Bar Graphs Worksheets Grade 4
Bar graphs are a valuable learning tool for students in Grade 4. These worksheets provide an engaging way to practice interpreting and creating bar graphs, helping students gain a deeper understanding of data representation and analysis.
Table of Images 👆
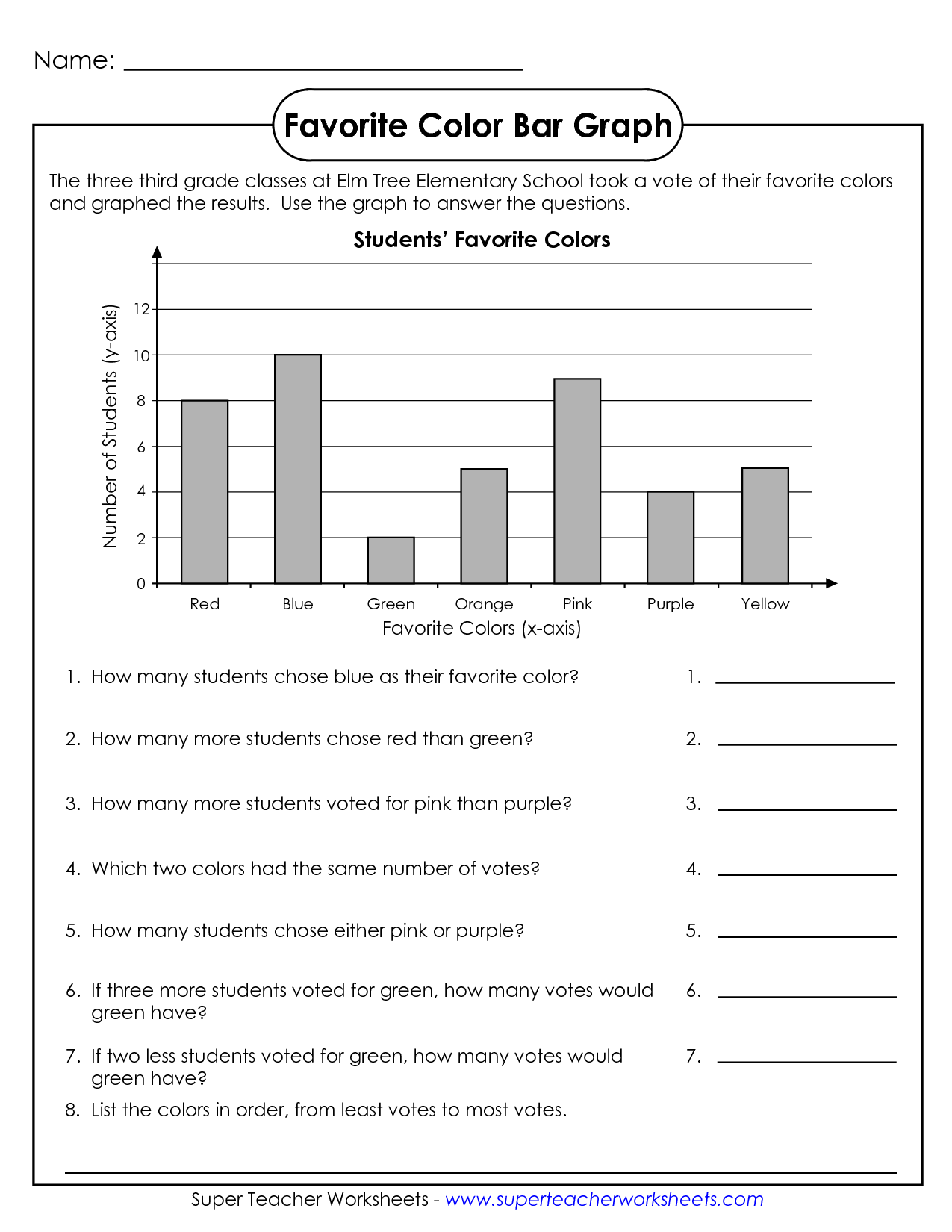
- Bar Graph Worksheets 3rd Grade
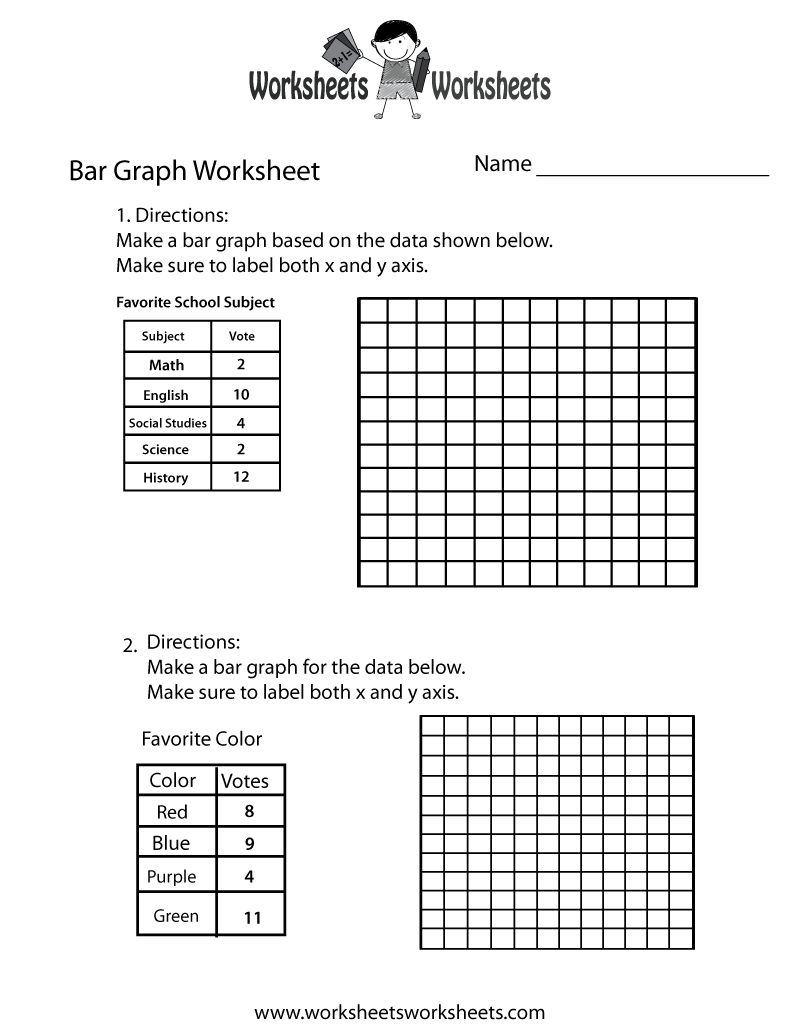
- Printable Bar Graph Worksheet
- Bar Graph and Pictograph Worksheets 3rd Grade
- 5th Grade Math Worksheets Graphs
- Bar Graph Worksheets
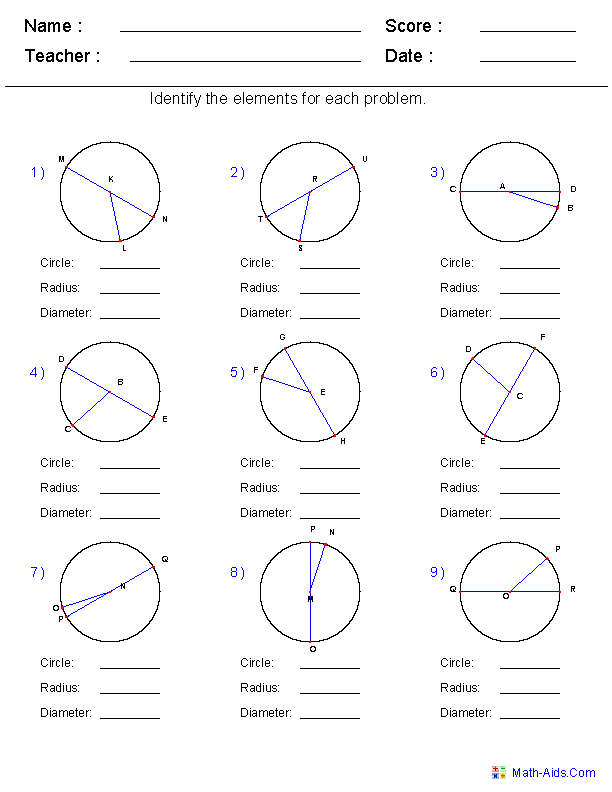
- Radius Diameter Circumference Worksheets
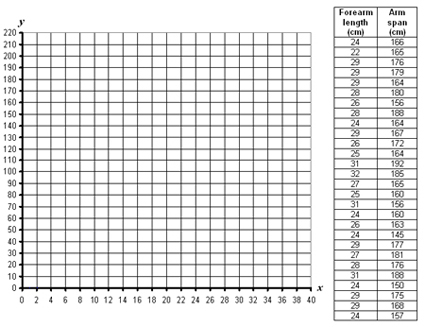
- Scatter Plot Graph Paper
- Kindergarten Graph Worksheets
- Blank Number Chart 1 100
- Subtraction Word Problems Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a bar graph?
A bar graph is a type of chart that represents data with rectangular bars where the length of each bar is proportional to the value it represents. It is commonly used to compare different categories or show changes over time by displaying the data along a horizontal or vertical axis.
How are bar graphs used to represent data?
Bar graphs are used to represent data by showing the relationship between different categories, typically displaying data as rectangular bars of varying lengths. The height or length of each bar corresponds to the quantity or value being represented, making it easy to compare and visualize differences in data among the categories. Bar graphs are particularly effective for showcasing trends, comparisons, and distributions in data sets with discrete categories or groups.
What is the purpose of labeling the x and y axes on a bar graph?
The purpose of labeling the x and y axes on a bar graph is to clearly indicate what each axis represents. The x-axis typically represents categories or groups being compared, while the y-axis represents the numerical values being measured. By labeling the axes, viewers can easily understand the data being presented and interpret the relationship between the categories and their corresponding values on the graph.
How do you read data from a bar graph?
To read data from a bar graph, start by identifying the x-axis and y-axis. The x-axis usually represents the categories or groups being compared, while the y-axis shows the values or quantities being measured. Look at the length or height of each bar to determine the magnitude of the data point it represents. Be mindful of the scale used on the graph to accurately interpret the values. The bar that is highest or longest typically corresponds to the highest value in the dataset, and the comparison between bars can help in understanding the relationships between different categories or groups.
How can you create a bar graph using collected data?
To create a bar graph using collected data, first organize your data into categories and corresponding values. Then, choose a suitable scale for the vertical axis based on the range of values in your data. Draw a horizontal axis and mark the categories along it. Next, draw bars for each category with heights corresponding to the values being represented. Ensure that each bar is of equal width and evenly spaced. Finally, label the axes, add a title to the graph, and provide any necessary context or explanations to make the graph clear and meaningful to the viewer.
What are the advantages of using a bar graph to display data?
Bar graphs are advantageous for displaying data as they easily allow for comparison between different categories or groups, making it simple to visualize patterns and trends within the data. The distinct bars make it easy to interpret the relationships between different sets of information, providing a clear and concise representation of the data. Additionally, bar graphs are an effective way to present numerical data in a visually appealing and easy-to-understand format, making it accessible to a wide audience with varying levels of data literacy.
How do you choose the appropriate scale for a bar graph?
To choose the appropriate scale for a bar graph, you should first determine the range of values being displayed in the data set. The scale should evenly distribute the values along the vertical axis without overcrowding or leaving too much empty space. It is important to use a scale that allows for clear differentiation between the bars while also ensuring that the graph is visually appealing and easy to interpret for the audience.
What types of data are best represented using a bar graph?
Bar graphs are best used to represent categorical, non-continuous data that can be easily divided into distinct, separate categories. This includes comparing data sets, showing relationships between different categories, and visualizing differences in quantities or frequencies of discrete data points. Bar graphs are particularly effective for displaying data that is easily counted or measured in distinct units, making them a popular choice for presenting survey results, demographic information, and other forms of categorical data analysis.
How do you compare data using a bar graph?
To compare data using a bar graph, you can analyze the height or length of the bars. The length or height of each bar represents the value of a specific category or group, making it easy to visually see and compare the differences in values between the categories. Additionally, you can look at the positioning of the bars relative to each other to understand the relationship between the data points being compared.
How can you interpret trends and patterns in a bar graph?
To interpret trends and patterns in a bar graph, you can examine the height and length of the bars to identify similarities or disparities between different categories. Look for any consistent increase or decrease in bar heights across the categories to identify trends. Pay attention to any outliers or anomalies that may indicate unique occurrences or discrepancies. Compare the sizes of the bars to each other as well as to a common reference point, such as a baseline or a benchmark, to gauge the magnitude of differences. Lastly, consider the overall shape of the graph and the arrangement of the bars to discern any patterns or relationships between the categories.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments