Bar Graph Worksheets 7th Grade
Bar graph worksheets are an essential tool for 7th-grade students to strengthen their understanding of analyzing and interpreting data. These worksheets provide a structured and comprehensive approach to learning about bar graphs, allowing students to grasp the fundamentals of representing information visually. By engaging with these worksheets, students can enhance their skills in identifying key elements of a bar graph, such as the title, labels, and scale, as well as interpreting the data accurately.
Table of Images 👆
- Science Charts and Graphs Worksheets
- Bar Graph 2nd Grade Math Worksheets
- Bar Graph and Pictograph Worksheets 3rd Grade
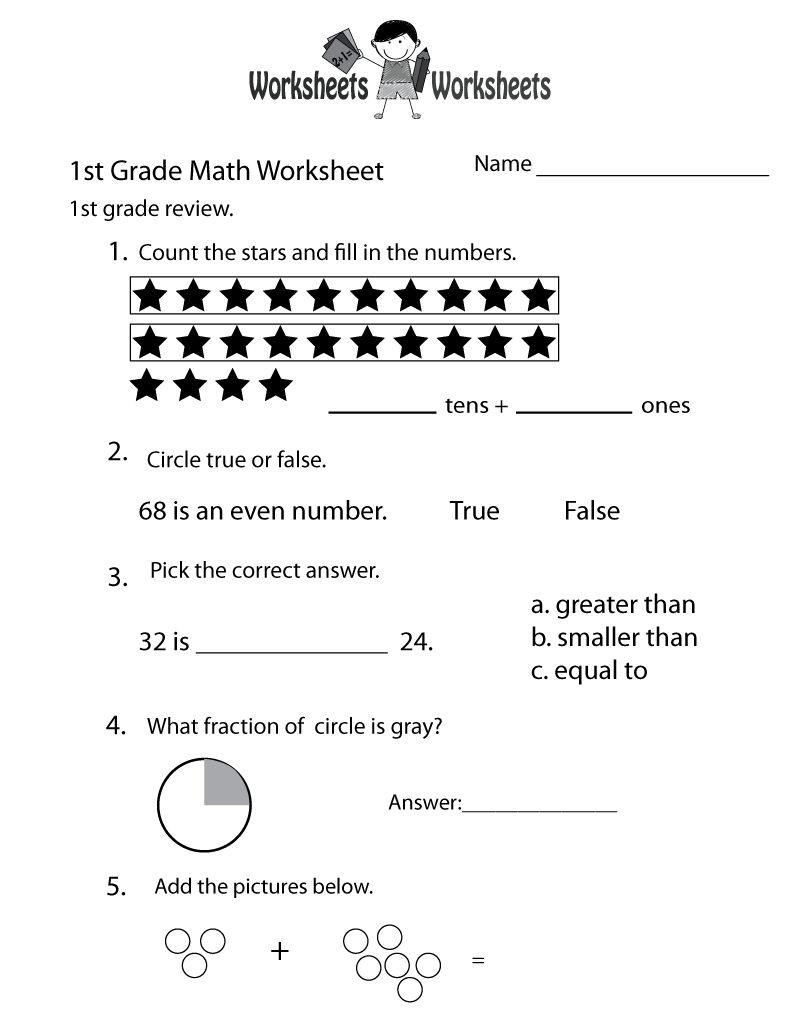
- 1st Grade Math Worksheets Printable
- Interpreting Line Graphs Worksheet
- Pythagorean Theorem Worksheets
- Common Core Fractions 3rd Grade Math Worksheets
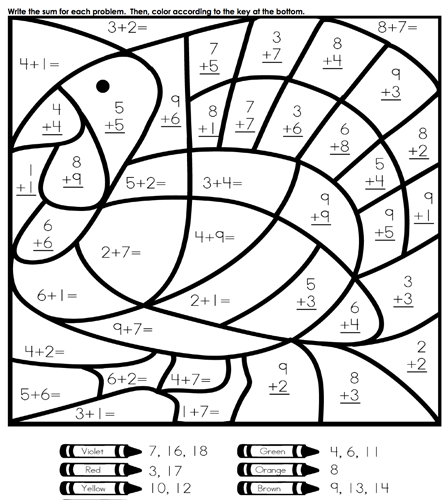
- 6th Grade Math Coloring Worksheets
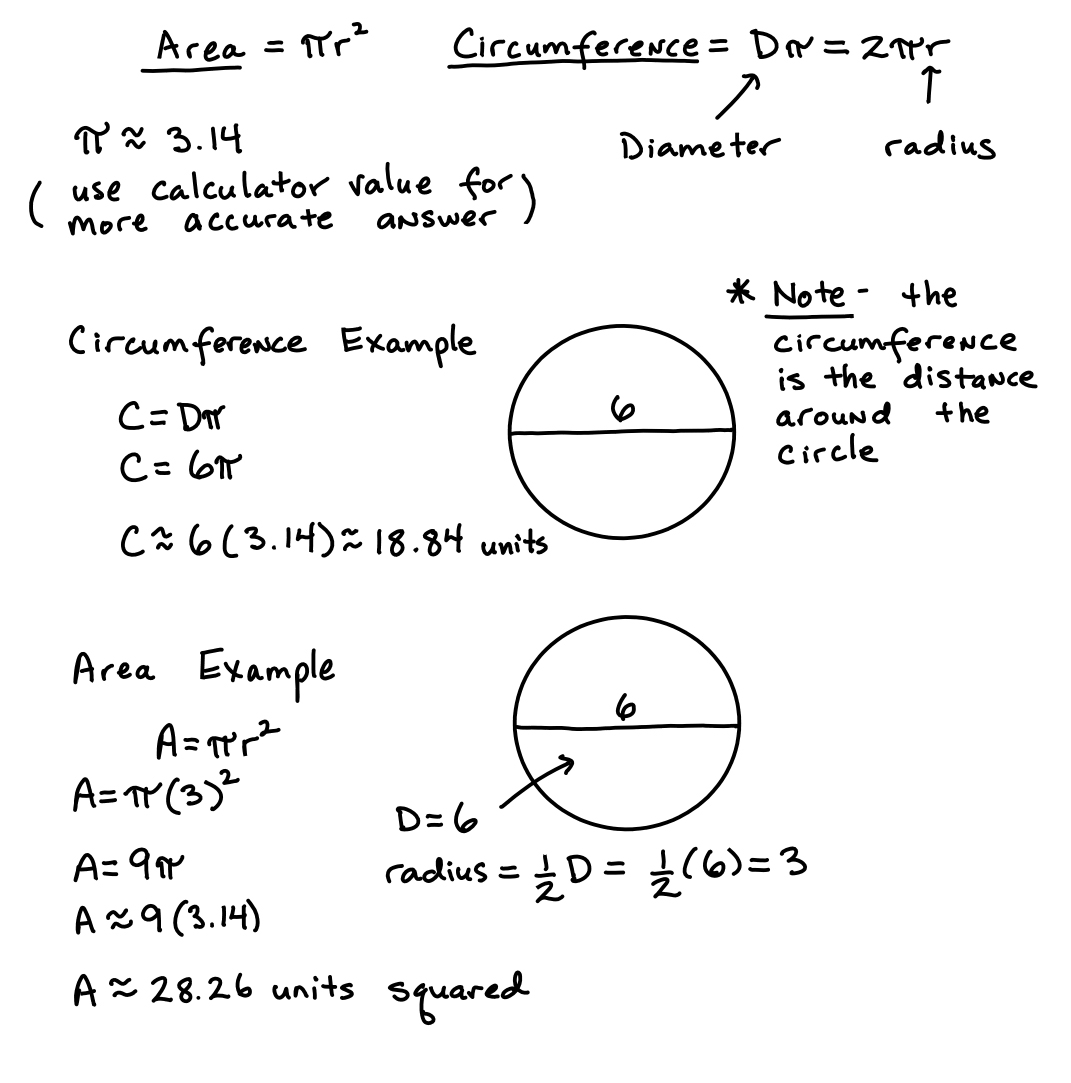
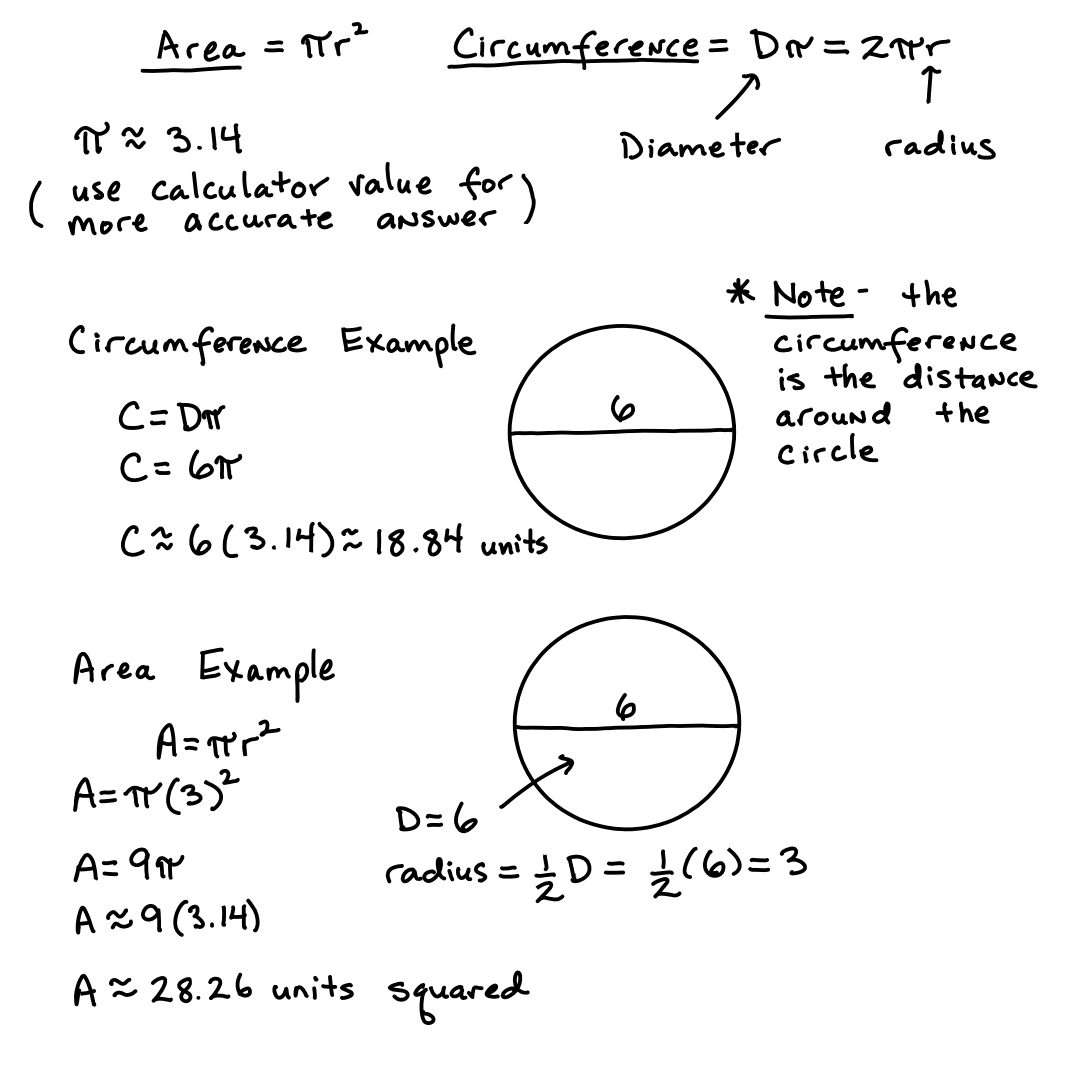
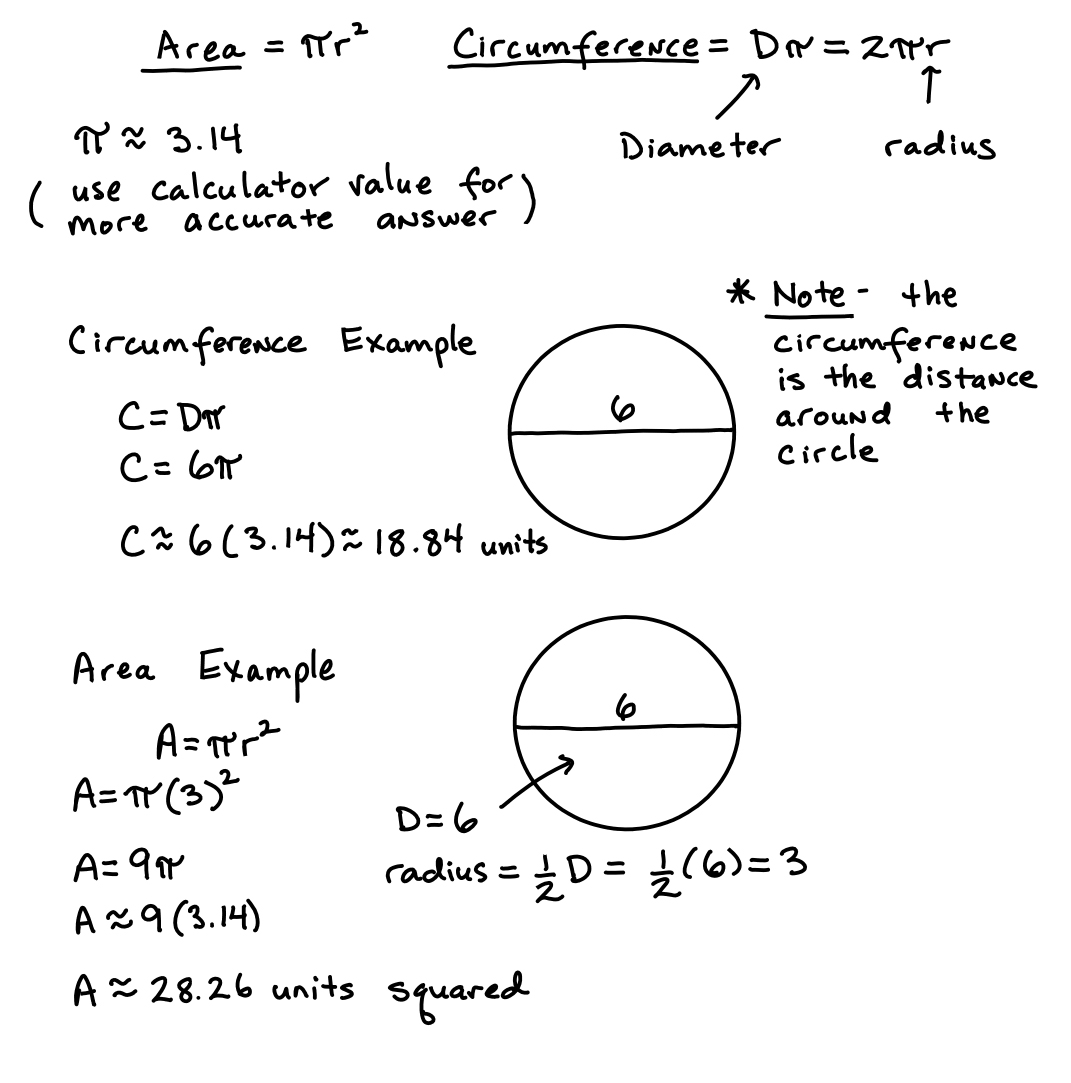
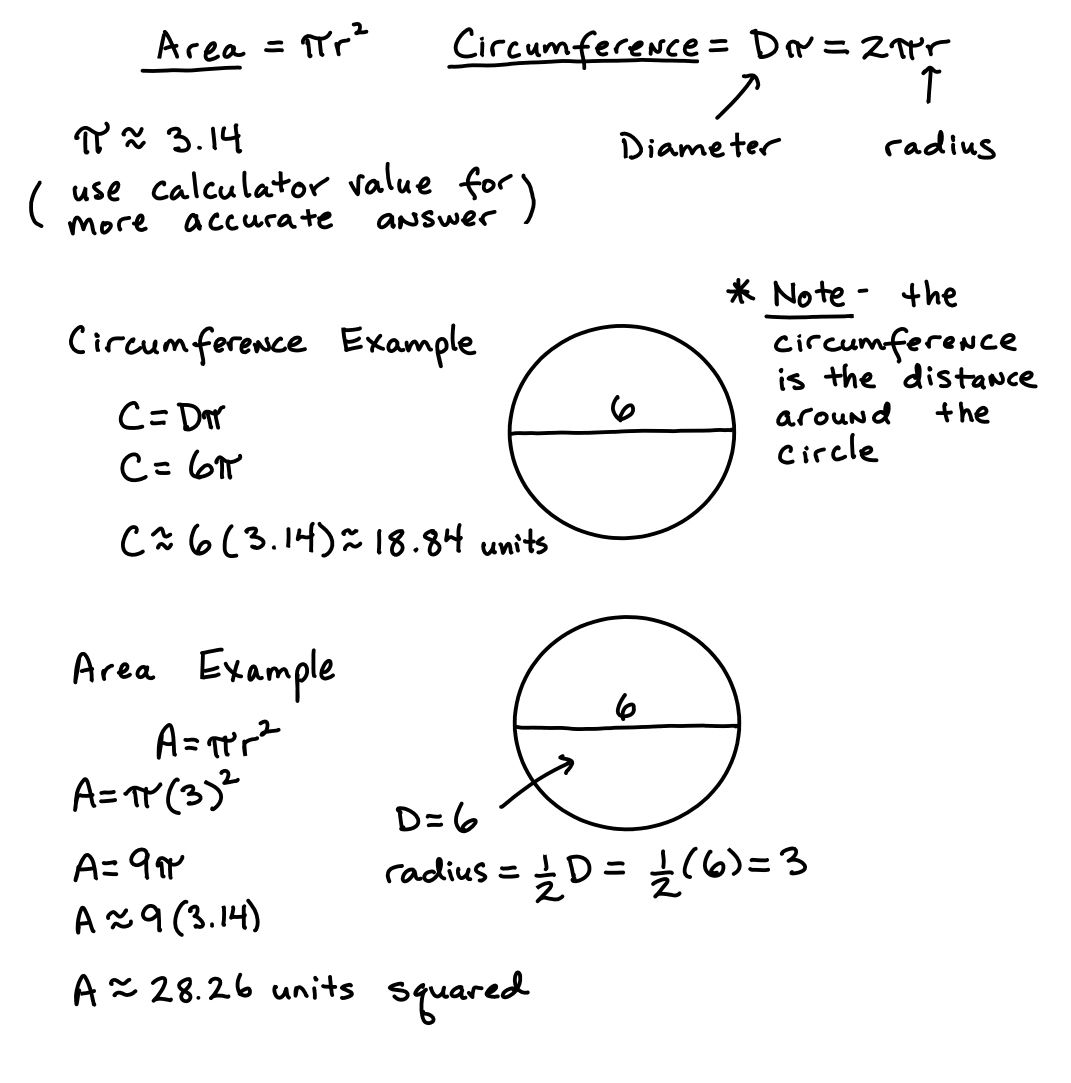
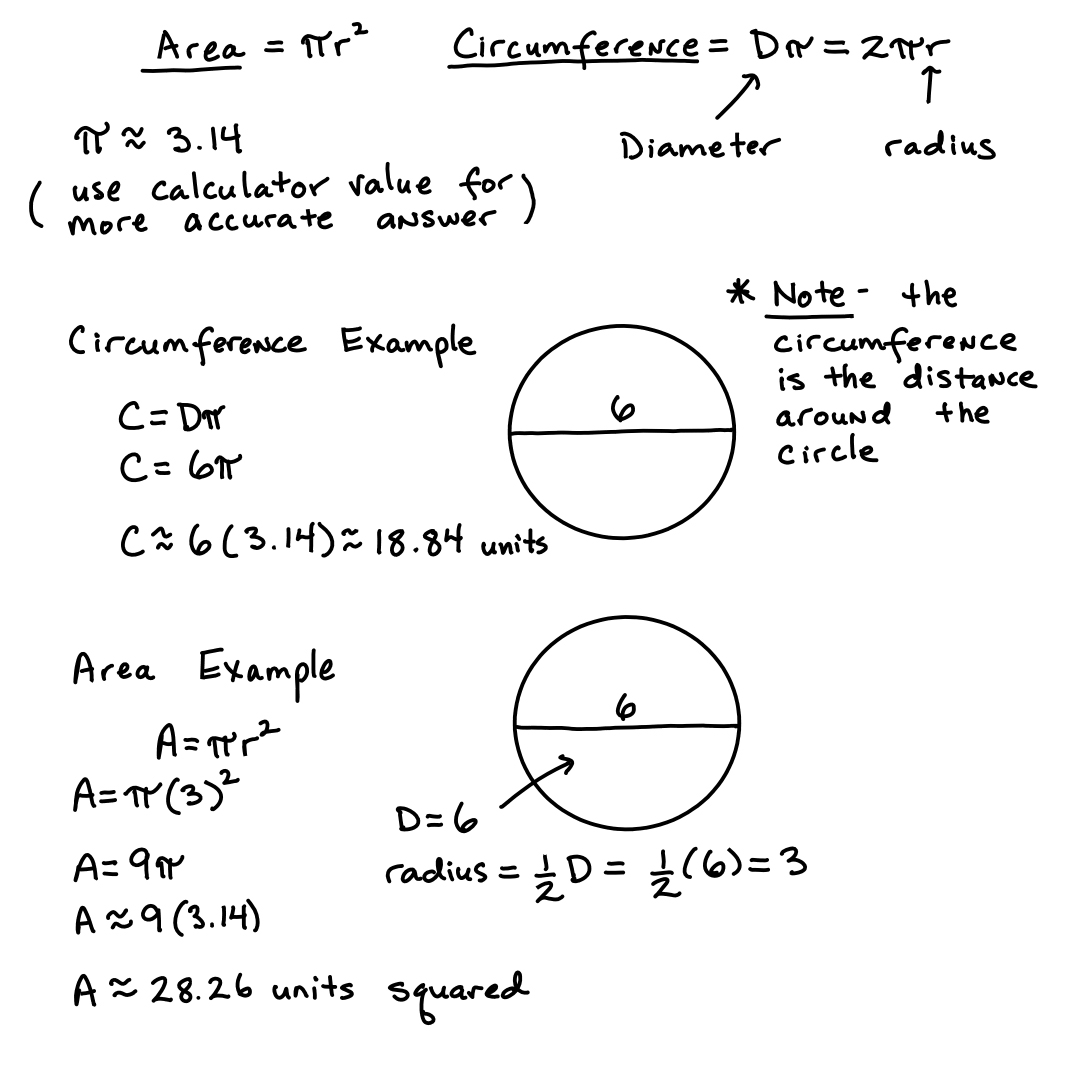
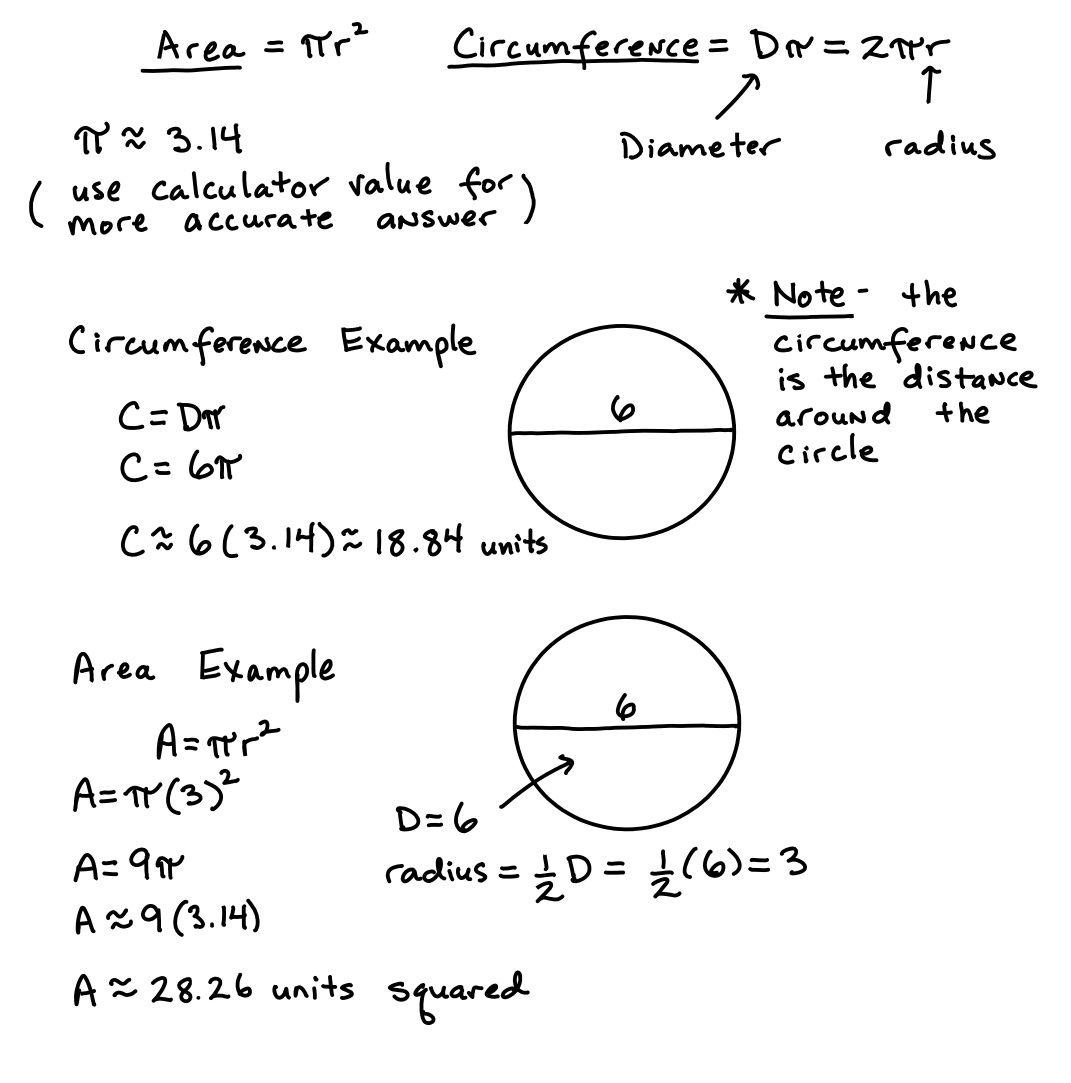
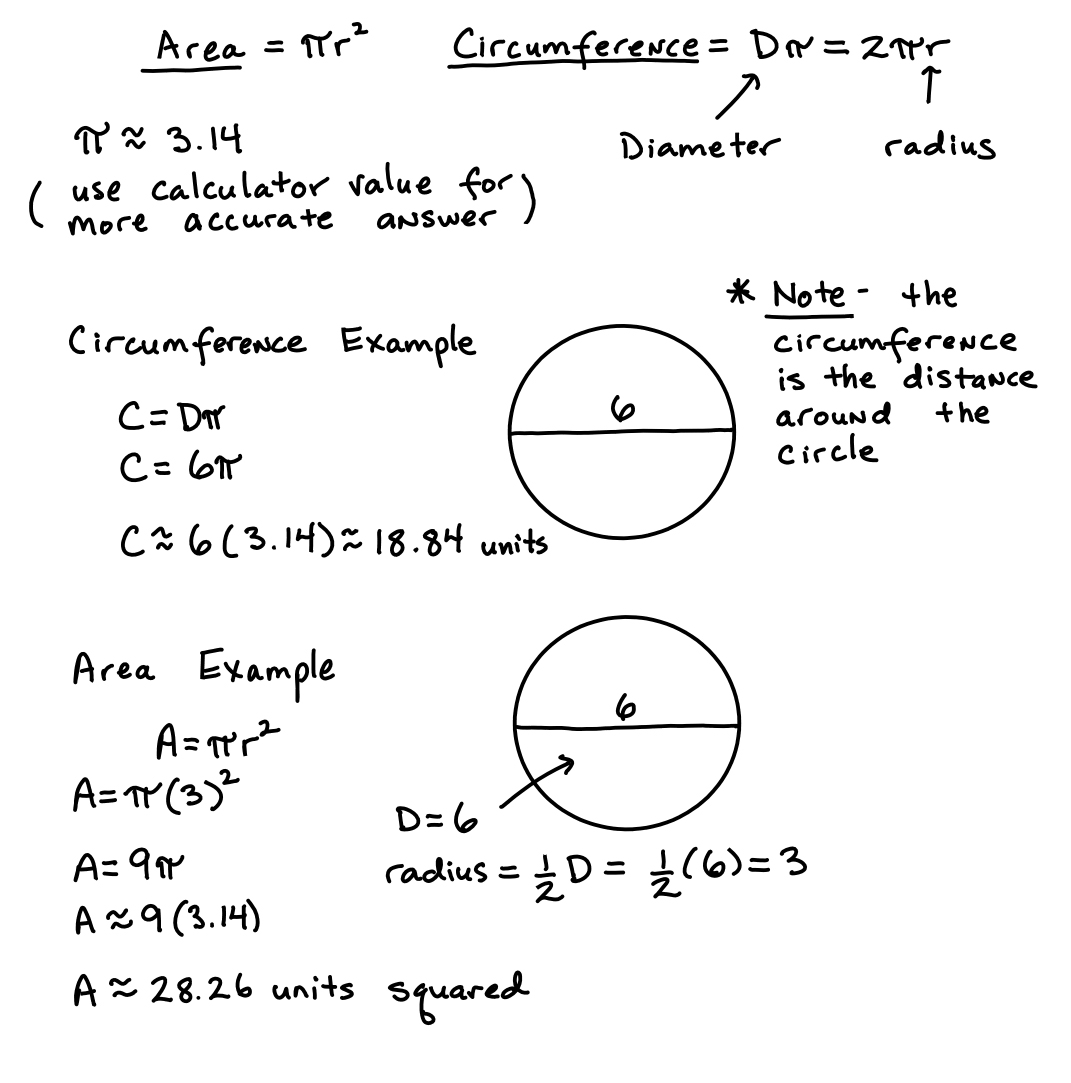
- Circle Circumference and Area Formula
More 7th Grade Worksheets
7th Grade Vocabulary WorksheetsPre-Algebra 7th Grade Math Worksheets
7th Grade Math Worksheets Proportions
Complex Sentence Worksheets 7th Grade
Geometry Angles Worksheet 7th Grade Math
What is a bar graph?
A bar graph is a visual representation of data that uses rectangular bars of varying lengths to show the frequency or distribution of a certain category or numerical value. Each bar represents a specific category, and the height or length of the bar corresponds to the amount or frequency of that category in the data set. Bar graphs are commonly used to make comparisons between different categories or display trends over time.
How is a bar graph different from other types of graphs?
A bar graph differs from other types of graphs because it represents data using bars of varying lengths to show the magnitude of each data point. Each bar is usually separate and distinct, making it easy to compare values visually. In contrast, line graphs connect data points with lines to show trends or changes over time. Pie charts represent proportions of a whole using slices of a circle, while scatter plots display the relationship between two variables through individual data points on a graph.
What are the different components of a bar graph?
The different components of a bar graph include a horizontal or vertical axis to represent the categories or values being compared, bars of varying lengths representing the data points, labels to provide context or identification for each bar, a title to summarize the data being displayed, and a scale to show the intervals or values along the axes.
How do you choose the appropriate scale for a bar graph?
To choose the appropriate scale for a bar graph, start by determining the range of your data values. Then, select a scale that clearly represents this range while also making it easy for viewers to interpret the data. Ensure that the scale increments are evenly spaced and labeled clearly to accurately depict the differences between data points. Additionally, consider the size of the graph and the amount of information to be displayed to ensure that the scale is not too crowded or sparse. Adjust the scale as needed to best represent the data in a clear and visually appealing manner.
How do you label the x-axis and y-axis on a bar graph?
To label the x-axis on a bar graph, you typically include the category or variable being represented. For the y-axis, you would label it with the scale or measurement being used. These labels help viewers understand what data the graph is displaying and interpret the information accurately.
What is the purpose of a title in a bar graph?
The purpose of a title in a bar graph is to provide a clear and concise description of the data being presented. This helps viewers quickly understand the main subject or theme of the graph without having to analyze the data points individually. Additionally, a title can also provide context and help facilitate interpretation of the information displayed in the graph.
How do you plot data on a bar graph?
To plot data on a bar graph, you will need to determine the categories or variables you want to represent on the x-axis and the corresponding values or frequencies on the y-axis. Then, draw rectangular bars for each category, where the height or length of the bar represents the value or frequency in the data set. Make sure to label the axes, title the graph, and use a consistent scale to accurately represent the data. You can use graphing software or tools like Microsoft Excel to easily create a bar graph for your data.
How do you interpret the information displayed on a bar graph?
To interpret information on a bar graph, look at the height of each bar to represent the quantity or value of the data. Compare the heights of the bars to see which values are larger or smaller. Check the labels on the axes to understand the categories or variables being compared. Pay attention to patterns, trends, or outliers in the data to draw insights from the bar graph and make informed conclusions.
How can you compare and contrast data using a bar graph?
To compare and contrast data using a bar graph, you can visually represent the different data sets on a common scale by using bars of varying lengths. The height of each bar corresponds to the value of the data it represents, allowing for easy comparison between different categories or groups. To contrast the data, you can analyze the differences in the heights of the bars, identifying patterns or trends in the data sets being compared. Additionally, different colors or patterns can be used for each category or group of data to further enhance the visual contrast in the bar graph.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating a bar graph?
Some common mistakes to avoid when creating a bar graph include using misleading scaling or unequal widths for the bars, not clearly labeling the axes and data points, cluttering the graph with unnecessary information or decorations, and using overly complex or confusing color schemes. It is important to keep the design simple, make sure data is accurately represented, and ensure that the graph is easy to interpret and understand at a glance.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments