Bill Nye Winds Worksheet
Are you an educator or parent searching for engaging and educational resources to enhance your lessons about weather? Look no further than the Bill Nye Winds Worksheet! This worksheet is designed to help students understand the concept of wind and its impact on our environment. With clear instructions and thought-provoking questions, this worksheet offers a valuable learning experience for students in middle school or high school.
Table of Images 👆
- Bill Nye Weathering and Erosion Worksheet
- Bill Nye the Science Guy Matter Worksheet
- Bill Nye Atoms Worksheet Answers
- Bill Nye Wind Worksheet Answers
- Bill Nye Video Worksheet Answer Key to Sound Waves
- Bill Nye Energy Worksheet Answers
- Ocean Current and Wind Worksheet
- Bill Nye Food Web Worksheet Answers
- Bill Nye Earthquakes Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet DNA and RNA
- Ocean Currents Map Worksheet
- Chemical Changes in Matter Worksheet Answers
- Bill Nye the Science Guy Comic
- Free Printable Simple Machines Worksheets
- Pacific Ocean Map with Latitude and Longitude
- Bird Worksheets
- Ohms Law Worksheet Answers
- Bill Nye Waves Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What does the term "wind" refer to?
The term "wind" refers to the natural movement of air in the Earth's atmosphere. It is caused by the uneven heating of the Earth's surface by the sun, which creates differences in air pressure. Wind plays a vital role in weather patterns, ocean currents, and the dispersal of seeds and pollen.
How is wind formed?
Wind is formed by the movement of air particles in the Earth's atmosphere. This movement is primarily caused by the uneven heating of the Earth's surface by the sun, leading to variations in air temperature and pressure. As warm air rises and cool air sinks, air masses with different temperatures and pressures create areas of high and low pressure. The air then moves from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure, resulting in the flow of wind.
What are the two main factors that influence wind speed?
The two main factors that influence wind speed are the pressure gradient and the frictional force. The pressure gradient is the difference in air pressure between two points, and the greater the difference, the stronger the winds. Frictional force, on the other hand, acts to slow down air movement near the Earth's surface, so wind speeds are generally higher at higher altitudes where there is less friction.
Describe how wind direction is determined.
Wind direction is determined by the direction from which the wind is blowing. To determine wind direction, one can use a wind vane or windsock, which aligns with the direction of the wind. Another method is to observe the movement of objects or vegetation in the wind, as they will generally point in the direction of the wind. Additionally, weather instruments such as anemometers or weather vanes can provide accurate readings of wind direction.
What is the Coriolis effect and how does it affect wind patterns?
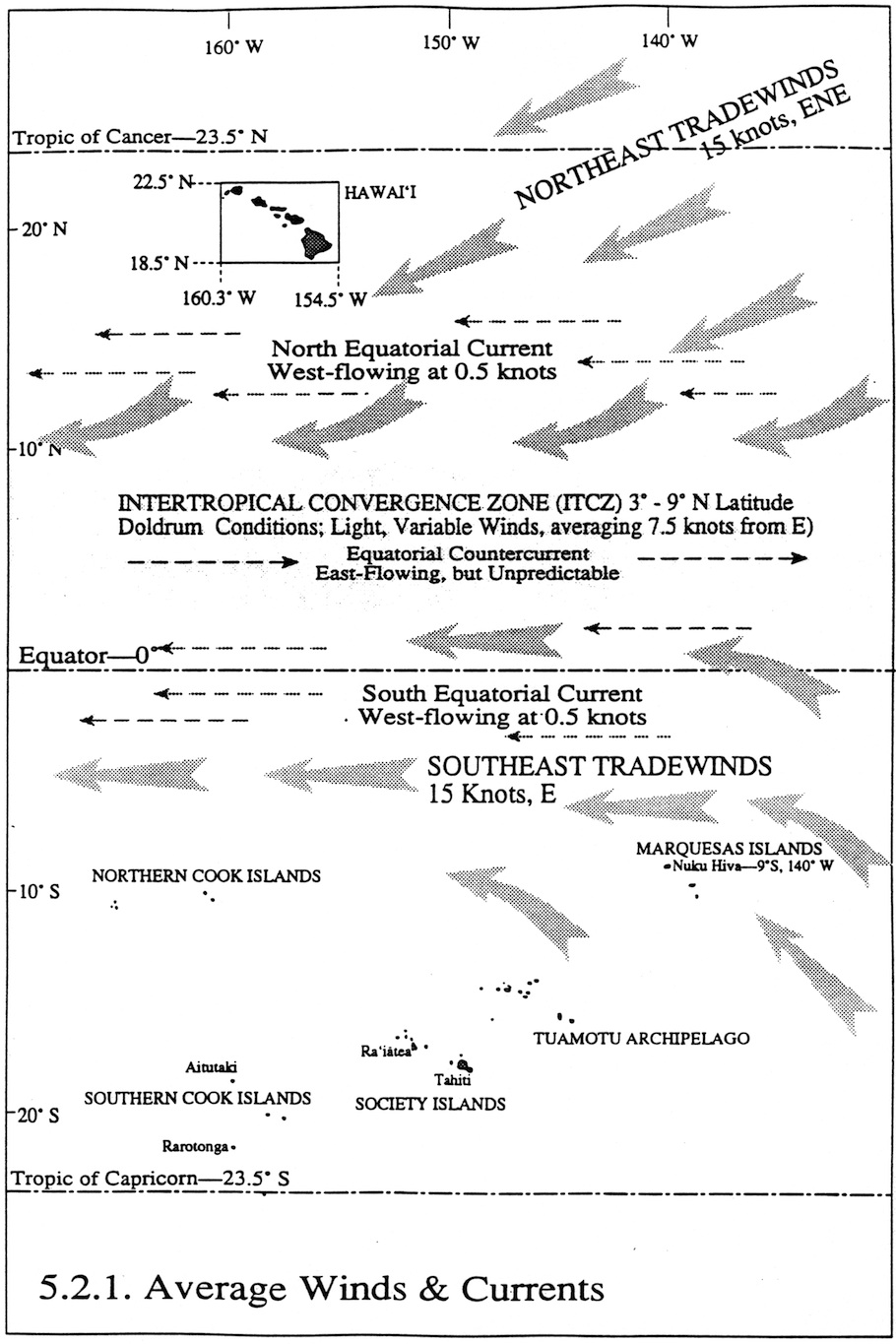
The Coriolis effect is a phenomenon caused by the rotation of the Earth, which deflects moving objects to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. In relation to wind patterns, the Coriolis effect influences the direction of air circulation around high and low-pressure systems, contributing to the creation of global wind patterns and steering the direction of winds across the Earth's surface. This results in the formation of prevailing winds, such as the trade winds and westerlies, which play a crucial role in shaping weather patterns and climate around the world.
Explain the difference between local winds and global winds.
Local winds are small-scale winds that occur within a limited area and are influenced by local geographic features like mountains, valleys, and bodies of water. They tend to change direction based on the time of day and local conditions, such as sea breezes or mountain/valley breezes. In contrast, global winds are large-scale wind patterns that occur on a global level and are driven by the Earth's rotation, the tilt of its axis, and the differential heating of the Earth's surface. These winds, such as the trade winds and westerlies, generally blow in consistent directions and play a significant role in shaping global weather patterns.
How do differences in air pressure create wind?
Differences in air pressure create wind by causing air to move from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. When high pressure and low pressure systems interact, the air molecules in the high pressure system move towards the low pressure system to try and balance out the pressure difference. The air moves in response to this pressure gradient force, resulting in the formation of wind as the air flows from one area to another.
Describe the process of convection and its role in wind formation.
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluid particles caused by density differences. In the atmosphere, warm air rises due to lower density, while cooler air sinks due to higher density, creating circulation patterns. This vertical movement of air leads to the formation of convection currents, which play a significant role in generating wind. As the air moves, it carries heat energy and moisture, influencing weather patterns and climate. The Earth's rotation and uneven heating of the planet's surface further contribute to the development of winds through convection, shaping global wind patterns.
What are the three types of winds in the atmosphere?
The three types of winds in the atmosphere are planetary winds, local winds, and upper-level winds. Planetary winds are large scale winds that blow consistently in specific directions due to the Earth's rotation and differences in temperature and pressure. Local winds are smaller scale winds influenced by local topography, temperature variations, and pressure gradients. Upper-level winds occur at high altitudes in the atmosphere and play a crucial role in shaping weather patterns by steering surface winds and affecting the movement of weather systems.
How are winds named and classified according to their speed?
Winds are named and classified based on their speeds. Tropical cyclones are categorized into different classes - tropical depressions, tropical storms, and hurricanes/typhoons based on their wind speeds. The Beaufort Wind Scale is another method used to classify winds based on their speeds, ranging from 0 (calm) to 12 (hurricane-force). Additionally, the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale categorizes hurricanes into five different levels based on their sustained wind speeds, with Category 5 being the most severe.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments