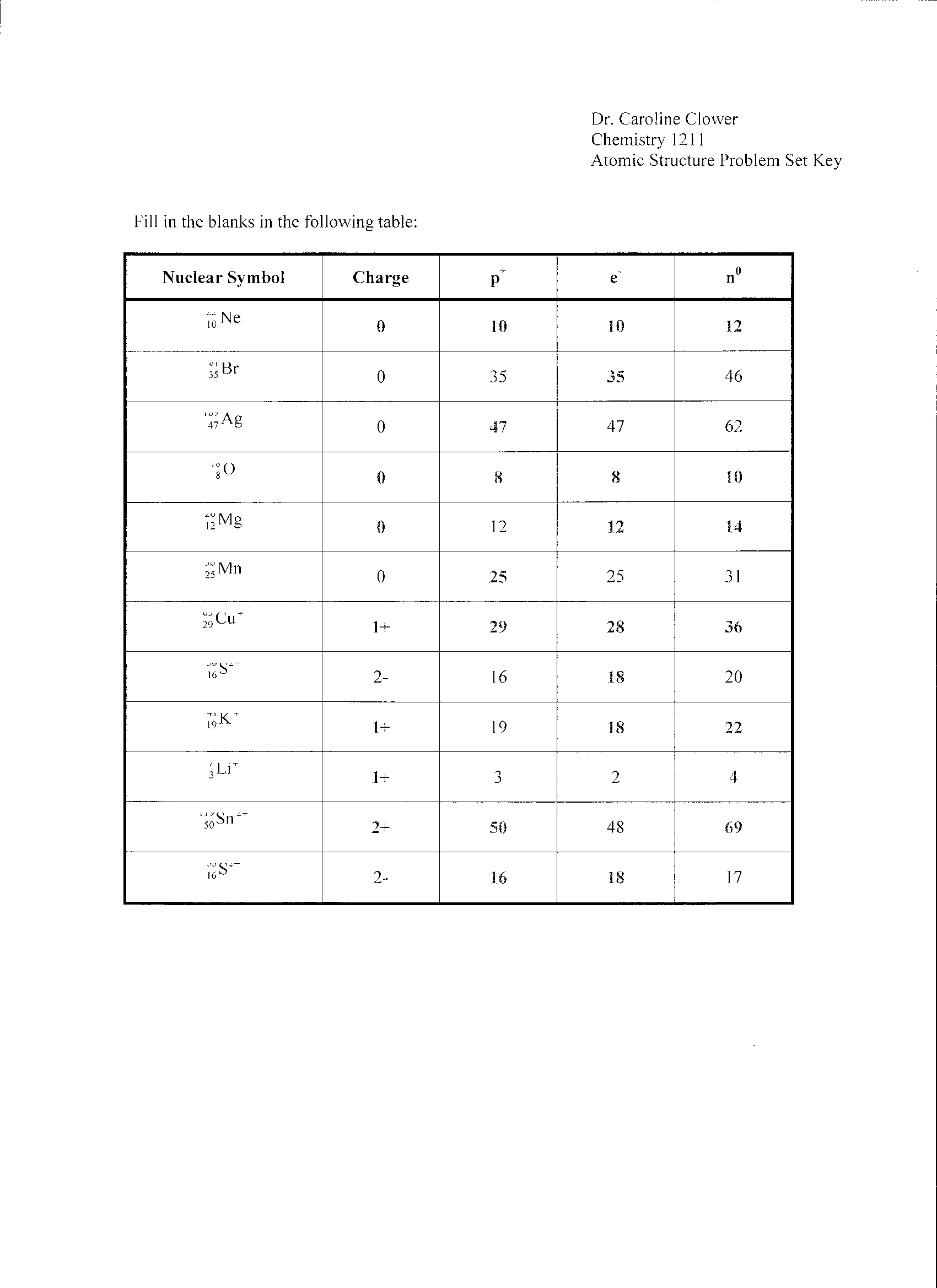
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
- Naming Ionic and Covalent Compounds Worksheet
- Lewis Dot Structure Covalent Bond Worksheet
- Ionic Bonding Dot Diagram and Worksheet
- Covalent Bonding Lewis Structures Worksheet
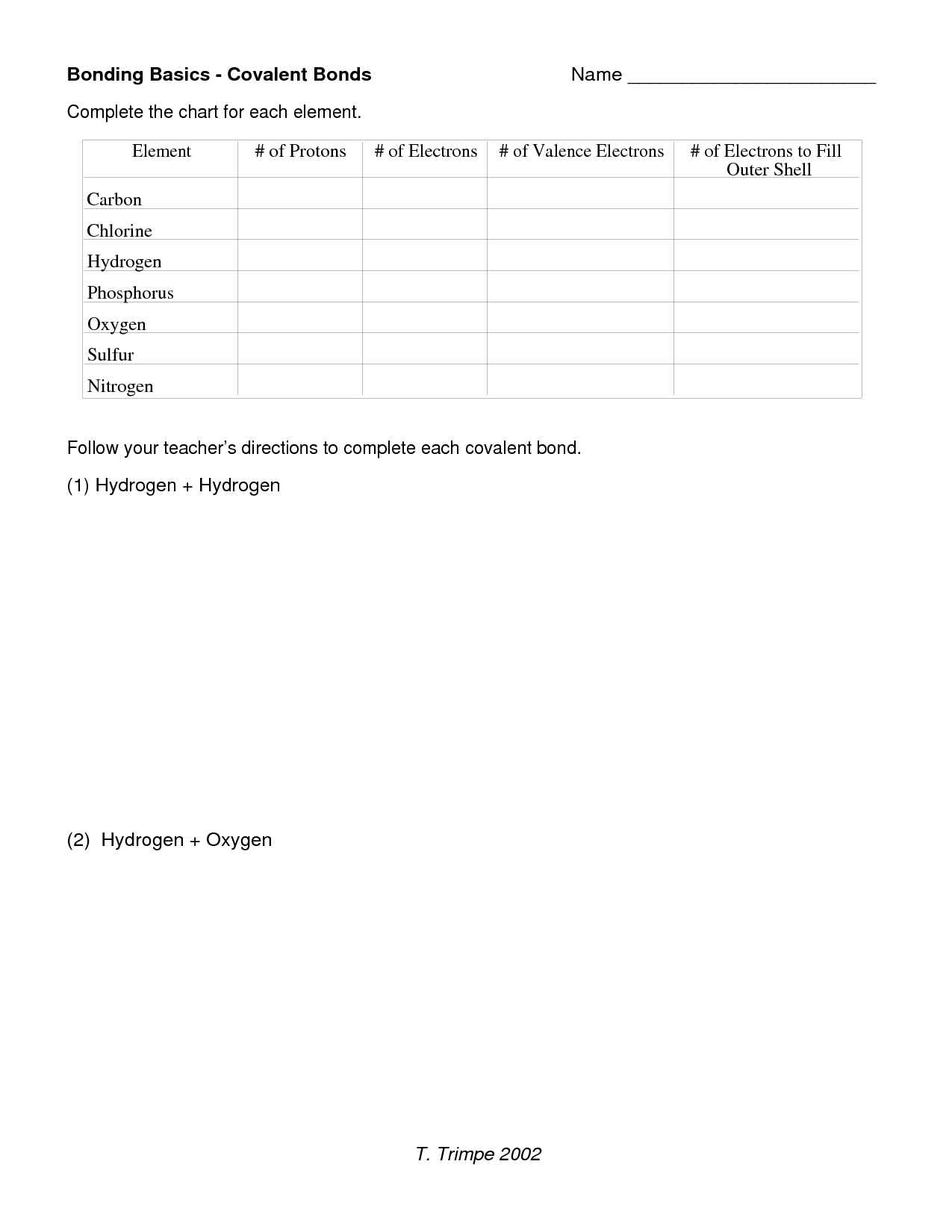
- Bonding Basics Covalent Bonds
- Balancing Chemical Equations Worksheet Answer Key
- Bohr Atomic Model Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is bonding?
Bonding is a process in which two or more individuals develop a close attachment, connection, or relationship based on trust, mutual understanding, and emotional connection. It can occur between family members, friends, romantic partners, or even between humans and animals. Bonding is important for creating a sense of security, belonging, and support in relationships, and it helps to strengthen emotional ties and promote overall well-being for individuals involved.
Define an ionic bond.
An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond that is formed through the transfer of electrons between atoms. In this bond, one atom loses electrons (becoming positively charged) while another atom gains these electrons (becoming negatively charged), leading to the attraction between the oppositely charged ions and the formation of a stable compound.
Explain a covalent bond.
A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. This sharing of electrons allows each atom to achieve a full outer shell of electrons, resulting in a stable molecular structure. Covalent bonds are typically found in non-metallic elements and compounds, where atoms have a strong attraction for electrons and prefer to share them to achieve stability.
What are valence electrons?
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons in an atom that are involved in the chemical reactions and bonding of that atom with other atoms. They determine the reactivity and stability of an element, as well as its ability to form bonds with other elements to create compounds.
How do atoms achieve a stable electron configuration through bonding?
Atoms achieve a stable electron configuration through bonding by either gaining, losing, or sharing electrons with other atoms to fill their outermost energy level. This process allows atoms to reach a more stable state, following the octet rule which states that most atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons in order to have a full outer shell with eight electrons. Ionic bonds form when atoms transfer electrons to one another, while covalent bonds are formed by atoms sharing electrons. Through these bonding mechanisms, atoms can achieve a stable electron configuration and form more stable compounds.
Describe why noble gases are often unreactive.
Noble gases are often unreactive because they have a full valence electron shell, making them very stable and unlikely to gain or lose electrons in chemical reactions. This full outer shell gives them little tendency to form chemical bonds with other elements, hence they do not readily react with other substances, leading to their inert nature.
What is the difference between an ion and an atom?
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element, consisting of a nucleus containing positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons, surrounded by negatively charged electrons. An ion, on the other hand, is an atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative electrical charge. In summary, ions are atoms with an electrical charge due to the gain or loss of electrons, while atoms are neutral particles with equal numbers of protons and electrons.
How does electronegativity play a role in bonding?
Electronegativity plays a vital role in bonding by determining the polarity of the bond formed between two atoms. When atoms with different electronegativities come together to form a bond, the more electronegative atom attracts the shared electrons more strongly, leading to the formation of a polar covalent bond. This results in unequal sharing of electrons and creates partial positive and negative charges on the atoms involved in the bond, leading to a bond with dipole characteristics. On the other hand, atoms with similar electronegativities form nonpolar covalent bonds, where electrons are shared equally. Thus, electronegativity helps in understanding the nature of chemical bonds and the distribution of charge within molecules.
What is a polar covalent bond?
A polar covalent bond is a type of chemical bond where electrons are unequally shared between two atoms. This results in one atom having a slightly negative charge and the other having a slightly positive charge, creating a dipole moment. This unequal sharing of electrons occurs when atoms with different electronegativities are bonded together, causing a partial separation of charges within the molecule.
Give an example of a compound formed by ionic bonding.
Table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), is an example of a compound formed by ionic bonding. Sodium (Na) donates an electron to chlorine (Cl), resulting in the formation of Na+ and Cl- ions that are held together by electrostatic forces in a crystal lattice structure.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments