Bill of Rights Worksheet Answers
Are you a history enthusiast or a student studying the United States Constitution and looking for a comprehensive resource on the Bill of Rights? Look no further! In this blog post, we will provide you with the answers to the Bill of Rights Worksheet, including detailed explanations for each question. Whether you are a teacher in search of a reliable answer key for your students or an individual seeking to enhance your knowledge, this post has got you covered.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the Bill of Rights?
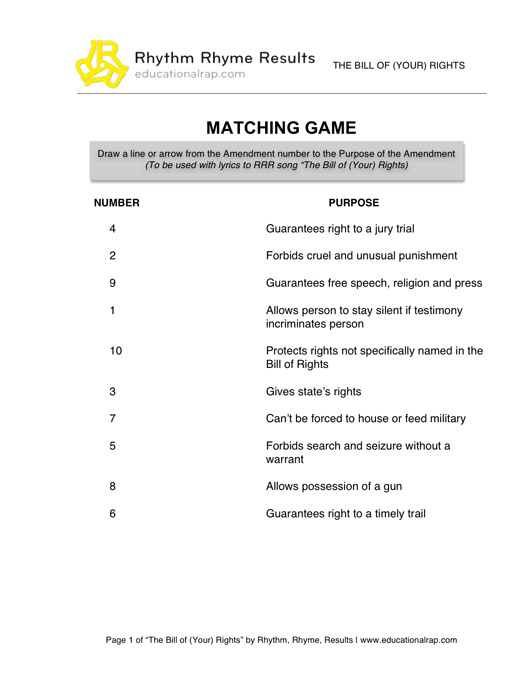
The Bill of Rights is the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. It outlines the fundamental rights and freedoms of individuals, including freedom of speech, religion, and the press, as well as the right to bear arms, fair trial, and protection against unreasonable searches and seizures by the government.
When was the Bill of Rights added to the Constitution?
The Bill of Rights was added to the United States Constitution on December 15, 1791.
What rights are protected by the First Amendment?
The First Amendment protects the rights of freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of religion, freedom of assembly, and the right to petition the government for redress of grievances.
What does the Second Amendment guarantee?
The Second Amendment guarantees the right of individuals to keep and bear arms, as a part of the United States Constitution's Bill of Rights.
What does the Fourth Amendment protect against?
The Fourth Amendment protects individuals against unreasonable searches and seizures by the government. It establishes the requirement for warrants based on probable cause and ensures that individuals have the right to privacy and protection from arbitrary intrusions into their personal belongings and property.
What is the meaning of the term "due process" in the Fifth Amendment?
The term "due process" in the Fifth Amendment refers to the principle that individuals have the right to fair treatment under the law and cannot be deprived of life, liberty, or property without proper legal procedures. This includes the right to notice of the charges against them, a fair hearing, and the opportunity to defend themselves. It ensures that the government must follow specific rules and procedures before taking away someone's rights or property.
What rights are contained in the Sixth Amendment?
The Sixth Amendment to the United States Constitution guarantees the rights of a speedy and public trial by an impartial jury, the right to be informed of the nature and cause of accusations, the right to confront witnesses, the right to compel witnesses to testify, and the right to assistance of counsel for defense.
What does the Eighth Amendment prohibit?
The Eighth Amendment prohibits cruel and unusual punishment, as well as excessive bail and fines, as a part of the United States Constitution's Bill of Rights.
What rights does the Ninth Amendment protect?
The Ninth Amendment protects rights not specifically enumerated in the Constitution, emphasizing that the people retain rights beyond those explicitly stated in the document. This amendment recognizes that individuals have additional fundamental rights that should not be restricted or denied by the government solely because they are not listed in the Constitution.
How does the Tenth Amendment impact the relationship between the federal government and the states?
The Tenth Amendment of the United States Constitution explicitly states that any powers not delegated to the federal government by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the states, are reserved to the states or to the people. This amendment reinforces the principle of federalism, which is the division of power between the federal government and the states. It serves to protect the rights and powers of the states by ensuring that the federal government does not encroach upon areas of governance that are more appropriately handled at the state level. Ultimately, the Tenth Amendment helps to maintain a balance of power between the federal government and the states, preserving the independence and autonomy of state governments in the United States.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments