Bonding Basics Ionic Bonds Worksheet
Are you in search of a comprehensive worksheet to enhance your understanding of bonding basics and ionic bonds? Look no further! This worksheet is designed to provide you with a clear and concise overview of the concept of ionic bonding. With carefully crafted questions and exercises, you will have the opportunity to deepen your knowledge and develop a strong foundation in this fundamental aspect of chemistry.
Table of Images 👆
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding Worksheet
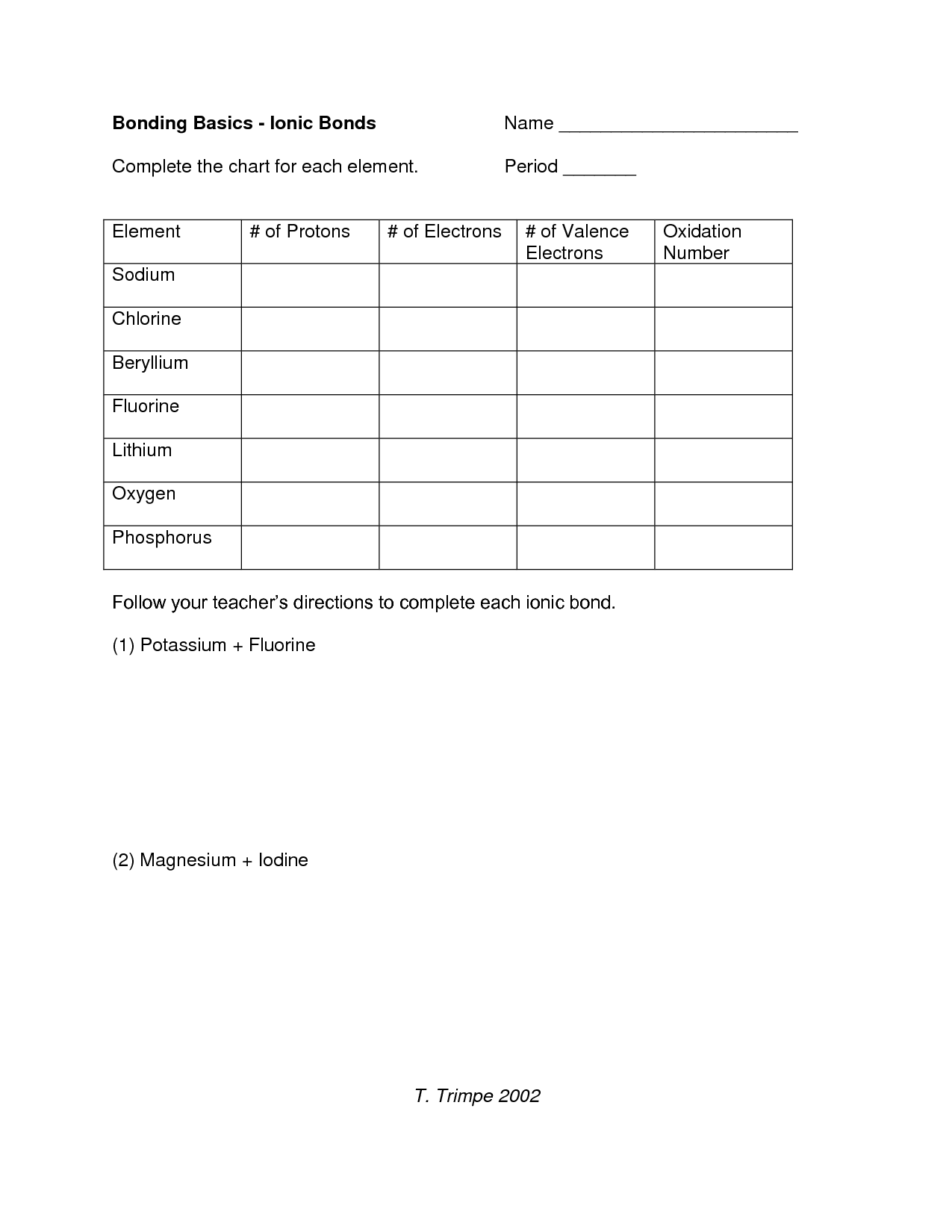
- Bonding Basics Ionic Bonds Worksheet Answers
- Drawing Ionic and Covalent Bonds Worksheet
- Lewis Dot Structure Covalent Bond Worksheet
- Ionic and Covalent Bonds Worksheet
- Ionic vs Covalent Worksheet
- Chemistry Chemical Bonding Worksheet Answers Activity
- Chemical Bonding Worksheet Answer Key
- Bonding Basics Ionic Bonds Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is an ionic bond?
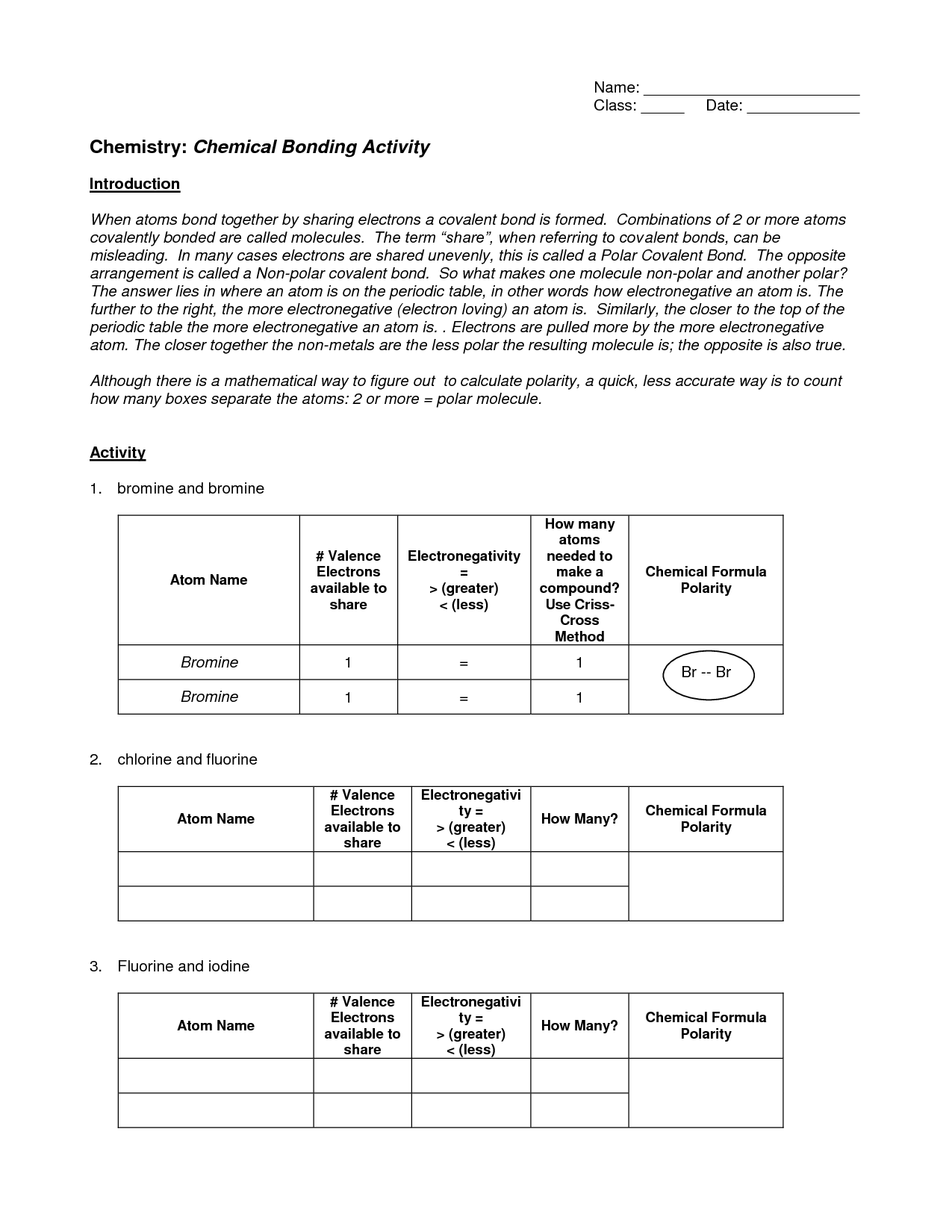
An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond that forms between two atoms when one atom transfers one or more electrons to another atom. This results in the formation of positive and negative ions that are attracted to each other due to their opposite charges, creating a strong electrostatic force that holds the atoms together in a molecule.
How are ions formed?
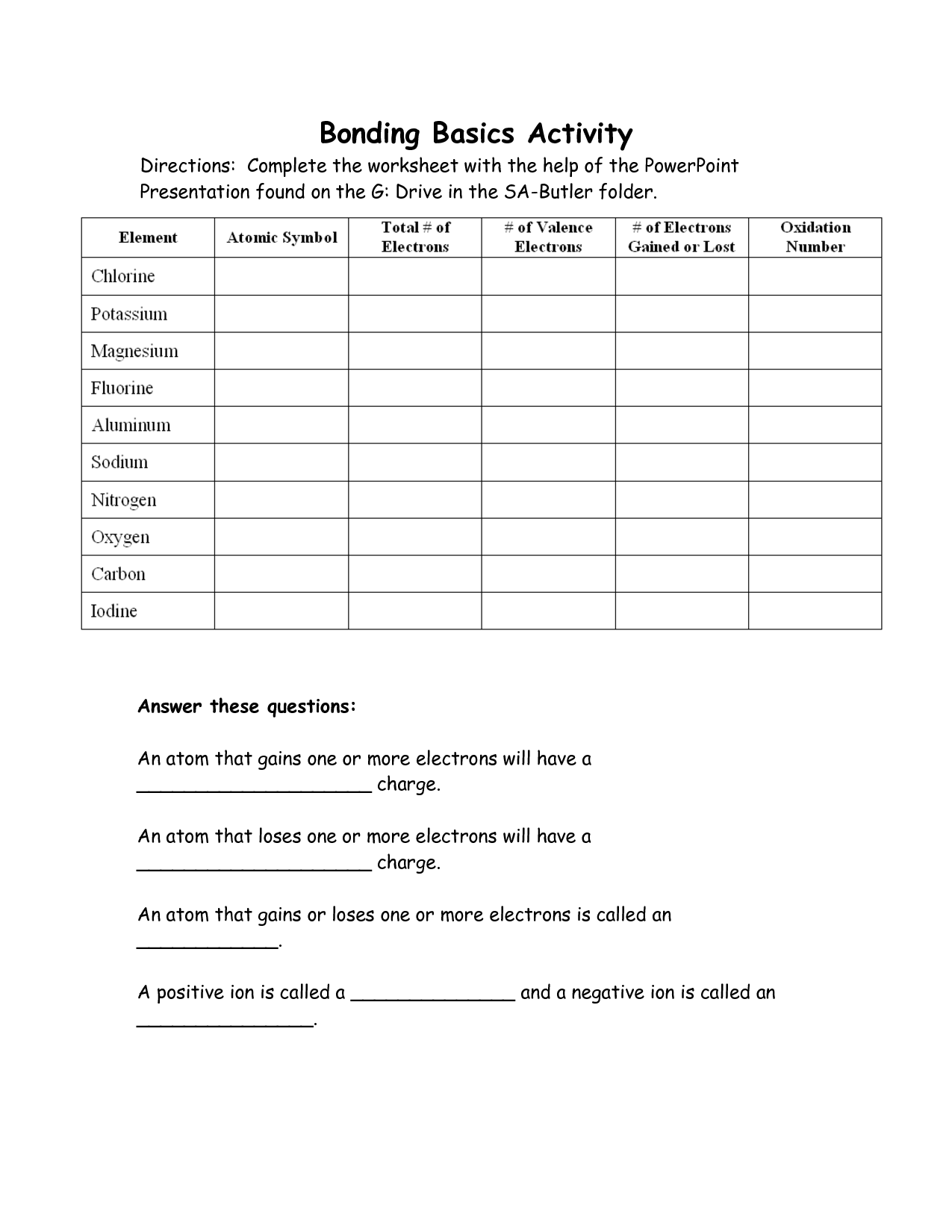
Ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons. When an atom loses one or more electrons, it becomes positively charged, forming a cation. Conversely, when an atom gains one or more electrons, it becomes negatively charged, forming an anion. This process occurs through chemical reactions or interactions with other atoms or molecules, resulting in the formation of ions with different charges.
What is the difference between a cation and an anion?
A cation is a positively charged ion that forms when an atom loses electrons, while an anion is a negatively charged ion that forms when an atom gains electrons. Essentially, cations have a net positive charge due to having more protons than electrons, whereas anions have a net negative charge due to having more electrons than protons.
How do oppositely charged ions attract each other in an ionic bond?
Oppositely charged ions attract each other in an ionic bond through electrostatic forces of attraction. The positive charge on one ion is attracted to the negative charge on the other ion, creating a strong bond between the two ions. This attraction allows for the formation of stable ionic compounds.
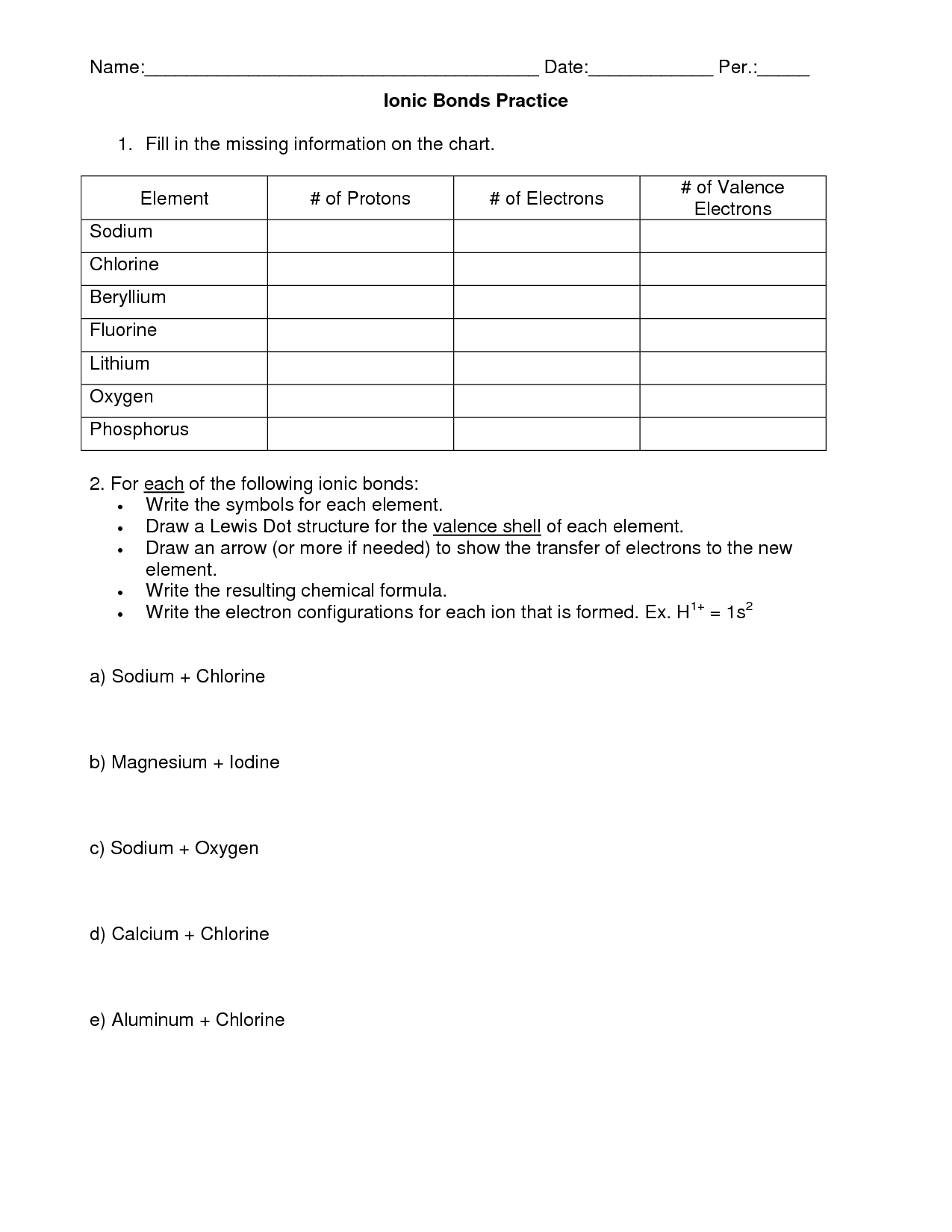
Give an example of a compound that is formed by an ionic bond.
Table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), is an example of a compound that is formed by an ionic bond. Sodium, a metal, donates its electron to chlorine, a non-metal, resulting in the formation of an ionic bond between the two ions.
What happens to the electrons in an ionic bond?
In an ionic bond, electrons are transferred from one atom to another to achieve a stable electron configuration. The atom that loses electrons becomes a positively charged ion, while the atom that gains electrons becomes a negatively charged ion. This electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions results in the formation of an ionic bond.
Why do ionic compounds usually have high melting and boiling points?
Ionic compounds usually have high melting and boiling points because they are held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction between positively and negatively charged ions. These ionic bonds are very stable and require a significant amount of energy to break, leading to higher melting and boiling points compared to other types of compounds like covalent molecules or metallic substances.
How do you determine the formula of an ionic compound?
To determine the formula of an ionic compound, you need to identify the charges of the ions involved and then balance them so that they cancel each other out. This involves using the crisscross method or simply matching the charges to find the correct ratio of positive and negative ions in the compound. For example, in sodium chloride (NaCl), sodium has a +1 charge and chloride has a -1 charge, so they combine in a 1:1 ratio to form NaCl. It's important to ensure that the overall charge of the compound is neutral to reflect the balance of positive and negative charges in the compound.
Can ionic compounds conduct electricity? Why or why not?
Yes, ionic compounds can conduct electricity when they are in a molten state or dissolved in a solution. This is because in these states, the ions are free to move and carry an electric charge, allowing them to conduct electricity. In their solid state, ions are fixed in place and unable to move, so solid ionic compounds do not conduct electricity.
Explain the concept of lattice energy in relation to ionic bonds.
Lattice energy is the energy required to completely separate one mole of a solid ionic compound into its gaseous ions. It is a measure of the strength of the ionic bond holding the ions together in the crystal lattice. Higher lattice energy indicates stronger ionic bonds due to the attraction between the positive and negative ions in the lattice structure. The magnitude of lattice energy is influenced by factors such as the charges of the ions and the distance between them, with higher charges and smaller ion sizes leading to higher lattice energies.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments