Angles and Algebra Worksheets
Angles and algebra worksheets are essential tools for students who are learning about geometry and mathematics. These worksheets provide a focused and structured way for students to practice and reinforce their understanding of angles and algebraic concepts. By engaging with these worksheets, students have the opportunity to develop their skills and become more confident in solving problems related to angles and algebraic equations.
Table of Images 👆
- 7th Grade Math Problems Worksheets
- 6th Grade Math Worksheets Angles
- 7th Grade Math Worksheets Algebra
- 6th Grade Math Worksheets
- Algebra Math Worksheets
- 5th Grade Math Worksheets Graphs
- Area Perimeter Worksheets 3rd Grade
- 1 Step Word Problems Worksheets
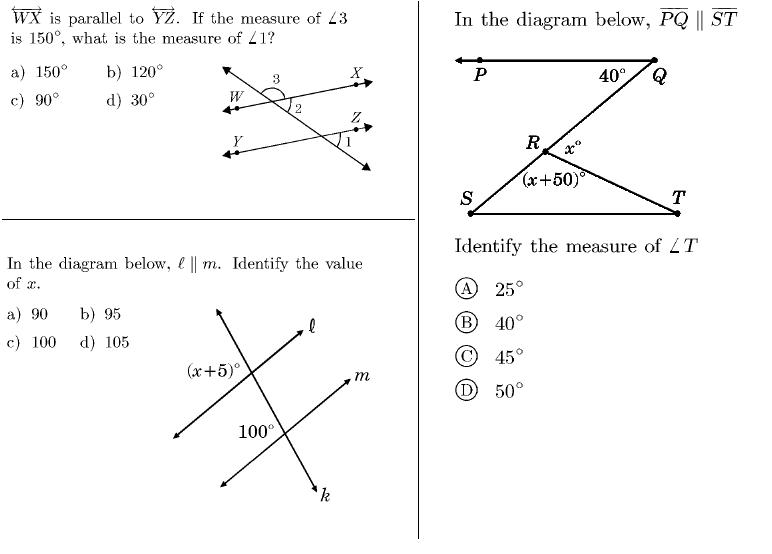
- Parallel Lines and Angles Worksheet
- Triangle Worksheets
- Angle Parallel Lines and Transversals Worksheet
- Trig Right Triangles Missing Angles and Sides
- Binomial Expansion Formula
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the definition of an angle?
An angle is a geometric figure formed by two rays or lines that meet at a common endpoint, known as the vertex. It is commonly expressed in degrees or radians and is used to measure the amount of rotation or turn between the two rays.
What are the different types of angles?
There are four main types of angles: acute angles measure between 0 and 90 degrees, obtuse angles measure between 90 and 180 degrees, right angles measure exactly 90 degrees, and straight angles measure exactly 180 degrees.
How do you classify angles based on their measurements?
Angles can be classified based on their measurements as acute angles, which are less than 90 degrees; right angles, which are exactly 90 degrees; obtuse angles, which are greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees; straight angles, which are exactly 180 degrees; and reflex angles, which are greater than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees.
How are angles named?
Angles are typically named by using three points. The middle point is the vertex of the angle, and the other two points represent the rays that form the angle. The vertex is always placed in the middle, with the first point on one ray followed by the vertex, and then the second point on the other ray. This naming convention helps to identify and distinguish between different angles.
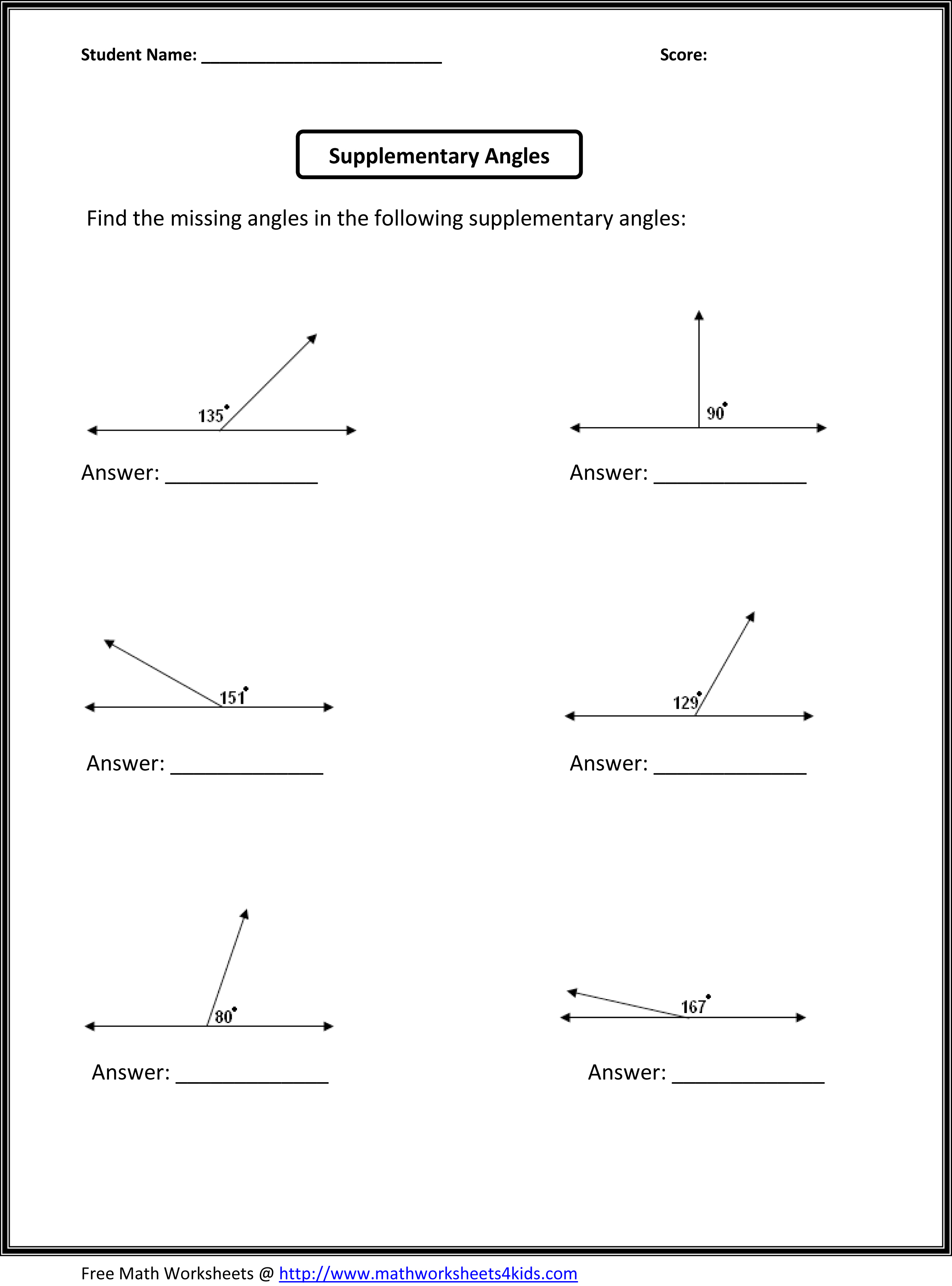
What is the relationship between the measures of angles in a straight line?
The measures of angles in a straight line add up to 180 degrees. This means that when two angles form a straight line, they are supplementary angles, and their measures combine to create a straight line.
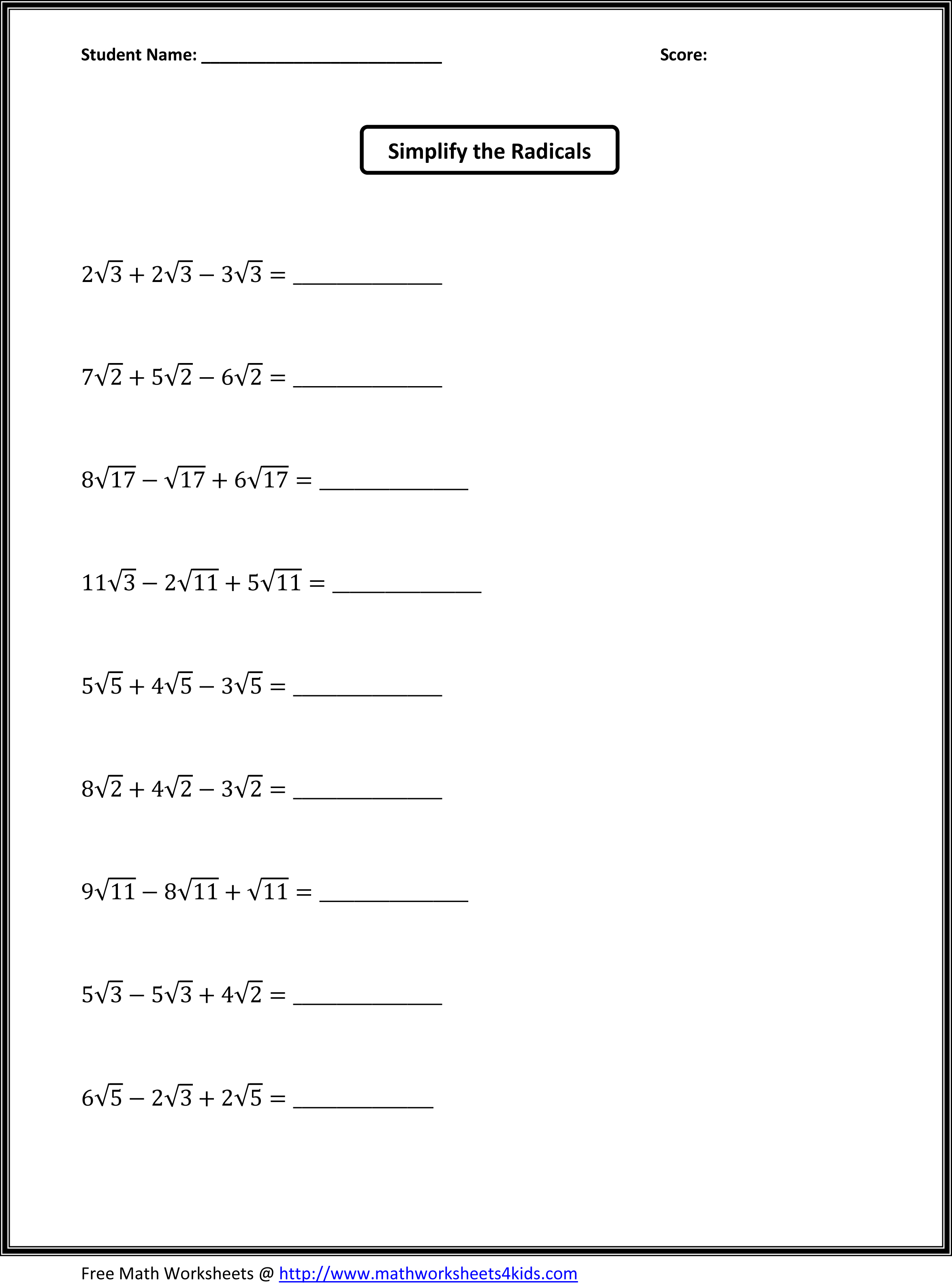
How can you find the measure of an unknown angle using algebraic expressions?
To find the measure of an unknown angle using algebraic expressions, you can set up an equation based on the information given in the problem. Use the properties of angles, such as supplementary angles adding up to 180 degrees, complementary angles adding up to 90 degrees, or any other angle relationships provided. Then, solve the equation using algebraic techniques like combining like terms, distributing, and isolating the variable to find the value of the unknown angle.
How do you solve equations involving angles?
To solve equations involving angles, you can use trigonometric functions like sine, cosine, and tangent. First, isolate the trigonometric function and simplify the equation. Then, apply inverse trigonometric functions if necessary to find the value of the angle. Remember to check for restrictions on the angle such as the domain of the trig function. Additionally, you may need to use trigonometric identities or properties to manipulate the equation and find the solution.
What are the properties of corresponding angles?
Corresponding angles are a pair of angles that are in the same relative position at the intersection of two lines and a transversal. They are equal in measure when the two lines are parallel. In other words, if you have two parallel lines and a transversal line intersecting them, corresponding angles will have the same measurement.
How do you use angle properties to prove geometric relationships?
To use angle properties to prove geometric relationships, you can rely on the fact that certain relationships hold for specific types of angles or in specific geometric shapes. For example, in a triangle, the interior angles always add up to 180 degrees, and in a circle, the angle subtended by an arc at the center is twice the angle subtended at the circumference. By applying these known properties and theorems, you can logically deduce and prove relationships between angles and shapes in geometric problems.
How can you use algebra to solve problems involving angle measures?
Algebra can be used to solve problems involving angle measures by setting up and solving equations based on geometric relationships. For example, in a triangle, the sum of the interior angles is always 180 degrees, so you can set up an algebraic equation to find the measure of a missing angle. Additionally, in a right triangle, the Pythagorean theorem can be used to find the measure of angles based on the side lengths. By using algebraic equations and properties of geometric shapes, you can efficiently solve problems involving angle measures.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.











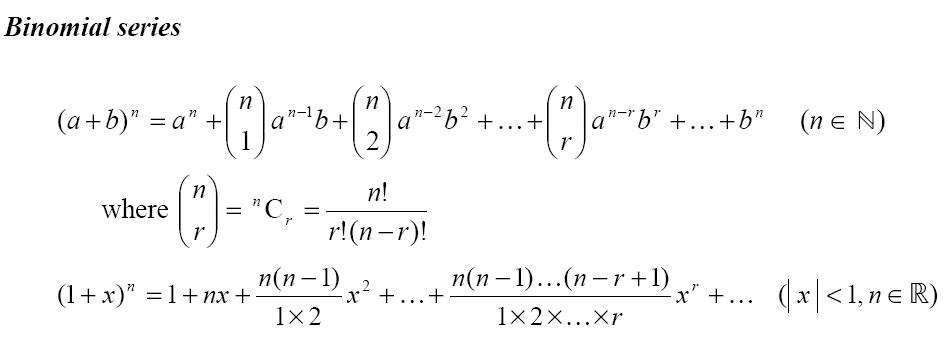
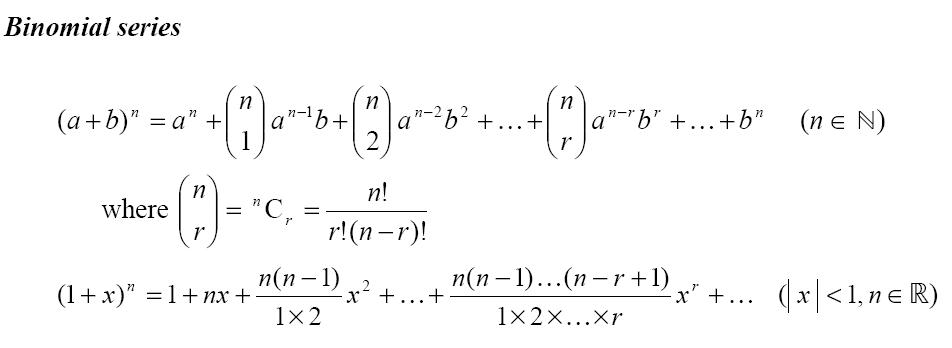














Comments