Basic Matrix Worksheets
Matrix worksheets are an invaluable tool for anyone seeking to gain a deeper understanding of the subject and improve problem-solving skills. These worksheets provide a structured format to practice various matrix operations, making them ideal for students studying mathematics or anyone looking to enhance their proficiency in linear algebra.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
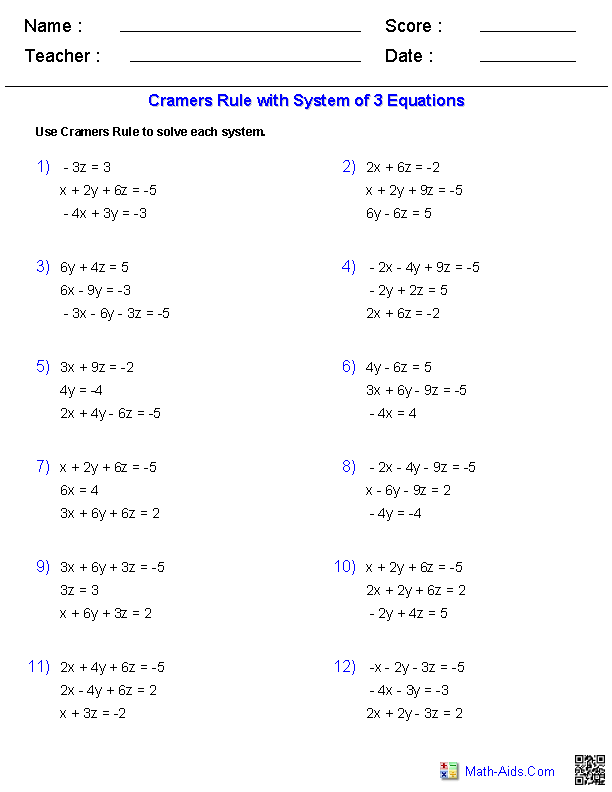
What is a matrix?
A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions arranged in rows and columns. It is often used in mathematics to represent mathematical concepts, perform calculations, and solve equations. Matrices are fundamental in linear algebra and have various applications in fields such as physics, engineering, computer science, and economics.
What are the dimensions of a matrix?
The dimensions of a matrix are determined by the number of rows and columns it contains. For example, a matrix with 3 rows and 4 columns would have dimensions 3x4.
What is the difference between a row matrix and a column matrix?
A row matrix is a matrix with only one row, where the elements are placed horizontally, whereas a column matrix is a matrix with only one column, where the elements are placed vertically. In other words, a row matrix is wider than it is tall, while a column matrix is taller than it is wide.
What is a square matrix?
A square matrix is a matrix that has the same number of rows and columns, making it a two-dimensional array of numbers arranged in a square shape.
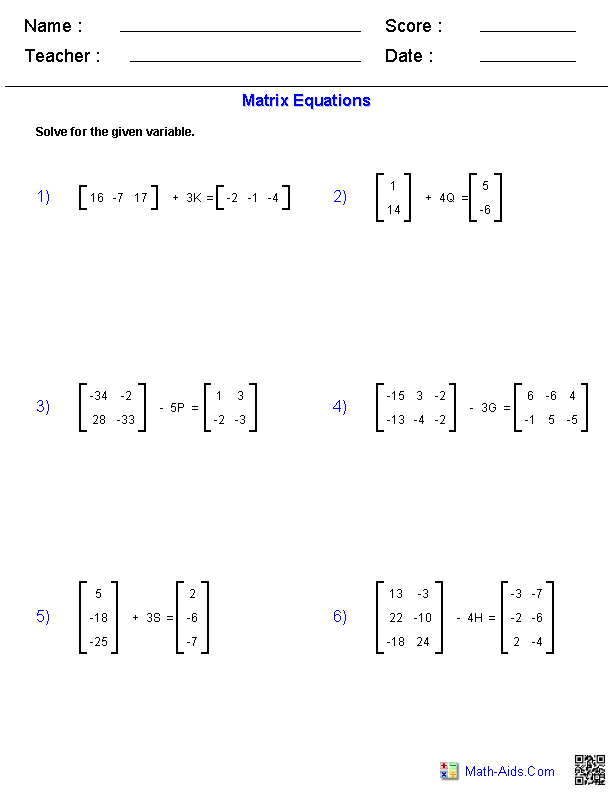
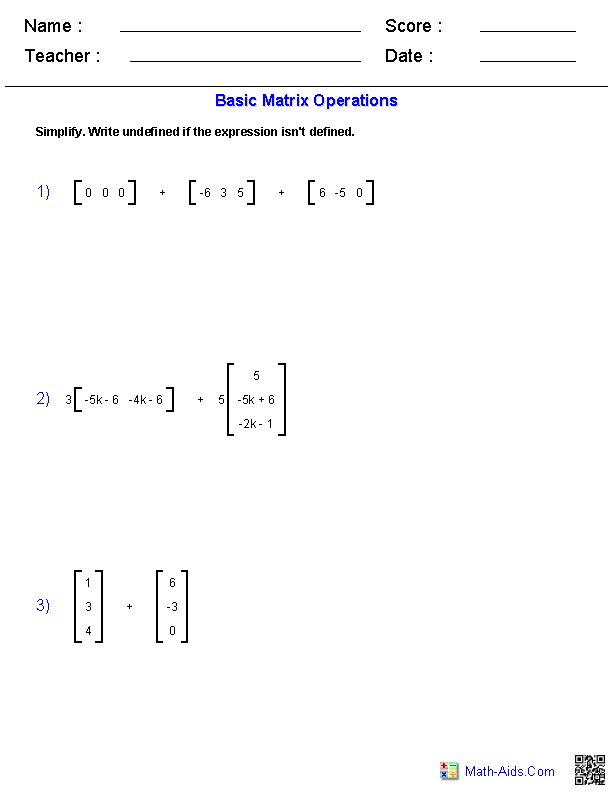
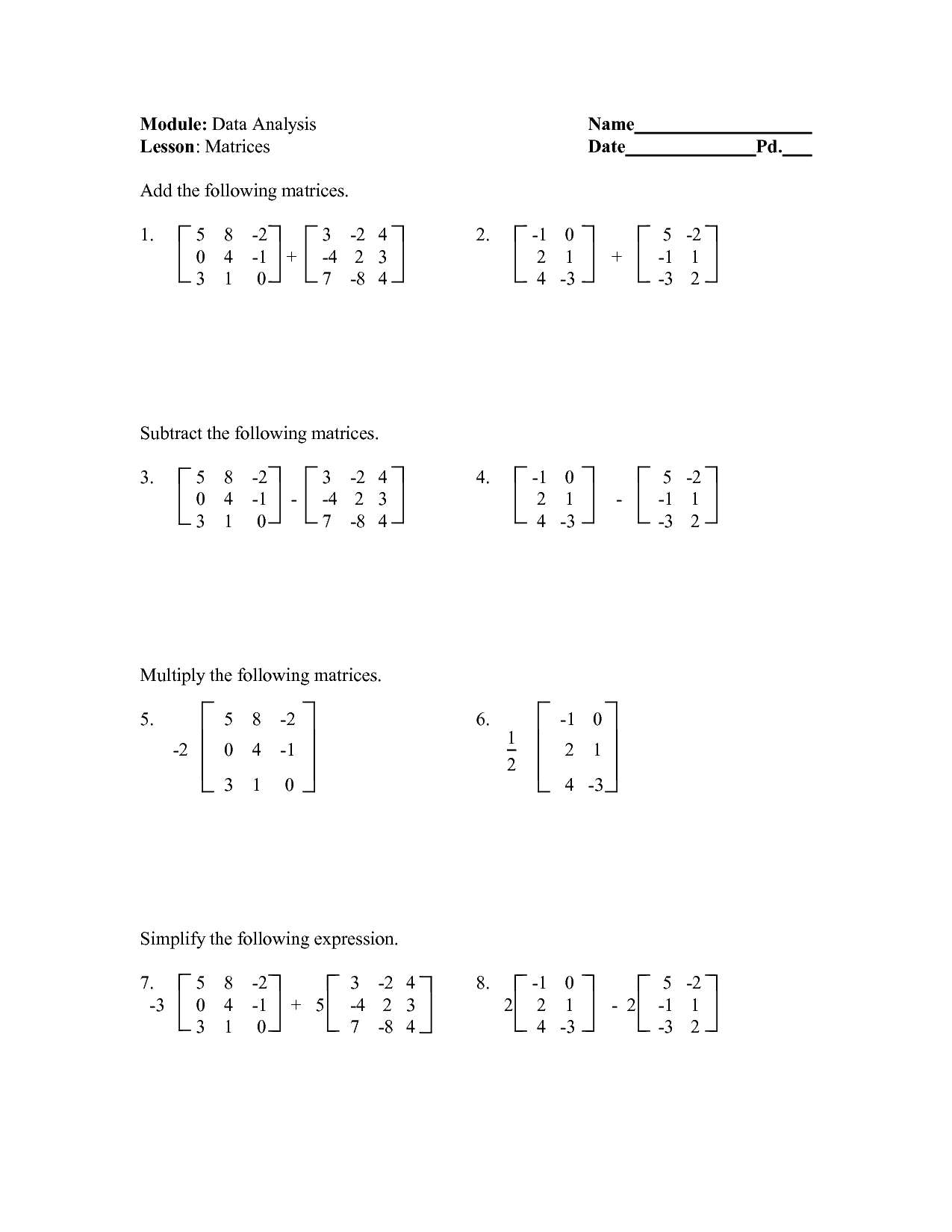
How do you add two matrices?
To add two matrices, you simply add the corresponding elements of each matrix together. This means that element (i, j) of the resulting matrix would be the sum of element (i, j) from the first matrix and element (i, j) from the second matrix. The matrices must have the same dimensions in order for addition to be possible.
How do you multiply a matrix by a scalar?
To multiply a matrix by a scalar, simply multiply every element in the matrix by the scalar value. Each element in the original matrix is multiplied by the scalar to yield the corresponding element in the resulting matrix. This operation allows scaling the entire matrix by the specified scalar value.
What is the transpose of a matrix?
The transpose of a matrix is a new matrix formed by flipping the rows and columns of the original matrix. This means that the rows of the original matrix become the columns of the new matrix, and vice versa. The transpose is denoted by adding a superscript "T" to the original matrix, such as A^T. Transposing a matrix does not change its diagonal elements, but it swaps the off-diagonal elements across the main diagonal.
How do you multiply two matrices?
To multiply two matrices, the number of columns in the first matrix must equal the number of rows in the second matrix. Take the dot product of each row of the first matrix with each column of the second matrix and sum the products to fill in each element of the resulting matrix. The resulting matrix will have the same number of rows as the first matrix and the same number of columns as the second matrix. The multiplication is not commutative, meaning the order of the matrices matters in matrix multiplication.
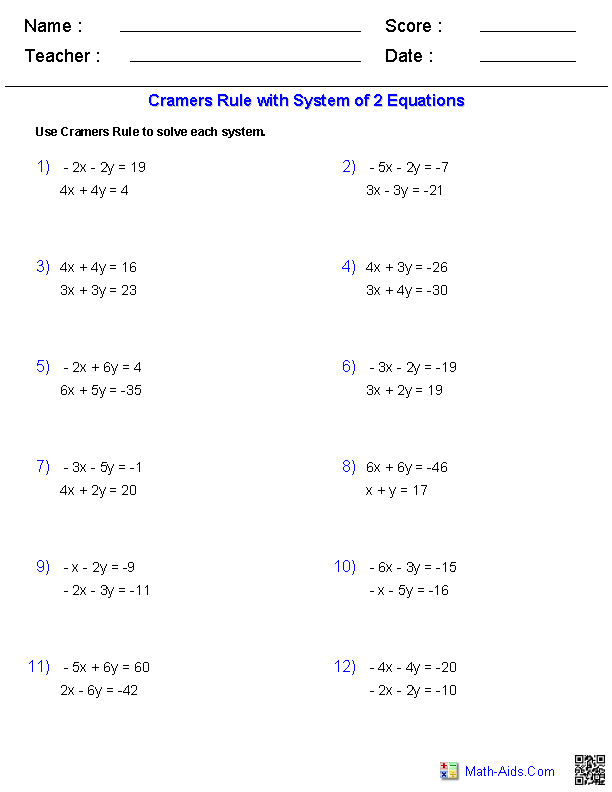
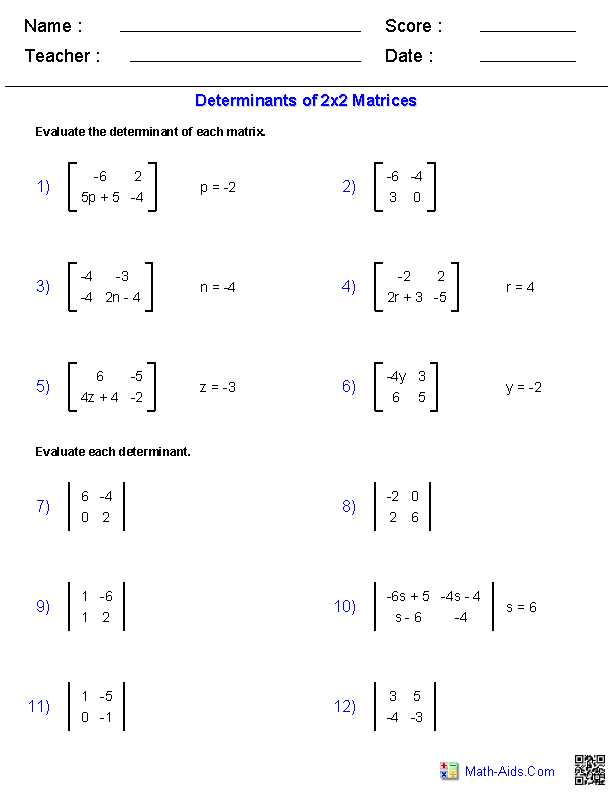
What is the determinant of a matrix?
The determinant of a matrix is a scalar value that can be calculated from the elements of a square matrix. It provides important information about the matrix, such as whether the matrix is invertible and if its columns are linearly independent. The determinant of a 2x2 matrix is calculated by subtracting the product of the top right and bottom left elements from the product of the top left and bottom right elements. For larger matrices, the determinant can be computed using different methods such as cofactor expansion or by using row operations.
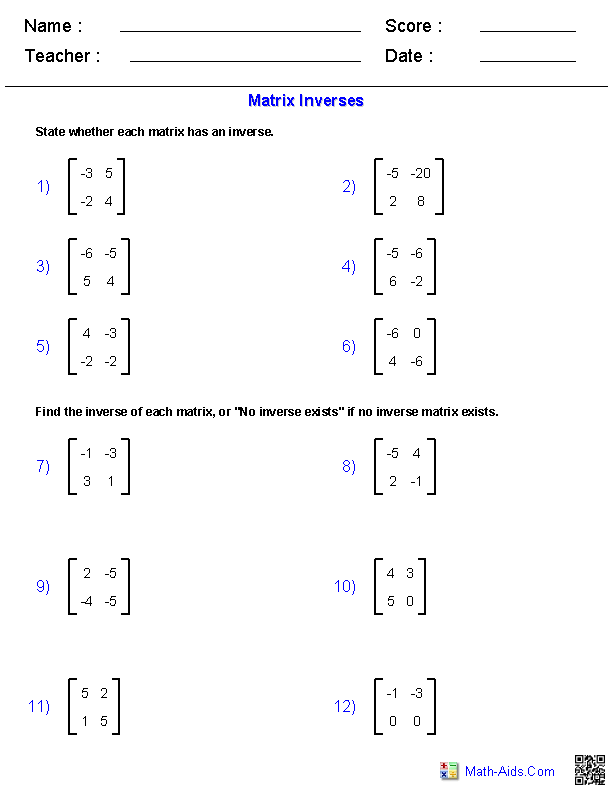
How do you find the inverse of a matrix?
To find the inverse of a matrix, you first need to check if the matrix is invertible by calculating its determinant. If the determinant is non-zero, you can proceed to find the inverse by using matrix operations such as row reduction to put the matrix into reduced row-echelon form, and then applying elementary row operations to transform it into the identity matrix. The resulting matrix on the right side will then be the inverse of the original matrix.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




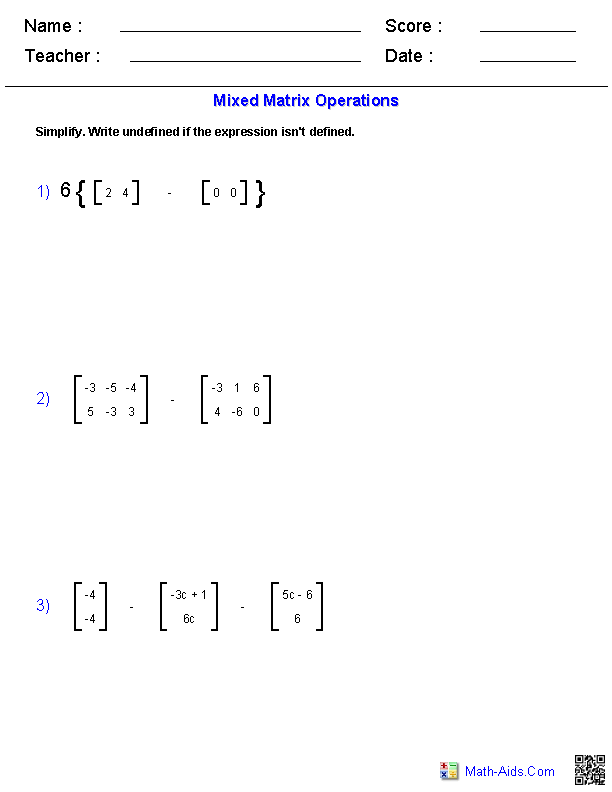
















Comments