Bohr Diagram Worksheet PDF
Are you interested in helping your students understand the arrangement of electrons in an atom? Look no further! This blog post introduces a Bohr Diagram Worksheet, designed to engage and educate middle school and high school science students. Whether you're a teacher searching for an interactive learning resource or a parent looking to support your child's science education, this worksheet is a valuable tool for teaching about electron configurations and the periodic table. In this post, we'll delve into the benefits of using this worksheet, its key features, and how to effectively incorporate it into your lessons. Let's dive in!
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
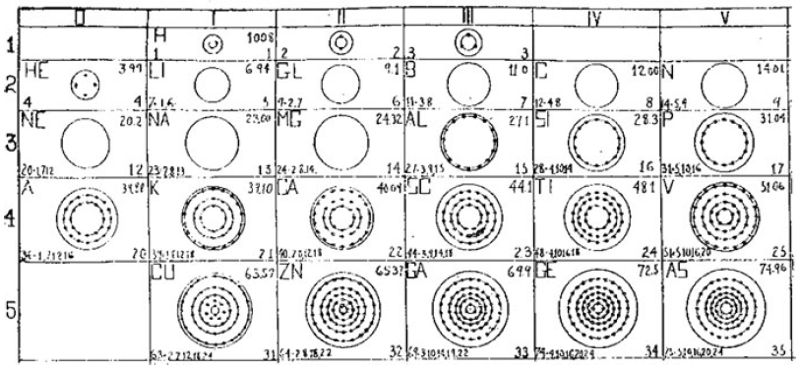
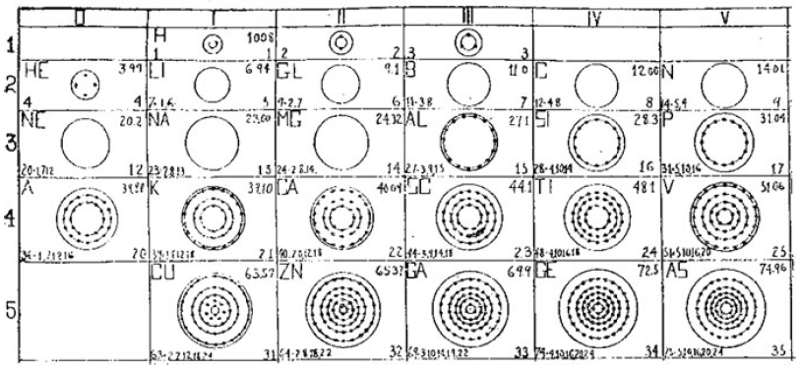
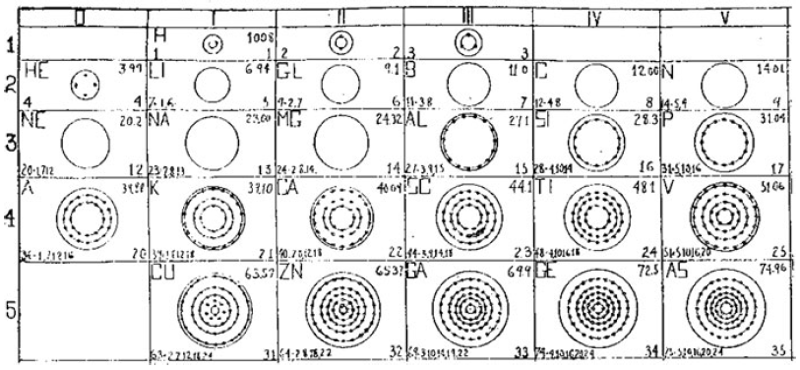
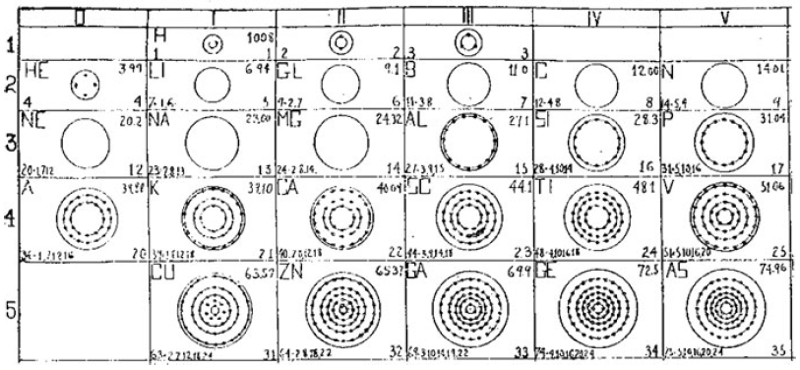
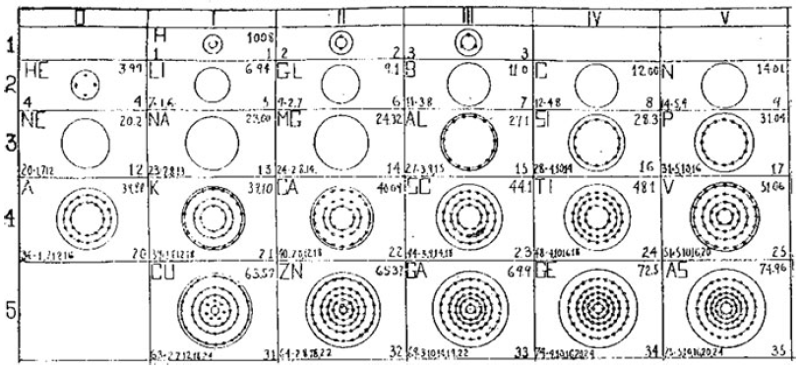
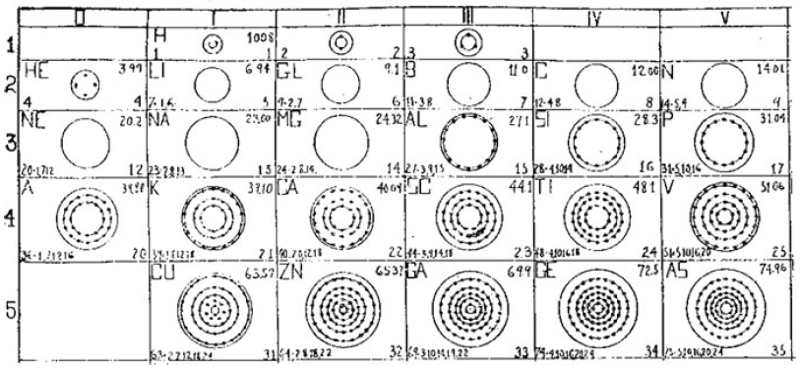
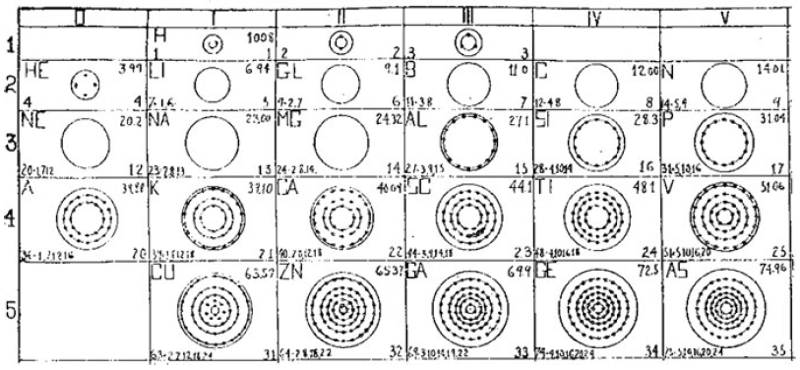
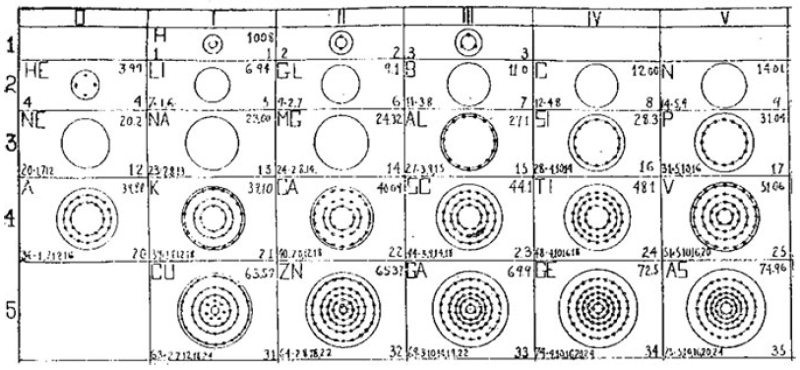
What is a Bohr diagram?
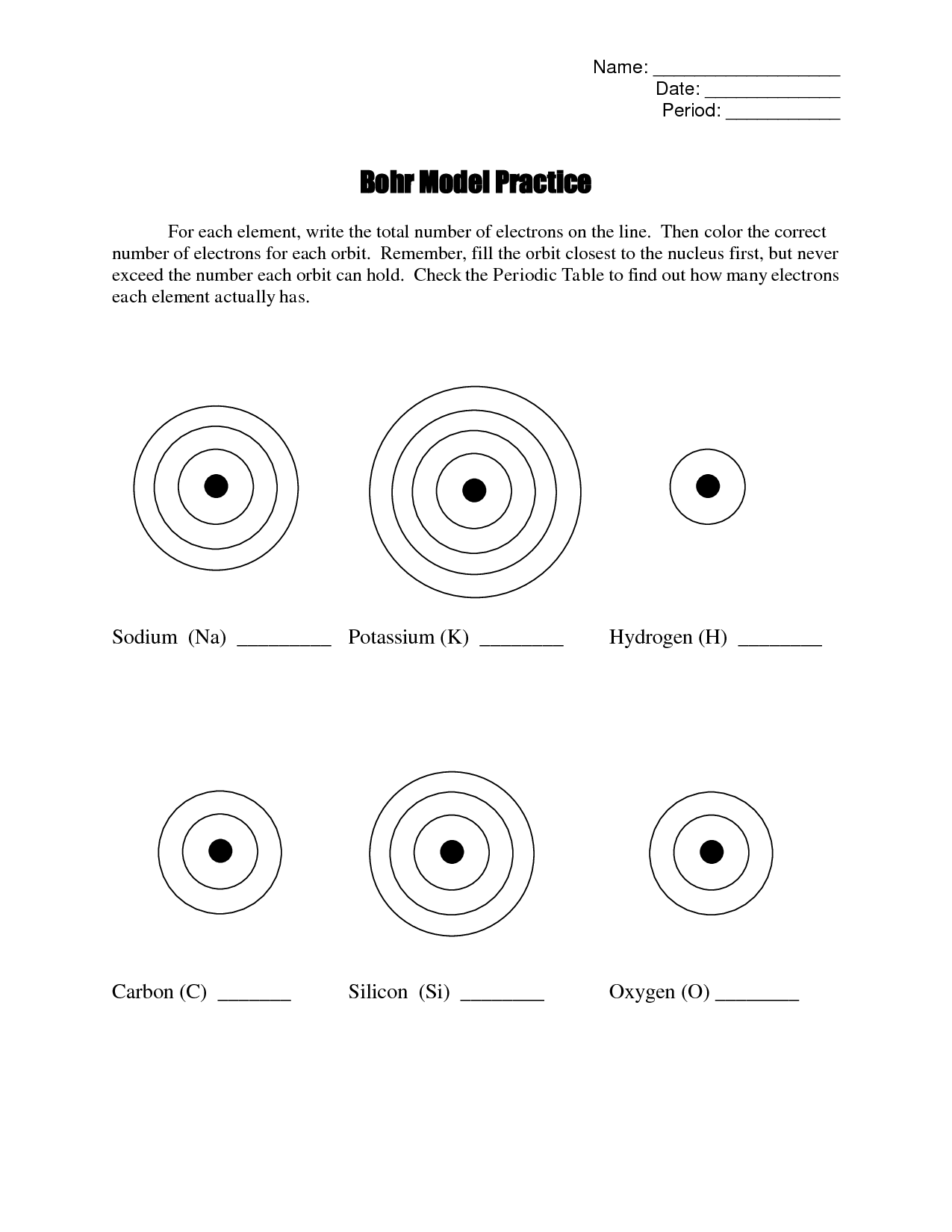
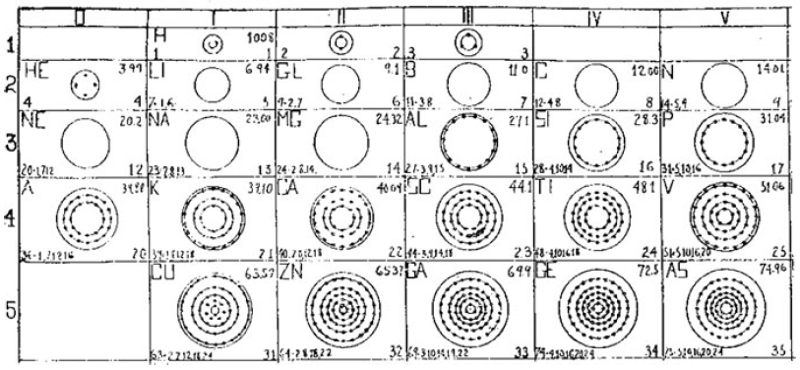
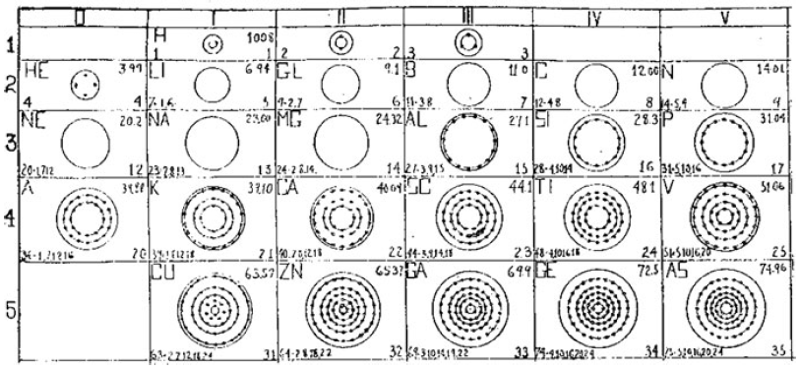
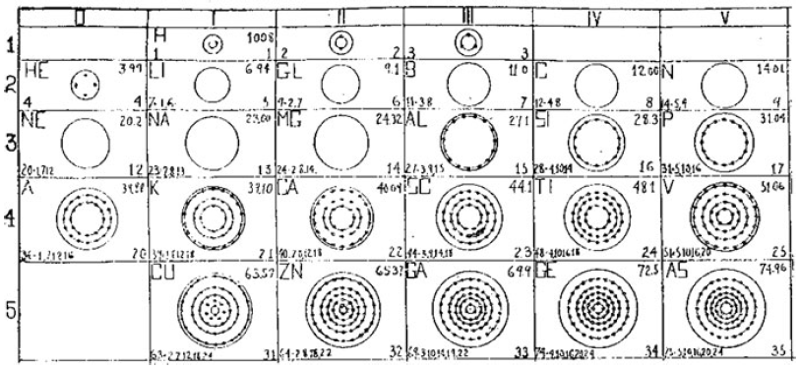
A Bohr diagram is a simple model representing the arrangement of electrons in an atom. In a Bohr diagram, electrons are depicted orbiting the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells, with each shell capable of holding a certain number of electrons. This diagram helps in understanding the basic structure of an atom and the distribution of electrons within it.
How do Bohr diagrams represent atoms?
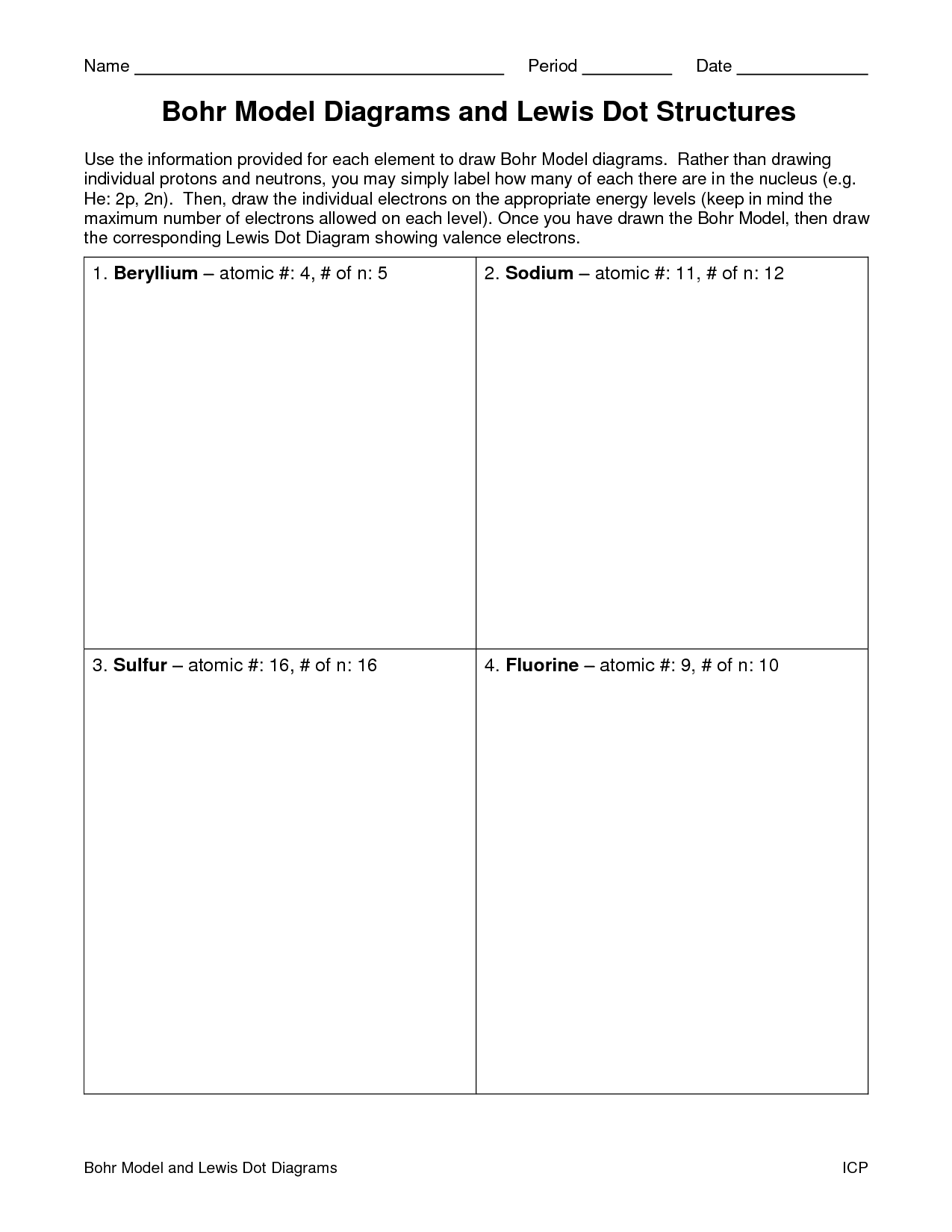
Bohr diagrams represent atoms by indicating the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom, as well as the electrons in their energy levels or shells surrounding the nucleus. The diagram shows the arrangement of these components in a simplified way to help visualize the structure and organization of an atom.
What parts make up a Bohr diagram?
A Bohr diagram consists of a nucleus represented by a dot in the center, with one or more energy levels or shells marked as circles around the nucleus. Electrons are shown as dots or dashes on the energy levels, indicating their specific distribution around the nucleus in accordance with the Bohr model of the atom.
How are the energy levels in a Bohr diagram represented?
In a Bohr diagram, the energy levels are represented by concentric circles around the nucleus of the atom, with each circle corresponding to a specific energy level. The closer the circle is to the nucleus, the lower the energy level, while circles further away represent higher energy levels. Each energy level can accommodate a specific number of electrons, with electrons typically filling the lowest energy levels first before moving to higher ones.
How do electrons occupy energy levels in a Bohr diagram?
In a Bohr diagram, electrons occupy specific energy levels around the nucleus of an atom. The lowest energy level is closest to the nucleus and can hold a maximum of 2 electrons, while subsequent energy levels can hold more electrons with increasing energy. Electrons fill the energy levels starting from the lowest energy level before moving to higher energy levels, following the principle that electrons must occupy the lowest energy levels available before moving to higher ones.
How can you determine the number of electrons in each energy level in a Bohr diagram?
To determine the number of electrons in each energy level in a Bohr diagram, you can use the formula 2n^2, where n represents the energy level. For example, the first energy level (n=1) can hold up to 2 electrons, the second energy level (n=2) can hold up to 8 electrons, the third energy level (n=3) can hold up to 18 electrons, and so on.
What does the symbol in the center of a Bohr diagram represent?
The symbol in the center of a Bohr diagram represents the nucleus of an atom, which contains protons and neutrons.
How do you determine the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom based on its Bohr diagram?
To determine the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom based on its Bohr diagram, you simply look at the atomic number of the element, which is typically provided. The atomic number represents the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Each element has a unique atomic number, which defines its identity on the periodic table and the number of protons it possesses.
How can you determine the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom based on its Bohr diagram?
To determine the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom based on its Bohr diagram, you would first need to identify the atomic number of the atom, which is typically located at the lower left corner of the element's symbol on the diagram. Next, you would subtract the atomic number (which represents the number of protons) from the mass number (which is typically located at the upper left corner of the element's symbol on the diagram). The difference between the mass number and atomic number gives you the number of neutrons in the nucleus of the atom.
How can you use a Bohr diagram to represent an ion or an isotope?
To represent an ion using a Bohr diagram, you would adjust the number of electrons to account for the ion's charge. For example, if you have a positive ion, you would remove electrons starting from the outermost shell to match the positive charge. Conversely, for a negative ion, you would add extra electrons starting from the outermost shell to match the negative charge. For representing an isotope, you would modify the number of neutrons in the nucleus while keeping the same number of protons and electrons in the Bohr diagram. This adjustment reflects the different atomic mass of the isotope compared to the standard element.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments