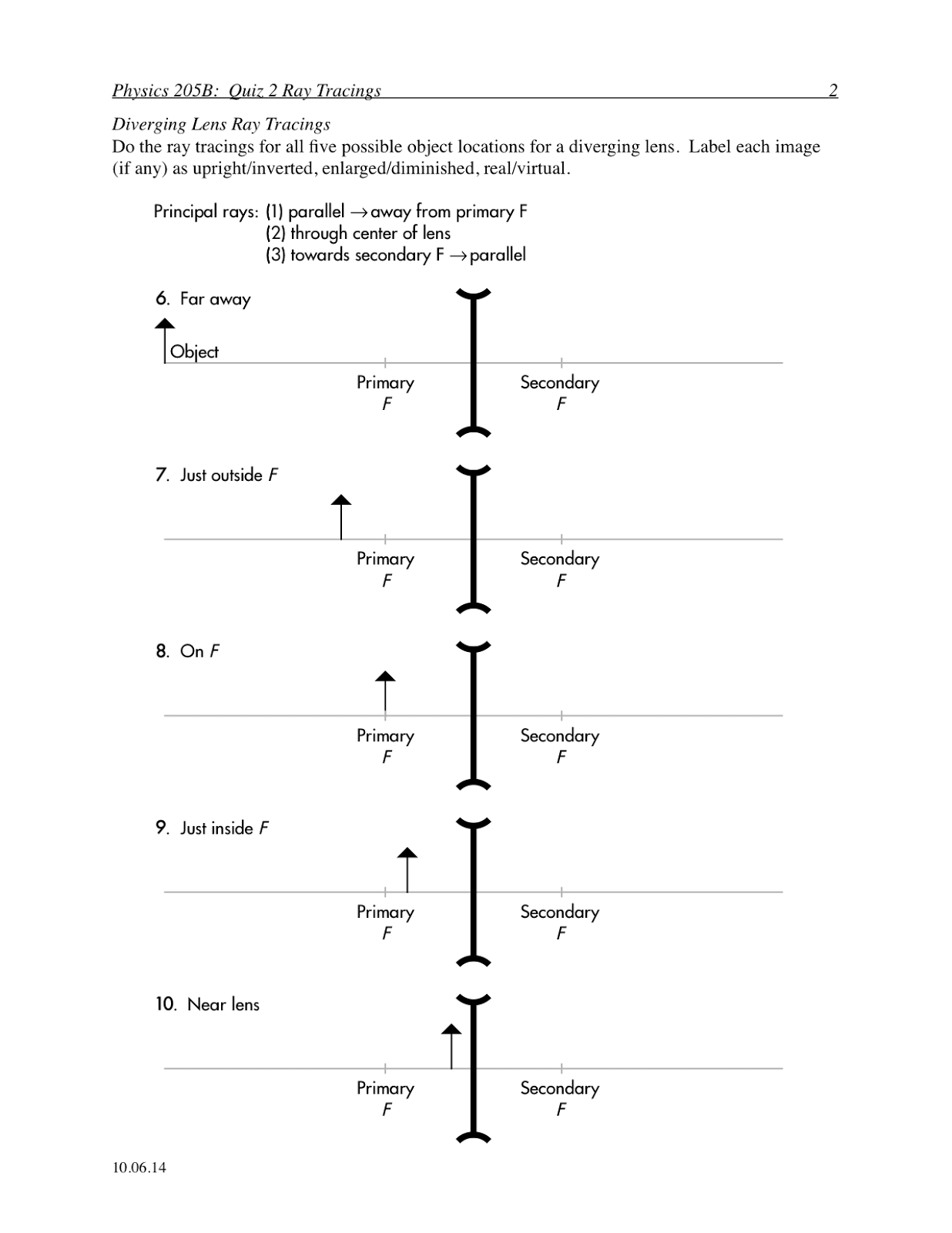
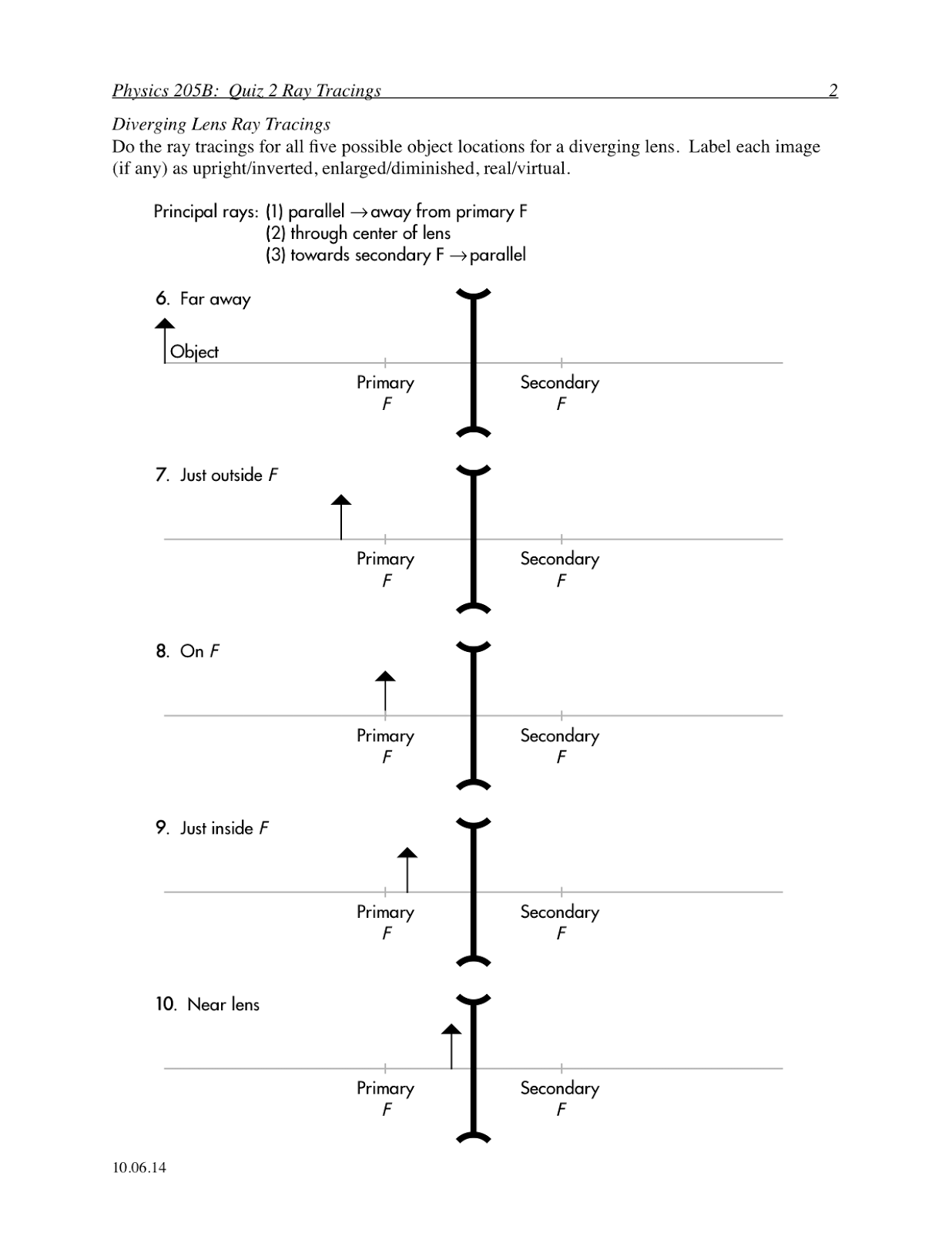
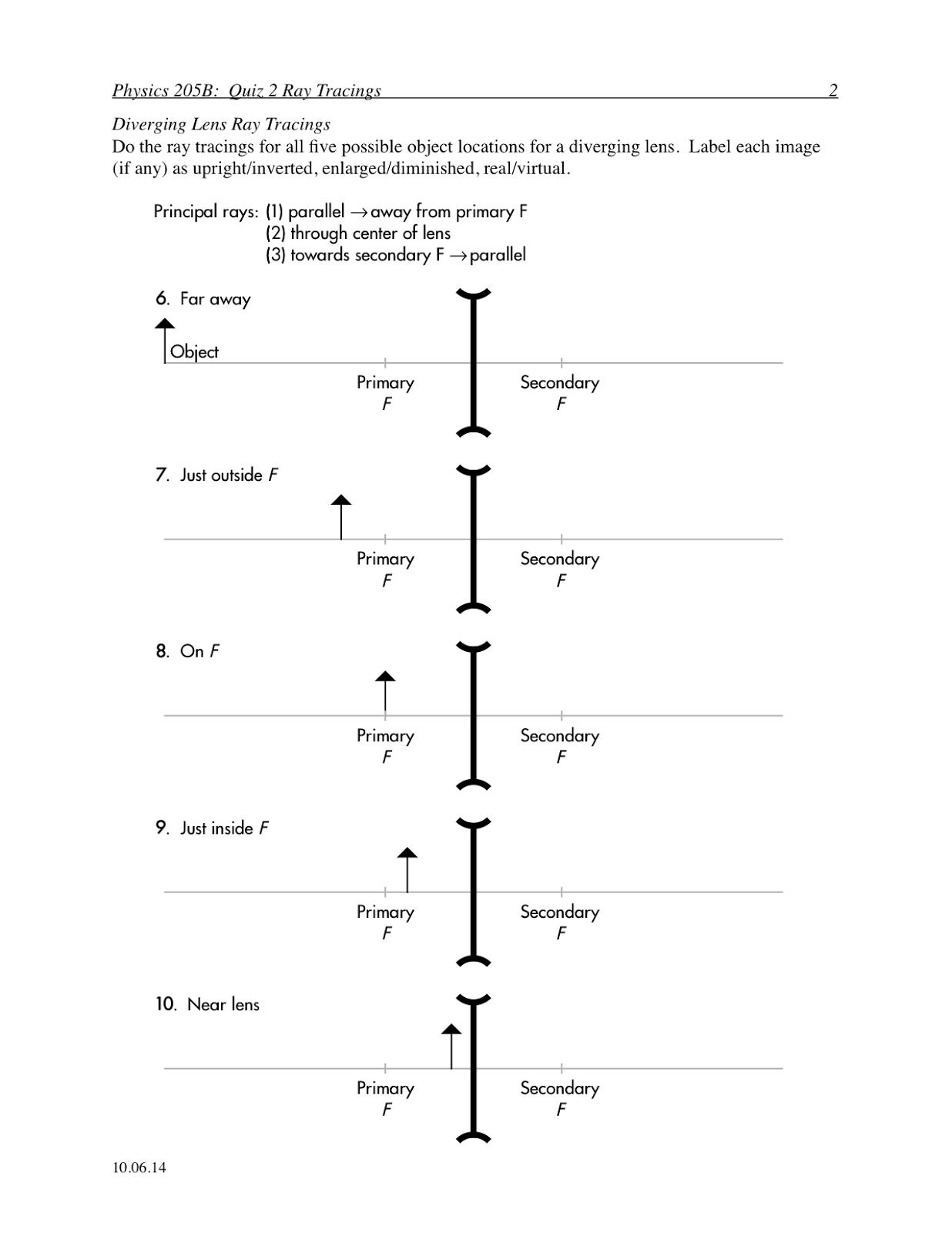
Bohr Atomic Model Worksheet Middle School
The Bohr atomic model worksheet is a helpful resource designed for middle school students to enhance their understanding of the structure of an atom. This interactive and engaging worksheet provides an opportunity for students to explore the various components of the Bohr atomic model, including electron shells, energy levels, and the placement of electrons. With clear instructions and detailed diagrams, this worksheet encourages students to actively participate in the learning process and grasp the fundamentals of atomic structure.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the main idea behind the Bohr atomic model?
The main idea behind the Bohr atomic model is that electrons orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels, or shells, rather than moving in random paths. This model proposed by Niels Bohr in 1913 revolutionized the understanding of atomic structure by introducing the concept of quantized energy levels for electrons, which helped explain the stability and spectral lines of elements.
Who developed the Bohr atomic model?
The Bohr atomic model was developed by Danish physicist Niels Bohr in 1913.
How does the Bohr atomic model explain the arrangement of electrons in an atom?
The Bohr atomic model explains the arrangement of electrons in an atom by proposing that electrons orbit the nucleus in specific, quantized energy levels or orbits. These orbits are characterized by a fixed energy and distance from the nucleus. Electrons can jump between these orbits by absorbing or emitting energy in discrete amounts, which correspond to the emission or absorption of specific wavelengths of light. This model laid the foundation for understanding the stability and behavior of electrons in atoms and explained the discrete spectral lines observed in the emission spectra of elements.
What are energy levels in the Bohr atomic model?
In the Bohr atomic model, energy levels refer to the specific, quantized orbits or shells around the nucleus where electrons can exist. These energy levels are designated by integer values (n = 1, 2, 3, etc.), with higher energy levels corresponding to orbits that are farther away from the nucleus. When electrons absorb or release energy, they move between these energy levels, emitting or absorbing photons in the process.
How are energy levels related to an electron's distance from the nucleus?
An electron's energy levels are directly related to its distance from the nucleus in an atom. The farther an electron is from the nucleus, the higher its energy level. This is because electrons in higher energy levels have more potential energy due to the increased distance from the positive charge of the nucleus, resulting in a less attractive force between the electron and the nucleus. Conversely, electrons closer to the nucleus have lower energy levels as they experience a stronger attraction from the positively charged nucleus, leading to a more stable state.
In the Bohr atomic model, what happens when an electron absorbs energy?
When an electron absorbs energy in the Bohr atomic model, it moves to a higher energy level or shell farther away from the nucleus. This results in the electron becoming excited or in an unstable state. Subsequently, the electron may release the absorbed energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation when it returns to its original energy level, emitting a specific amount of energy in the form of a photon with a corresponding wavelength.
How does the Bohr atomic model explain the emission of light by atoms?
The Bohr atomic model explains the emission of light by atoms through the concept of electrons transitioning between energy levels within the atom. When an electron moves from a higher energy level to a lower one, it releases energy in the form of light. This emitted light corresponds to a specific wavelength or color based on the energy difference between the two levels. Thus, the Bohr model provides insight into how atoms emit light through quantized energy levels and the movement of electrons within the atom.
What are quantum leaps in the context of the Bohr atomic model?
In the context of the Bohr atomic model, quantum leaps refer to the abrupt transitions of electrons between energy levels within an atom. According to the model, electrons orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells. When an electron absorbs or emits energy, it jumps from one energy level to another, without passing through the intermediate levels. These discrete changes in energy levels are known as quantum leaps, and they are essential to understanding the behavior of electrons within an atom.
How does the Bohr atomic model differ from earlier atomic models?
The Bohr atomic model differs from earlier models by introducing the concept of quantized energy levels for electrons in atoms, based on the idea that electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed, specific orbits. This was a departure from earlier models that depicted electrons moving in continuous paths around the nucleus. Bohr's model also accounted for the emission and absorption of energy by electrons as they jump between different energy levels, explaining the spectral lines observed in the hydrogen spectrum and providing a more accurate description of atomic structure.
What are the limitations or drawbacks of the Bohr atomic model?
The Bohr atomic model has limitations and drawbacks, including the inability to explain the spectral lines of atoms with more than one electron, as it only accurately describes hydrogen-like atoms. It also does not account for the wave nature of electrons and only considers them as particles, leading to inconsistencies with the principles of quantum mechanics. Additionally, it oversimplifies the behavior of electrons by assuming they move in circular orbits around the nucleus, whereas electrons actually move in more complex, 3-dimensional orbitals.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments