Anatomy On Human Eye Worksheet
Anatomy worksheets on the human eye provide a comprehensive and structured way to learn about the intricate details of this remarkable sensory organ. These worksheets are designed to guide students in their exploration of the eye's structure, function, and various associated concepts. Whether you are a student studying biology, a teacher seeking engaging resources for your classroom, or a curious individual interested in understanding the complexities of the human eye, these anatomy worksheets offer a valuable learning tool.
Table of Images 👆
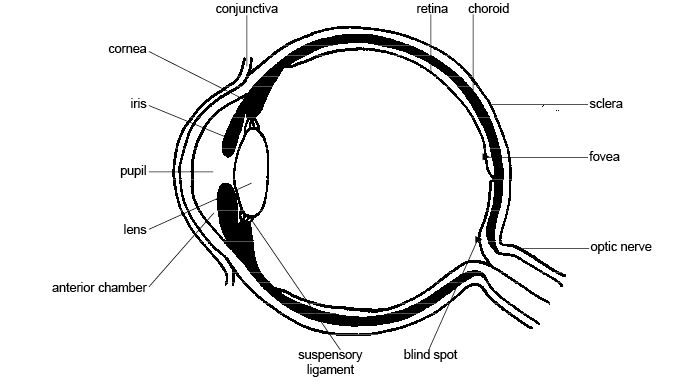
- Human Eye Diagram Unlabeled
- Human Eye Anatomy Diagram Worksheet
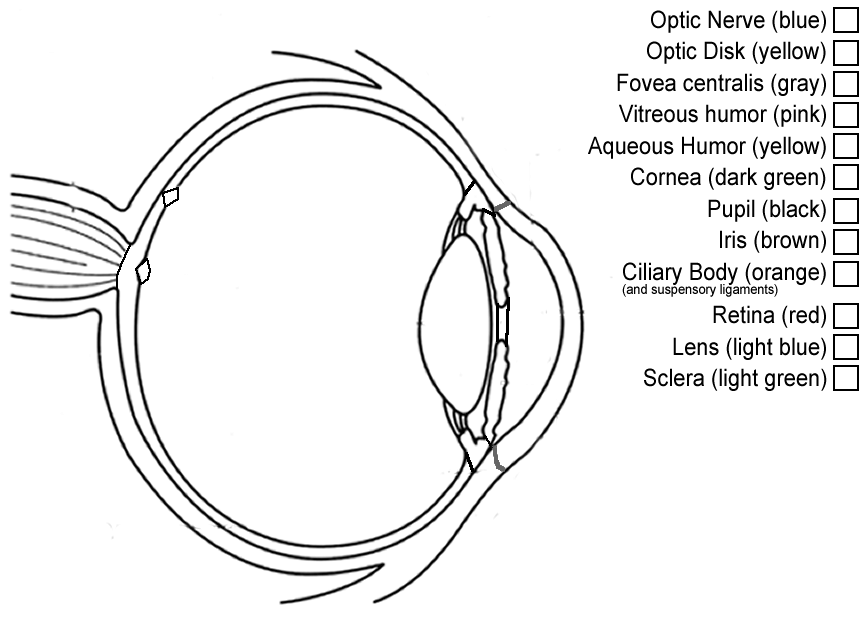
- Eye Anatomy Coloring Page
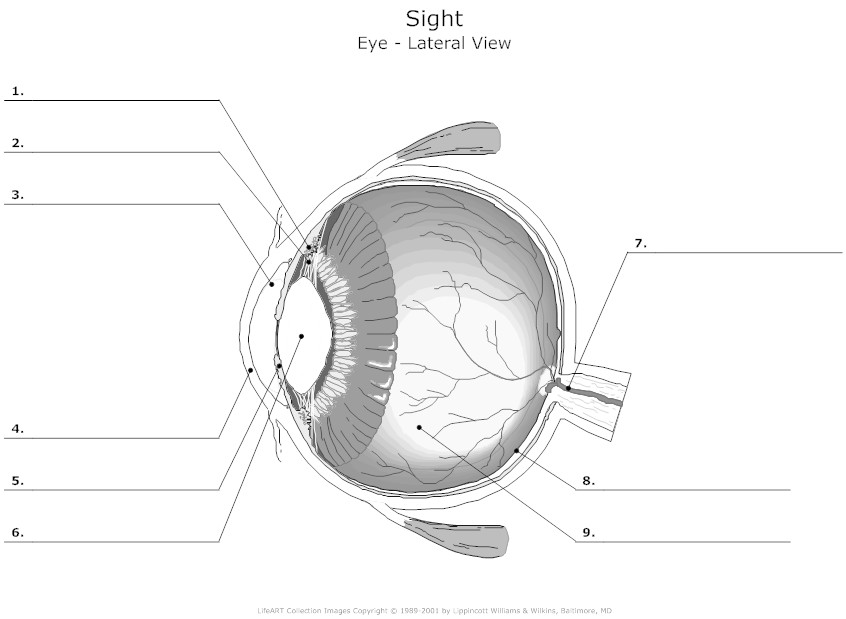
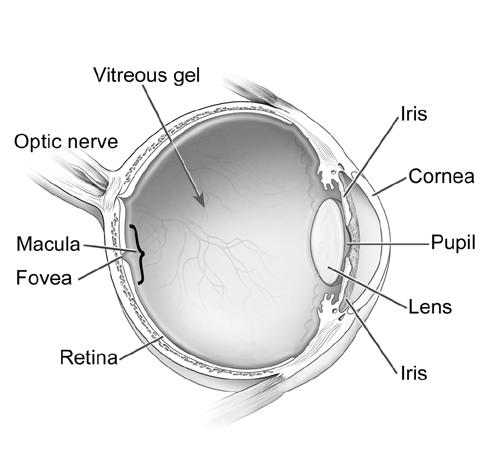
- Human Eye Diagram
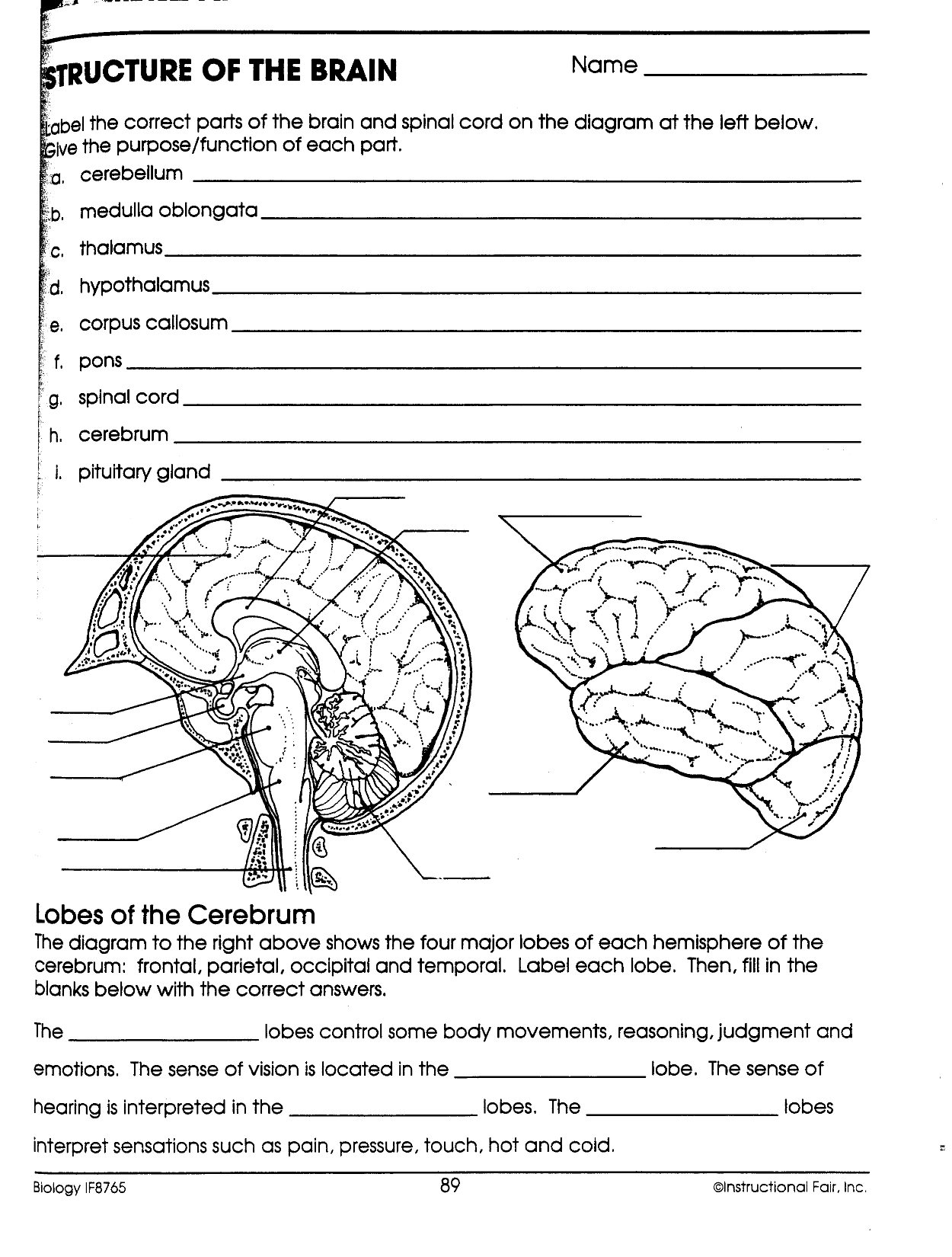
- Brain Diagram and Functions Worksheet
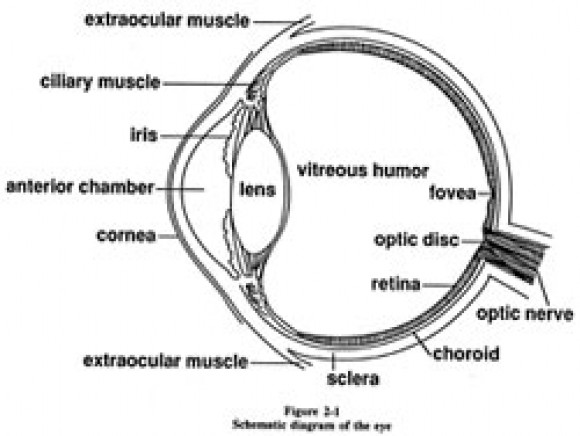
- Parts of the Human Eye Diagram
- Human Eye Worksheet Answers
- Printable College Anatomy Worksheets
- Human Ear Diagram Worksheet
- Anatomy and Physiology Eye Diagram Label
- Human Brain Diagram Outline
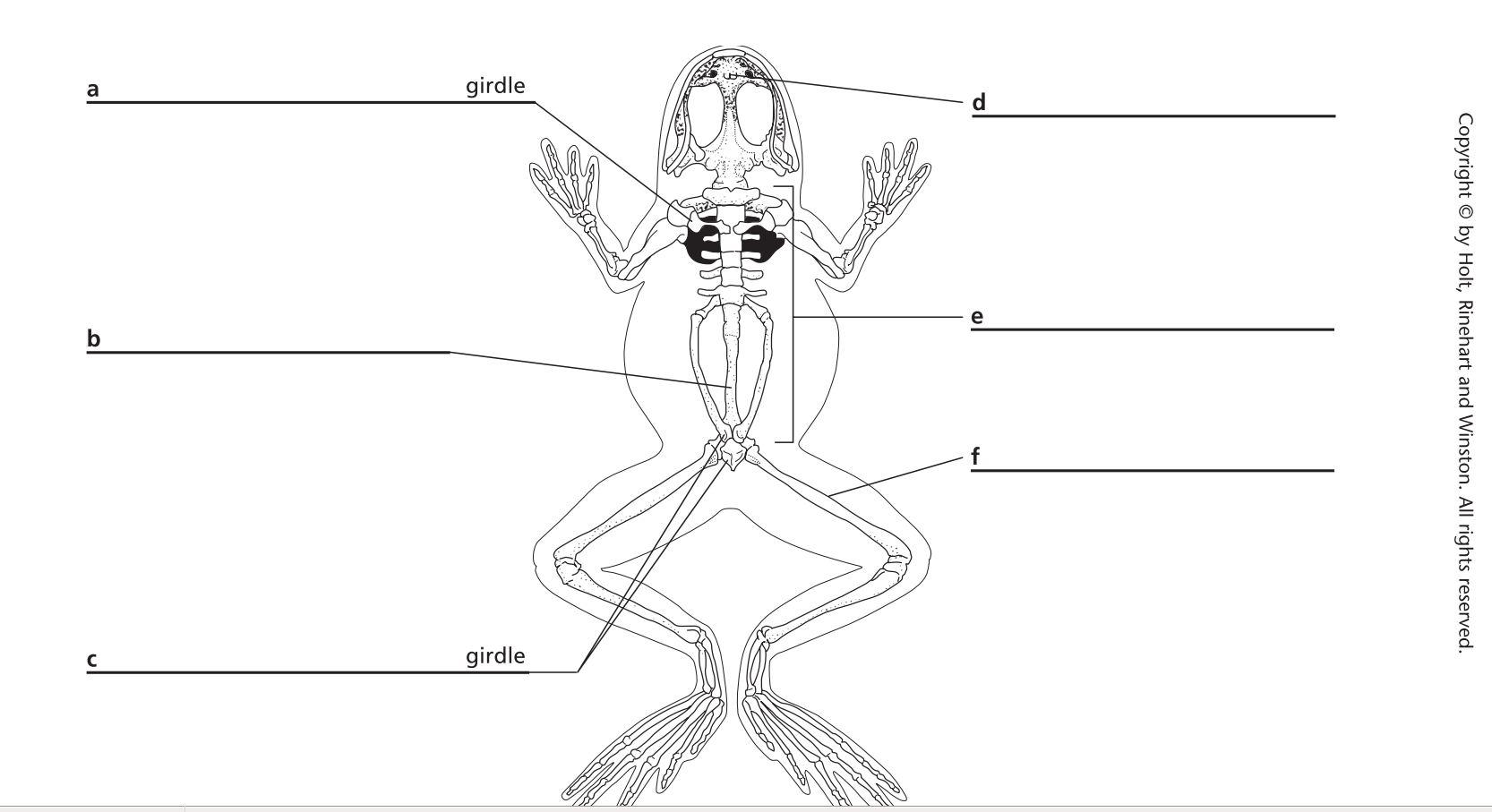
- Frog Dissection Worksheet Diagram
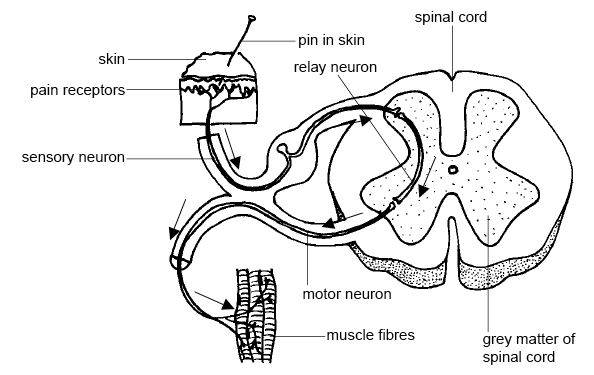
- Sensory and Motor Neurons Spinal Cord Anatomy
- Polar Bear Skin Diagram
- Human Heart Diagram Unlabeled
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the shape of the human eye?
The human eye is roughly spherical in shape, with a slight bulge in the front known as the cornea. The cornea is transparent and helps to focus light onto the retina, which is located at the back of the eye. The shape of the eye allows light to enter and be focused properly on the retina, enabling us to see clearly.
What is the function of the cornea?
The cornea acts as the eye's outermost lens, providing majority of the focusing power and helping to protect the eye from dust, germs, and other harmful particles. It plays a crucial role in allowing light to enter the eye and in bending or refracting that light to focus it properly on the retina at the back of the eye for clear vision.
What is the purpose of the lens?
The purpose of the lens is to refract and focus light onto the camera sensor or film in order to create a clear and sharp image. Lenses help to control the amount of light entering the camera, adjust the depth of field, and determine the level of sharpness and detail in the final photograph.
How does the iris control the amount of light entering the eye?
The iris controls the amount of light entering the eye by adjusting the size of the pupil. In bright conditions, the iris contracts the pupil, making it smaller to reduce the amount of light that enters the eye. In dim conditions, the iris dilates the pupil, making it larger to allow more light to enter the eye. This mechanism helps in regulating the amount of light reaching the retina, allowing for optimal vision in various lighting conditions.
What is the role of the retina in vision?
The retina is a crucial part of the eye that is responsible for capturing and processing light. It contains specialized cells called photoreceptors (rods and cones) that convert light into electrical impulses, which are then transmitted to the brain through the optic nerve. These signals are interpreted by the brain to create images and allow us to see. The retina also contains other types of neurons that help enhance visual information before sending it to the brain. Overall, the retina plays a vital role in the initial processing of visual stimuli and is essential for clear vision.
How is the image formed on the retina?
The image is formed on the retina through a process involving light entering the eye through the cornea and pupil, getting focused by the lens, and then projecting onto the retina at the back of the eye. The lens adjusts its shape to ensure the image is focused precisely on the retina, which contains light-sensitive cells called photoreceptors that convert the light signals into electrical impulses, which are sent to the brain through the optic nerve for processing and interpretation.
What is the function of the optic nerve?
The optic nerve is responsible for transmitting visual information from the retina to the brain, allowing us to see and process visual stimuli. It plays a crucial role in vision by carrying visual signals from the eye to the visual cortex in the brain where the information is interpreted and processed.
How does the vitreous humor contribute to maintaining the eye's shape?
The vitreous humor contributes to maintaining the eye's shape by filling the space between the lens and the retina, providing support and pressure to keep the eyeball round and prevent it from collapsing. This clear, gel-like substance also helps to maintain the structural integrity of the eye and allows light to pass through to the retina for visual perception.
What role do the rods and cones play in vision?
Rods and cones are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that play a crucial role in vision. Rods are highly sensitive to low levels of light, allowing us to see in dimly lit environments, while cones are responsible for color vision and detail in well-lit conditions. Together, rods and cones work to capture and transmit visual information to the brain, enabling us to perceive the world around us with clarity, depth, and color.
How does the brain interpret the signals received from the eye to form images?
The brain interprets signals received from the eye by processing the electrical impulses sent along the optic nerve to the visual cortex located at the back of the brain. These signals are then analyzed and decoded to create a cohesive image based on factors such as color, shape, motion, and depth. The brain integrates this information with past experiences and memories to formulate a complete and coherent visual perception.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments