Biology Scientific Method Worksheets
If you are a biology student or teacher searching for a helpful resource to reinforce your understanding of the scientific method, these biology scientific method worksheets could be just what you need.
Table of Images 👆
- Blank Flow Chart Scientific Method Worksheet
- Gummy Bear Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet
- Simple Scientific Method Worksheet
- Forensic Science Worksheet Answers
- Scientific Method Variables Worksheet
- Scientific Method Simpsons Worksheet Answers
- Scientific Method Graphic Organizer Worksheet
- Scientific Method Worksheet High School
- Scientific Method Worksheet
- Science Lab Safety Rules Worksheets
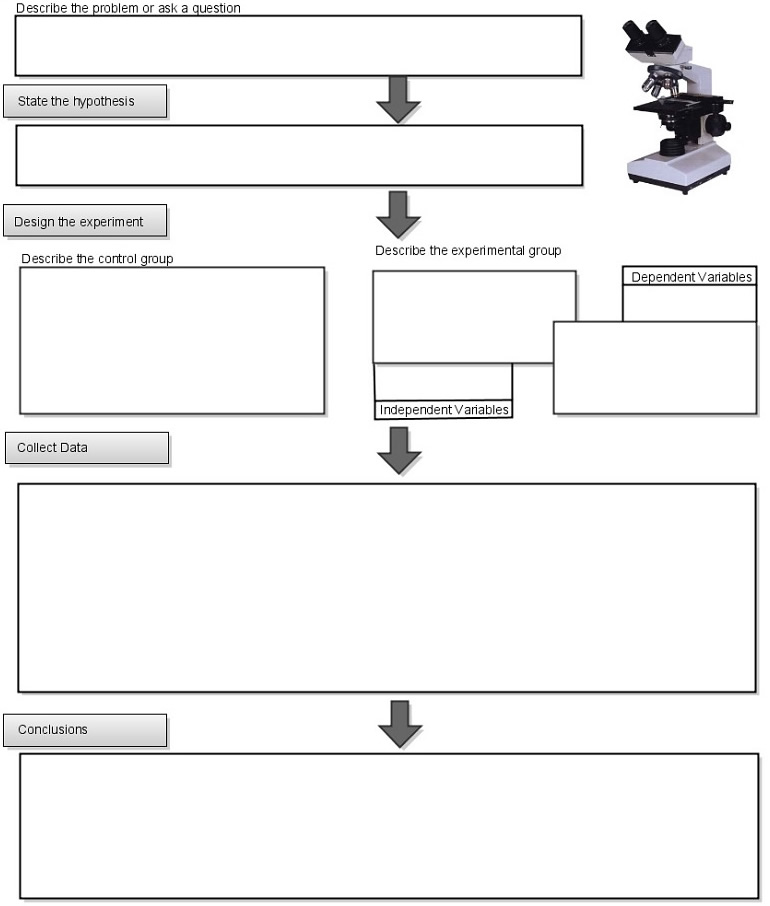
What is the first step of the scientific method?
The first step of the scientific method is to make an observation or identify a question or problem that can be studied through experimentation and analysis.
What does it mean to formulate a hypothesis?
Formulating a hypothesis involves creating a testable statement or proposition that predicts the outcome of a scientific experiment or investigation. It serves as an educated guess or tentative explanation for a phenomenon based on existing knowledge and observations. Hypotheses are essential in the scientific method as they guide the research process, providing a framework for designing experiments, collecting data, and drawing conclusions.
How can a scientist design an experiment to test a hypothesis?
To design an experiment to test a hypothesis, a scientist should start by clearly defining the hypothesis they want to test. Then, they should identify the variables involved and determine the best way to manipulate and measure them. Next, the scientist should design a detailed experimental procedure, including the materials needed, the methods for data collection, and the control group if necessary. It is important to ensure that the experiment is well-controlled to minimize any confounding factors that could affect the results. Finally, the scientist should analyze the data collected and draw conclusions based on the results obtained from the experiment.
What is the purpose of a control group in an experiment?
The purpose of a control group in an experiment is to serve as a baseline for comparison to the experimental group. By keeping all variables constant except for the one being tested in the experimental group, researchers can determine the true effect of the treatment or intervention being studied. This helps to ensure that any observed changes are due to the manipulation of the independent variable and not to external factors.
What is meant by the term "independent variable"?
An independent variable is a variable in an experiment or study that is manipulated or changed by the researcher to observe its effects on the dependent variable. It is the variable that is believed to cause a change in the dependent variable.
How does a scientist collect and analyze data during an experiment?
During an experiment, a scientist collects data by carefully recording observations, measurements, and other relevant information. This may involve using tools such as sensors, meters, or recording devices. After collecting data, the scientist typically analyzes it by organizing, interpreting, and drawing conclusions based on patterns, trends, and relationships observed in the data. This analysis may involve statistical techniques, graphical representations, or qualitative assessments to determine the significance and implications of the findings in relation to the research question or hypothesis being investigated.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data?
Qualitative data refers to non-numerical information that is based on characteristics, attributes, or descriptions, providing insights into the underlying reasons and motivations behind a phenomenon. On the other hand, quantitative data involves numerical values and measurements that can be quantified and analyzed statistically, allowing for objective and structured analysis of trends and patterns.
What is a conclusion in the scientific method?
A conclusion in the scientific method is the final step where the results of an experiment are analyzed and interpreted to determine whether the hypothesis was supported or not. It involves summarizing the findings, discussing their significance, and suggesting potential next steps for further research. The conclusion should be based on the data collected and should aim to provide insights or explanations based on the evidence gathered during the experiment.
How can a scientist communicate their findings to the scientific community?
A scientist can communicate their findings to the scientific community through peer-reviewed journals by submitting their research paper for publication. They can also present their findings at conferences, workshops, and seminars to share their work with other researchers in the field. Additionally, scientists can use social media platforms, academic networking sites, and research collaboration networks to disseminate their findings and engage with other experts in the scientific community.
Why is replication important in scientific research?
Replication is important in scientific research because it allows for the verification and validation of results, ensuring that findings are reliable and robust. By independently repeating experiments and studies and obtaining consistent results, researchers can be more confident in the accuracy and generalizability of their findings. Replication also helps to identify any potential errors or biases in the original study, ultimately leading to a more credible and trustworthy body of scientific knowledge.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments