Atomic Structure Worksheet PDF
Are you searching for a useful resource to help your students understand the concepts of atomic structure? Look no further! We have gathered a comprehensive collection of atomic structure worksheets in a convenient PDF format. These worksheets are designed to engage students and reinforce their understanding of key topics such as subatomic particles, electron configuration, and periodic trends. Whether you are an educator looking for supplementary material or a student seeking extra practice, these worksheets are the perfect tool to enhance your study of atomic structure.
Table of Images 👆
- Atomic Structure Practice Worksheet
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
- Mass and Atomic Number Worksheet
- Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- Theory and Atomic Structure Worksheet
- Chemistry Atomic Structure Worksheet
- Atomic Structure of an Atom Worksheet
- Electron Orbital Diagram Worksheet
- Atomic Theory Worksheet
- Periodic Table Worksheet Answer Key
- Models of the Atom Worksheet Answers
- Drawing Atoms Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
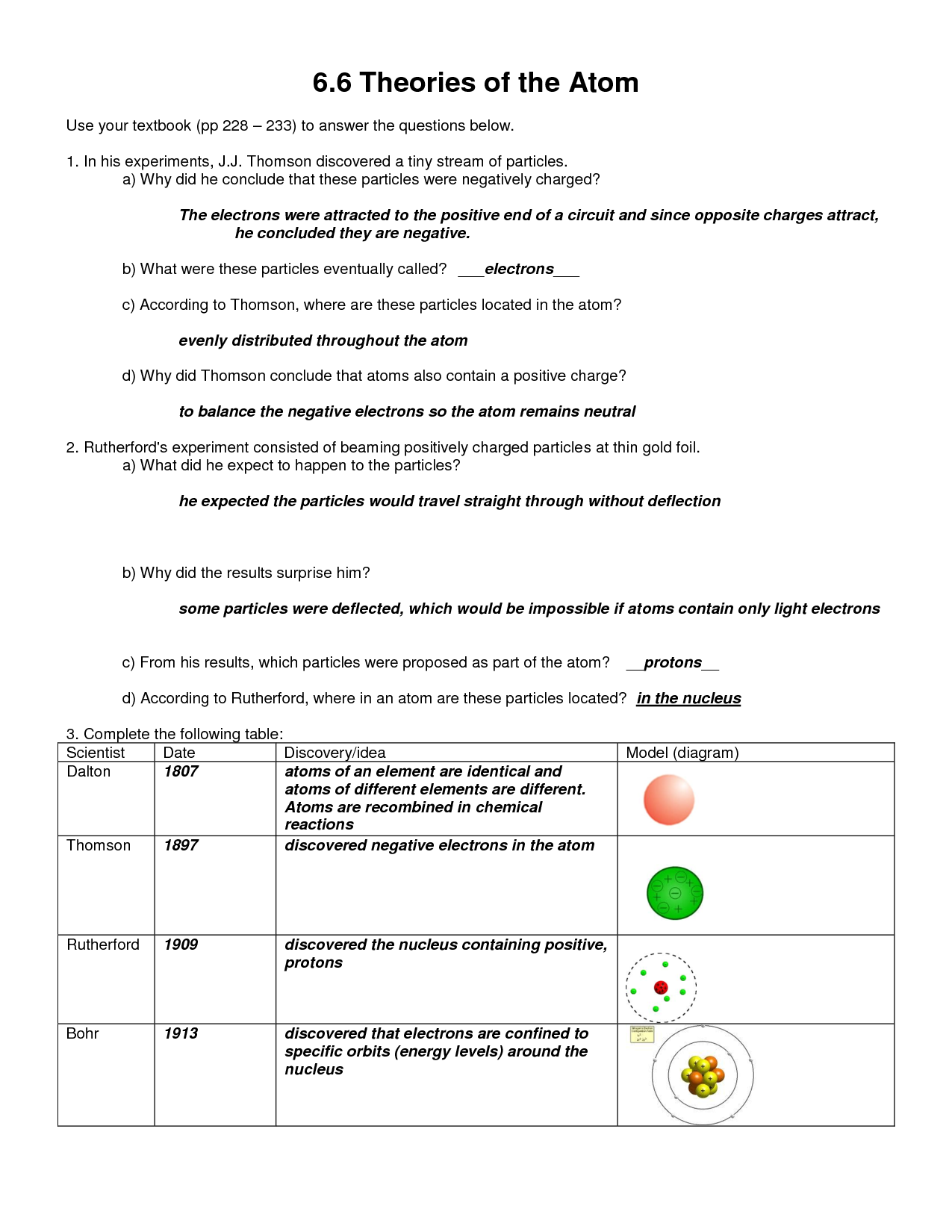
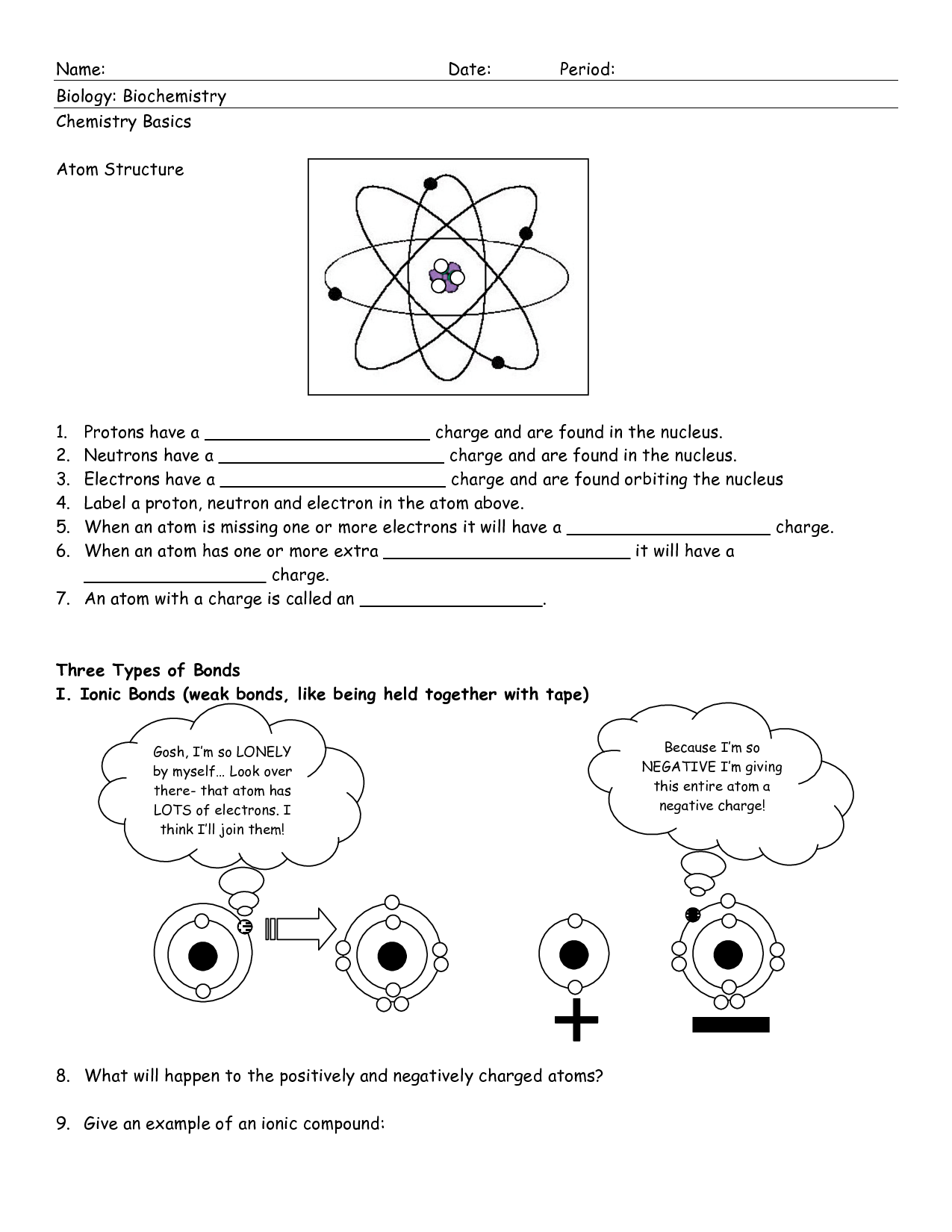
What is an atom?
An atom is the basic unit of matter that consists of a nucleus, containing positively charged protons and neutral neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. Atoms are the building blocks of all elements and combine to form molecules through chemical bonding, defining the properties and behavior of substances.
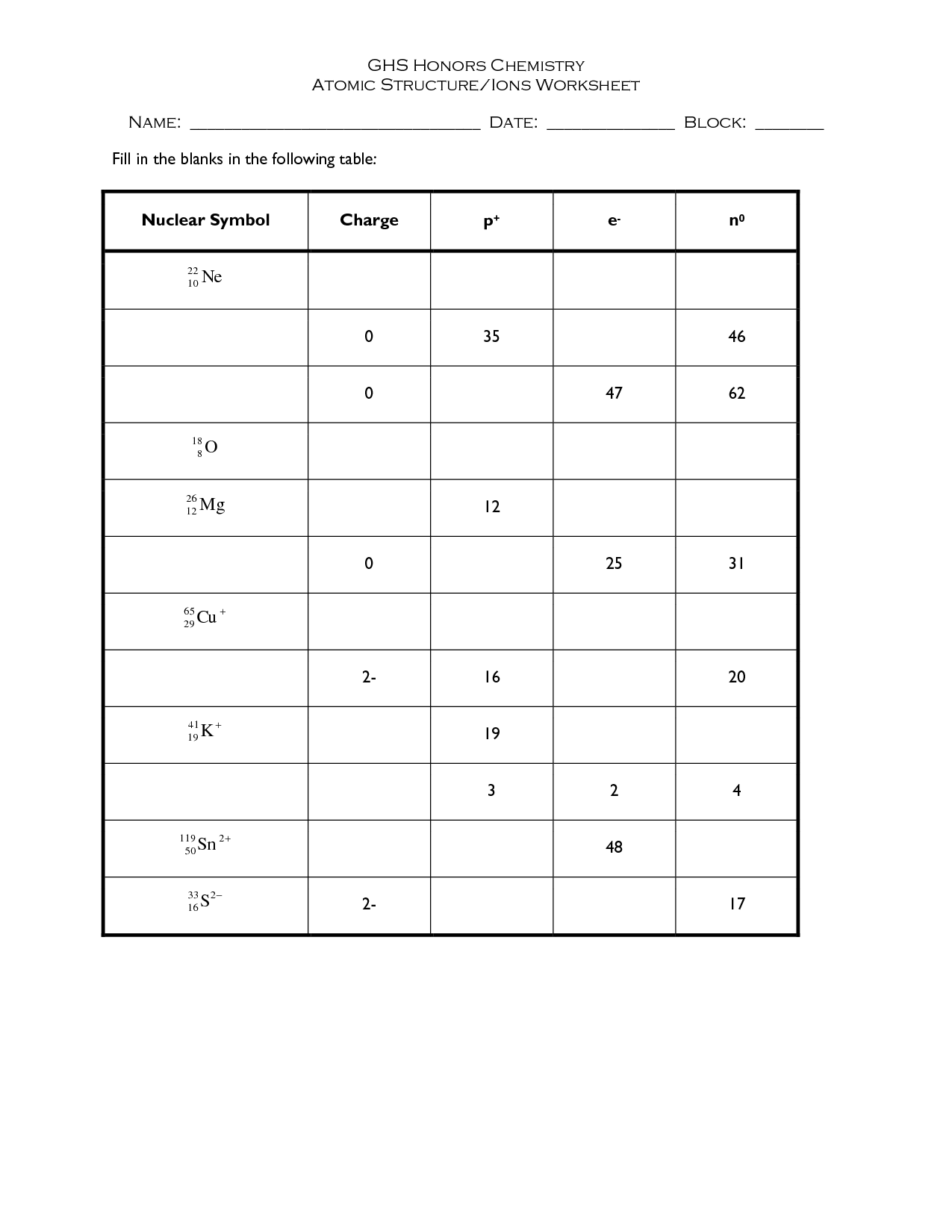
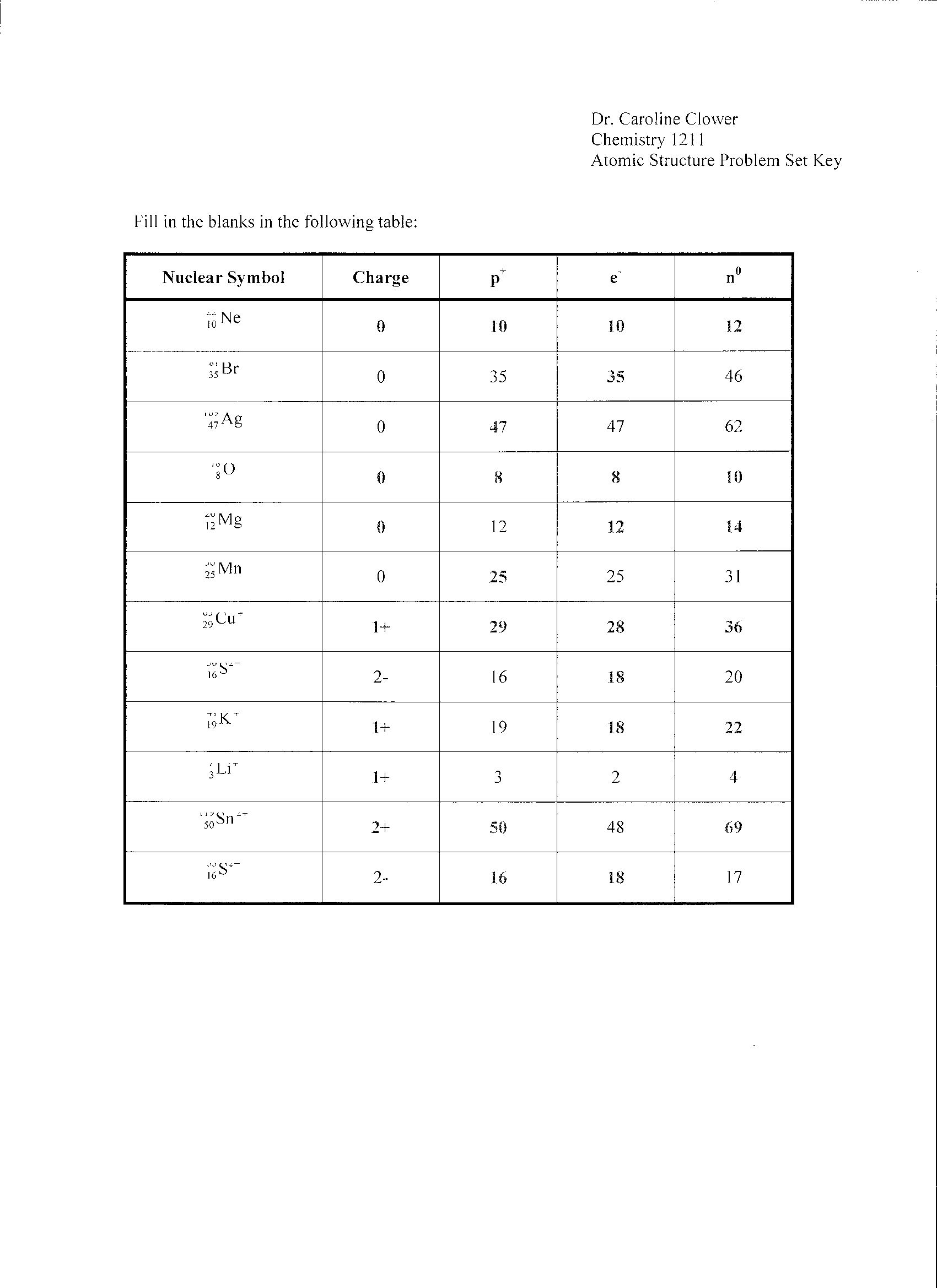
What are the three subatomic particles and their respective charges?
The three subatomic particles are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons have no charge (neutral), and electrons have a negative charge.
How are protons and neutrons different?
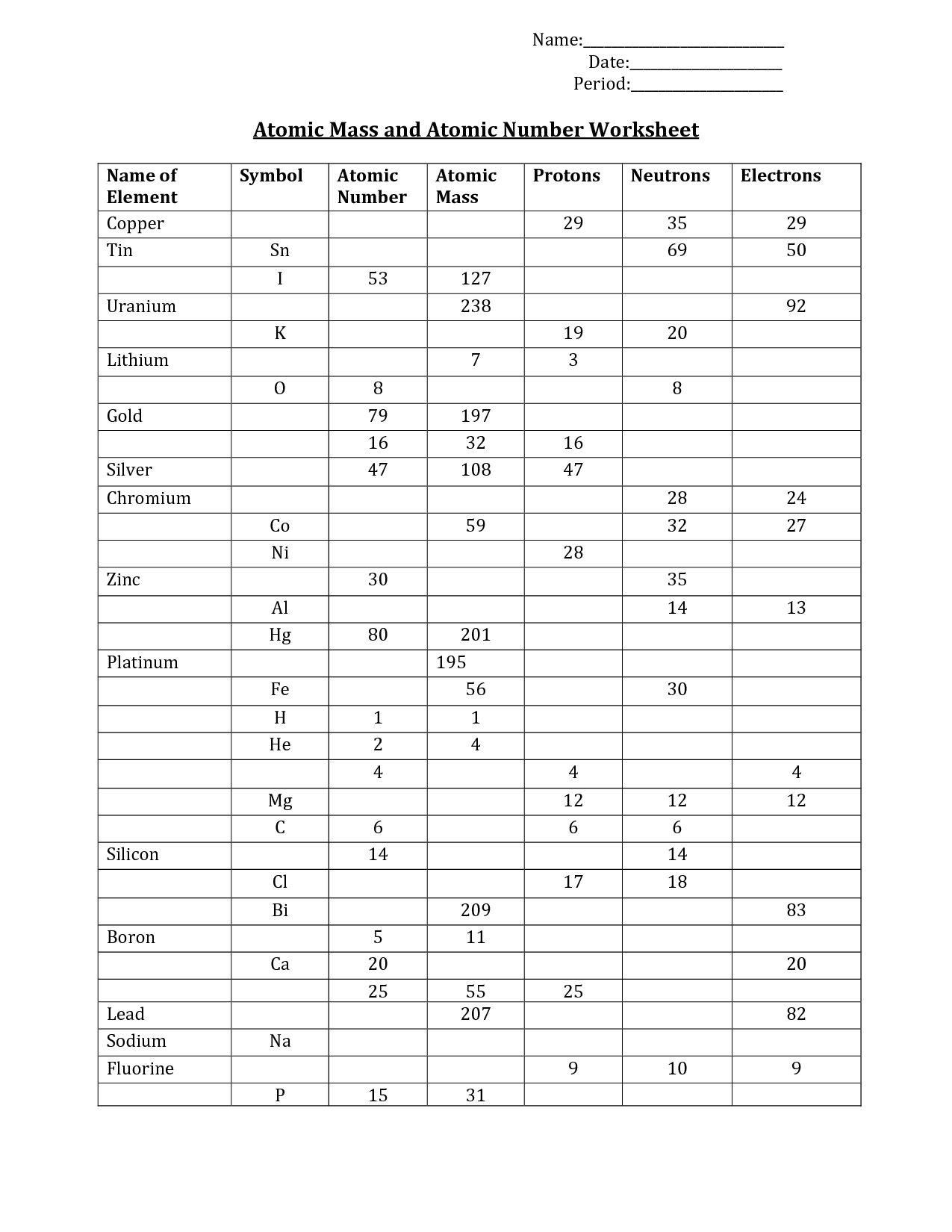
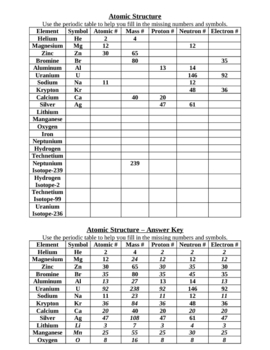
Protons are positively charged subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom, while neutrons are neutral subatomic particles found alongside protons in the nucleus. Protons determine the identity of an element, as the number of protons in an atom's nucleus determines its atomic number and defines its chemical properties. Neutrons help stabilize the nucleus and contribute to the atomic mass of the atom.
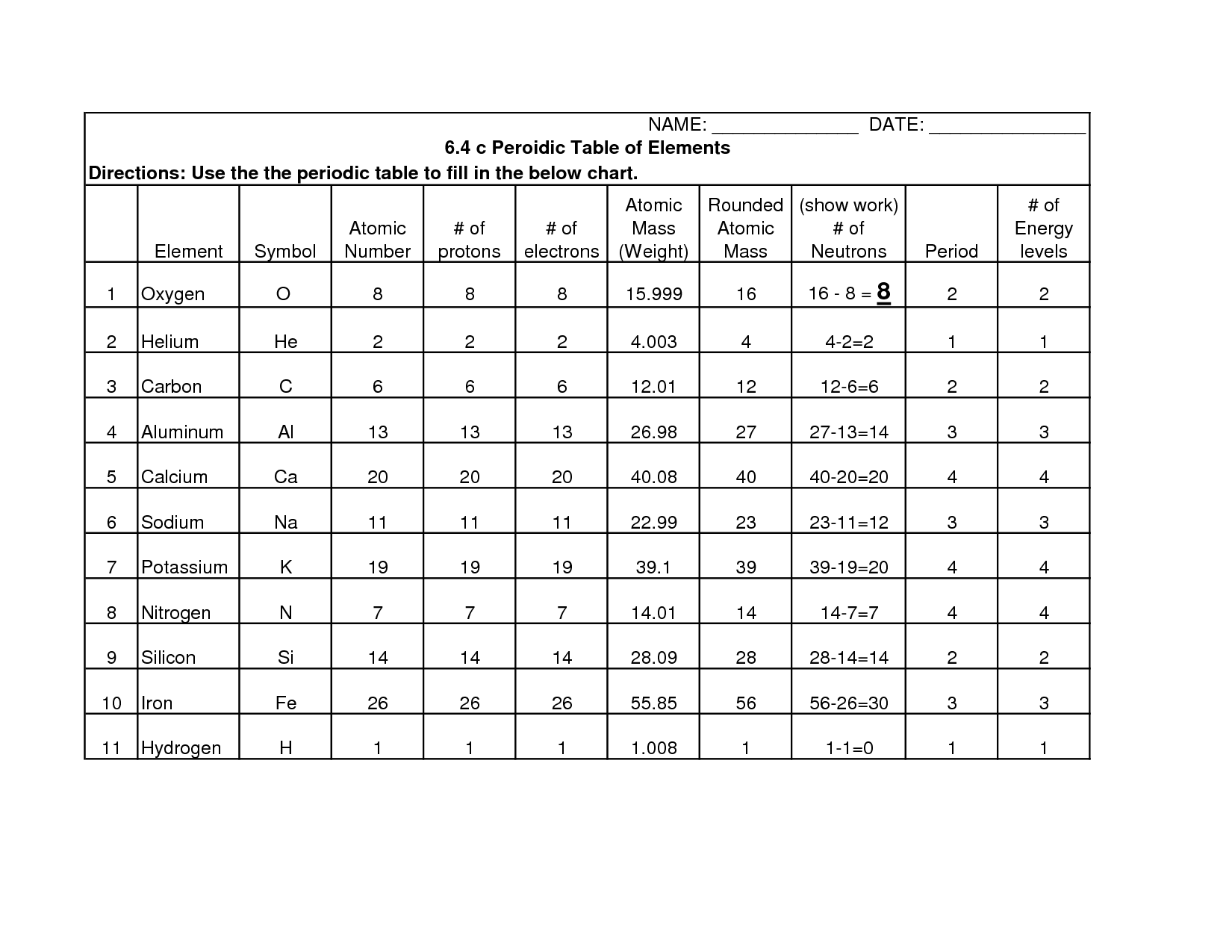
What determines the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number of an element is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Each element has a unique atomic number that corresponds to the number of protons it contains, which also dictates its chemical properties and its position on the periodic table.
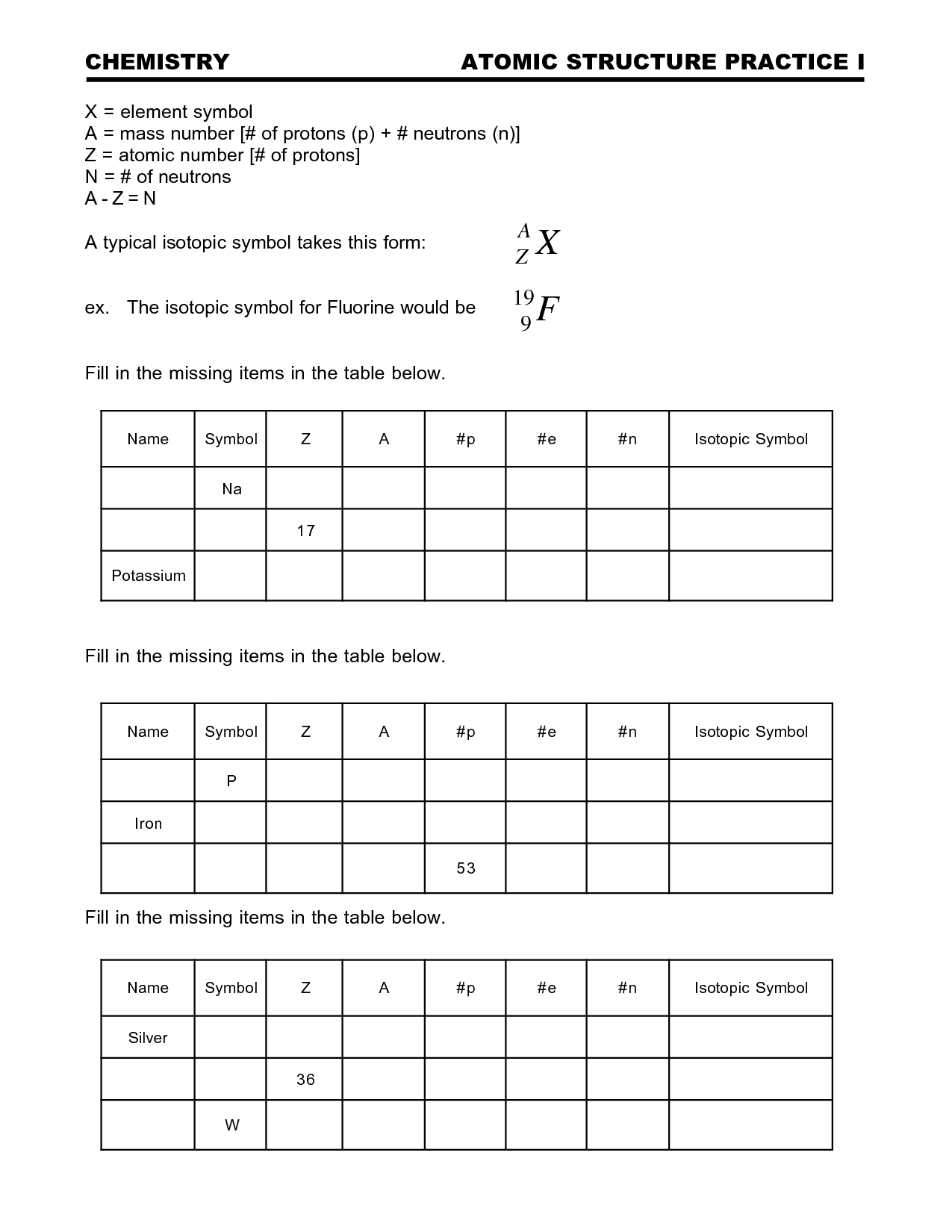
Define isotopes.
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons in their nucleus but differ in their number of neutrons, resulting in variations in atomic mass.
What is the mass number and how is it calculated?
The mass number of an atom is the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. It is calculated by adding the number of protons (which is the atomic number) to the number of neutrons in the nucleus. The mass number is an important characteristic of an atom and is used to determine the mass of the atom in atomic mass units (amu).
What is an electron shell?
An electron shell is a designated region surrounding an atomic nucleus where electrons are most likely to be found. The shells are organized in specific energy levels and are labeled with principal quantum numbers (n=1, 2, 3, etc.). Electrons occupy these shells in accordance with the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle, forming the structure of an atom.
What is the maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in each shell?
The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in each shell is determined by the formula 2n^2, where n is the principle quantum number of the shell. For example, the first shell can hold a maximum of 2 electrons (2*1^2 = 2), the second shell can hold a maximum of 8 electrons (2*2^2 = 8), the third shell can hold a maximum of 18 electrons (2*3^2 = 18), and so on.
What is the relationship between energy levels and electron shells?
Electron shells refer to the specific energy levels where electrons are found orbiting around an atom's nucleus. Each shell represents a different energy level, with electrons in the inner shells having lower energy levels than those in the outer shells. As electrons move to higher energy levels, they occupy outer electron shells, farther away from the nucleus. This relationship between energy levels and electron shells determines the arrangement of electrons in an atom and influences its chemical properties.
How does the arrangement of electrons in an atom determine its chemical properties?
The arrangement of electrons in an atom determines its chemical properties because it dictates how the atom will interact with other atoms to form chemical bonds. The number of electrons in the outermost energy level, known as the valence electrons, determines the atom's reactivity and its ability to form bonds with other atoms. Atoms will gain, lose, or share electrons in order to achieve a stable electron configuration, following the octet rule, which states that atoms tend to react in a way that gives them a full outer shell of electrons like the noble gases. This electron arrangement ultimately determines the atom's ability to form different types of chemical bonds, such as ionic, covalent, or metallic bonds, which in turn influence the atom's chemical properties.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments