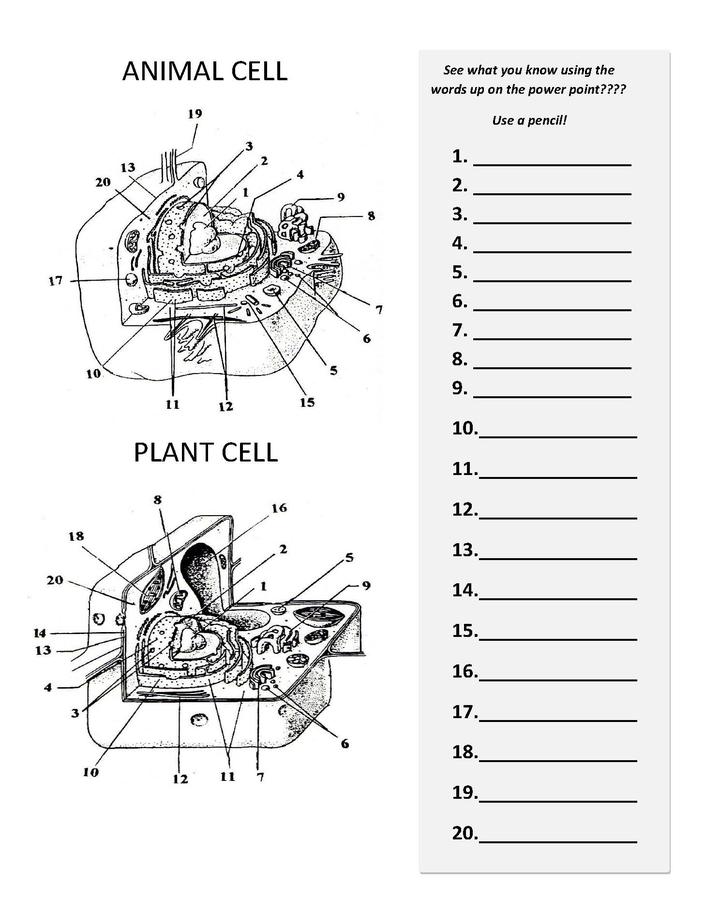
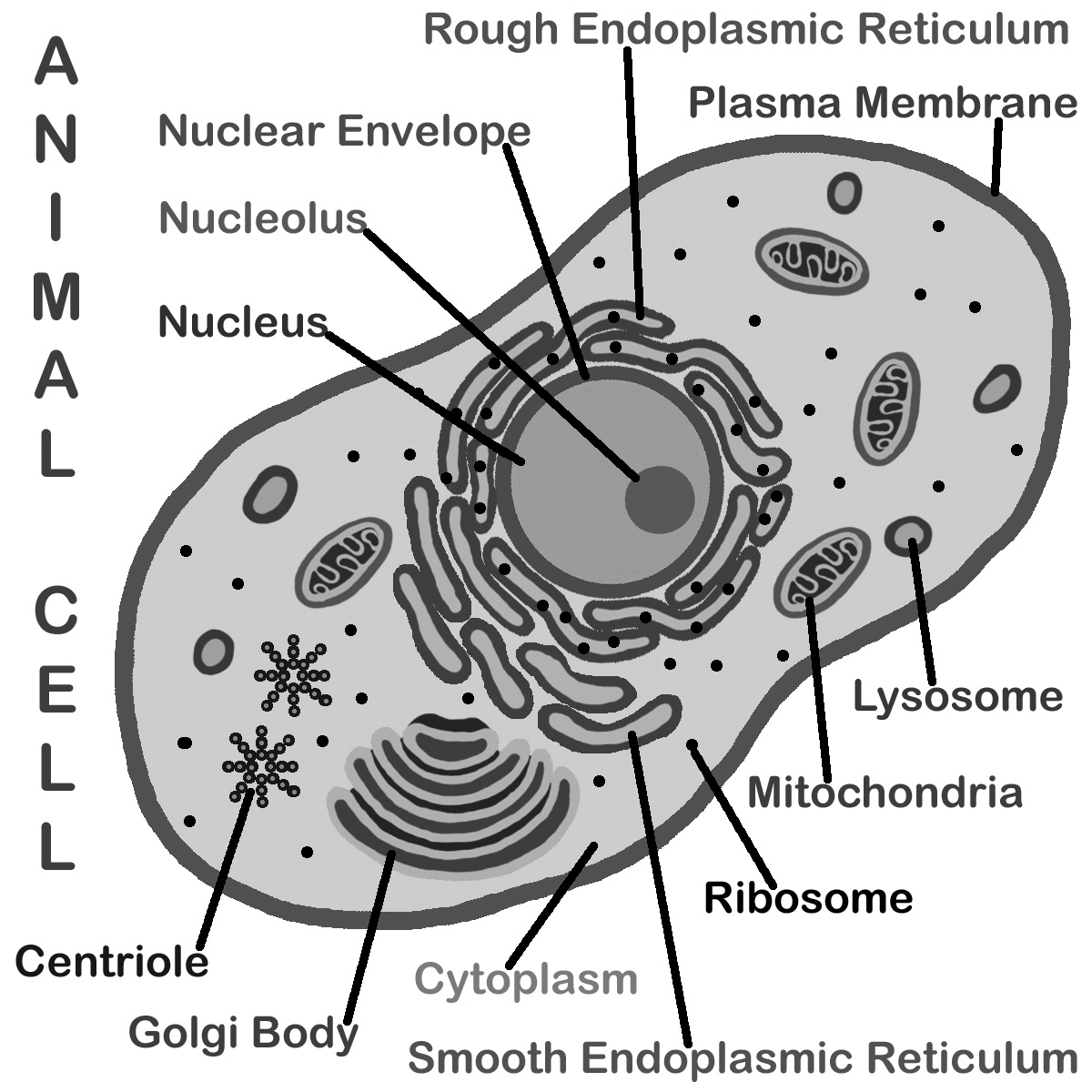
Animal Cell Diagram Worksheet PDF
Are you searching for a comprehensive and educational resource to teach your students about animal cell structure? Look no further! We have created an engaging and informative animal cell diagram worksheet in PDF format. This worksheet is designed for biology teachers and homeschooling parents who are looking to provide an in-depth understanding of the different components and functions within an animal cell.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What are the main components of an animal cell?
The main components of an animal cell include the cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, ribosomes, and the cytoskeleton. These structures work together to carry out various cellular functions such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
Where is the nucleus located in an animal cell?
The nucleus is located in the center of an animal cell, usually closer to the cell's outer edge. It is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which contains pores that regulate the entry and exit of molecules like proteins and RNA. The nucleus houses the cell's genetic material, including DNA, and is responsible for controlling gene expression and cellular activities through the production of messenger RNA and ribosomes.
What is the function of the mitochondria in an animal cell?
The function of the mitochondria in an animal cell is to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through the process of cellular respiration. Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell because they generate the majority of the cell's ATP, which is essential for various cellular processes and functions.
What is the purpose of the endoplasmic reticulum in an animal cell?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in an animal cell serves multiple purposes, including protein synthesis, folding, and transport. It also plays a key role in lipid and steroid biosynthesis, calcium storage, and detoxification of harmful substances. The two types of ER, rough ER (with ribosomes attached) and smooth ER (no ribosomes), work together to maintain cellular homeostasis and provide a structured network for various cellular processes.
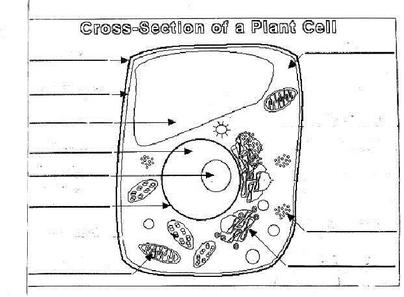
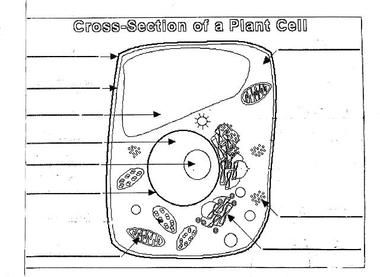
How is a vacuole different from a vesicle in an animal cell?
A vacuole is a larger membrane-bound organelle found in plant and fungal cells that stores nutrients, waste products, and sometimes even enzymes, while a vesicle is a smaller membrane-bound sac used for transporting materials within the cell or between cells in animal cells. Vacuoles are typically permanent structures with specific functions, such as maintaining turgor pressure in plants, while vesicles are temporary structures that transport molecules like proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus in an animal cell?
The main function of the Golgi apparatus in an animal cell is to modify, sort, and package proteins and lipids into vesicles for transport to other organelles or secretion out of the cell. It is responsible for receiving newly synthesized proteins and lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum, modifying them by adding carbohydrates or other molecules, sorting them based on their destination, and packaging them into vesicles for transport.
What are the main functions of the cytoplasm in an animal cell?
The main functions of the cytoplasm in an animal cell include housing organelles and structures within the cell, providing a medium for cellular processes to occur, serving as a site for metabolic reactions, facilitating intracellular transport of materials, maintaining cell shape and structure, storing nutrients and ions, and playing a role in cell signaling and communication.
Describe the structure and function of the cell membrane in an animal cell.
The cell membrane in an animal cell is a selectively permeable phospholipid bilayer that surrounds the cell, maintaining its shape and protecting its contents. Embedded in the membrane are proteins that aid in cell communication, transport of molecules in and out of the cell, and cell recognition. The membrane also contains cholesterol, which adds stability to the structure. Overall, the cell membrane regulates the passage of substances in and out of the cell, allowing for the maintenance of cellular homeostasis and proper cellular function.
What role does the ribosomes play in an animal cell?
Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis in animal cells. They read the messenger RNA (mRNA) and use the information contained within to assemble amino acids into proteins. Ribosomes can be found either floating freely in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, and they play a vital role in producing the proteins necessary for various cellular functions and structures.
Explain the significance of the centrioles in an animal cell.
Centrioles are crucial organelles in animal cells as they play a key role in cell division by organizing the microtubules that form the mitotic spindle. This allows for the equal distribution of chromosomes during cell division, ensuring genetic material is properly segregated into daughter cells. Additionally, centrioles are involved in the formation of cilia and flagella, which are important for cell motility and sensory functions. Overall, centrioles are essential for maintaining the structural integrity of the cell and facilitating various cellular processes.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments