Amendments 1-10 Worksheet
For students studying American government and civics, the Amendments 1-10 worksheet serves as a valuable tool for understanding the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. This worksheet provides an opportunity to delve into the specifics of each amendment, examining their meaning, historical context, and implications. With a focus on the entity of the United States Constitution and the subject of the first ten amendments, this worksheet is designed to enhance students' understanding of this crucial part of American law and democracy.
Table of Images 👆
- 27 Amendments Worksheet
- First Amendment Worksheet
- Printable Bill of Rights Worksheets
- Bill of Rights Worksheet
- Bill of Rights Worksheet Answers
- Delaware Certificate of Amendment Name Change
- First 10 Amendments Bill Rights
- Third Party Real Estate Purchase Contract Template
- Bill of Rights Ten Amendments
- 27 Amendments Chart
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
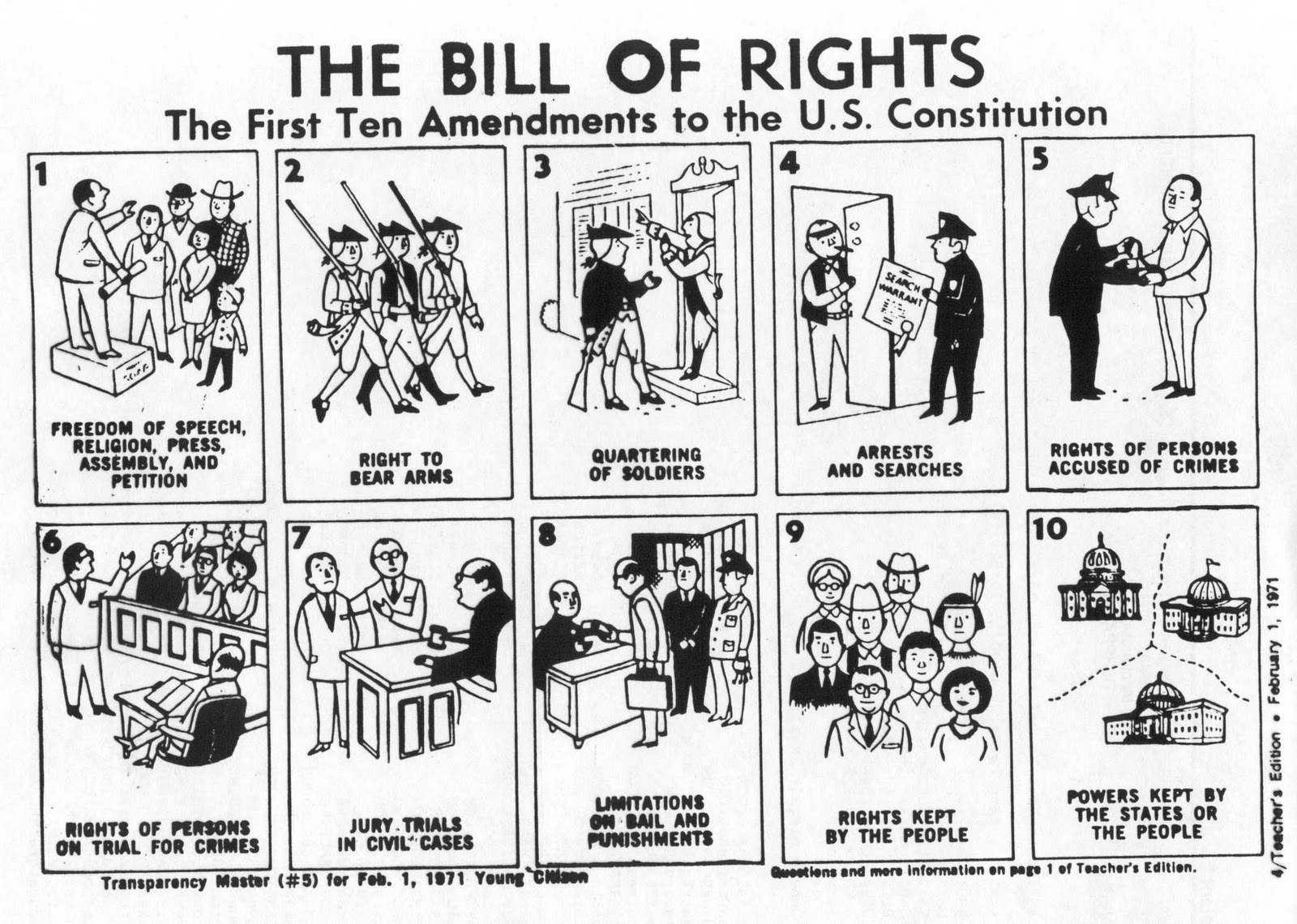
What does the First Amendment protect?
The First Amendment protects freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of religion, the right to assemble peacefully, and the right to petition the government for a redress of grievances.
Why is freedom of speech important?
Freedom of speech is important because it enables individuals to express themselves, share ideas, and engage in open discourse without fear of censorship or repercussions. It ensures a diversity of viewpoints, promotes accountability of those in power, and drives societal progress by challenging established norms and fostering innovation. Protecting freedom of speech is essential for a free and democratic society where individuals can participate fully in public debate and hold differing opinions without threat of oppression.
What does the Second Amendment guarantee?
The Second Amendment guarantees the right of individuals to keep and bear arms as part of a well-regulated militia, allowing for the defense of themselves, their families, and the state.
How has the interpretation of the Second Amendment evolved over time?
The interpretation of the Second Amendment has evolved over time, with varying perspectives on the right to bear arms. Initially seen as a collective right linked to state militias, the Supreme Court's decisions in District of Columbia v. Heller (2008) and McDonald v. Chicago (2010) established an individual right to gun ownership for self-defense. Additionally, ongoing debates and legal challenges continue to shape the understanding and application of the Second Amendment in modern society.
What does the Third Amendment prohibit?
The Third Amendment prohibits the government from quartering soldiers in private homes without the owner's consent during times of peace, stating that citizens cannot be forced to house or feed soldiers in their private residences without permission.
Why was the Third Amendment included in the Bill of Rights?
The Third Amendment was included in the Bill of Rights to protect citizens from the forced quartering of soldiers in their homes during peacetime without their consent. This amendment was a response to the Quartering Acts passed by the British during colonial times, which allowed soldiers to be housed in private homes against the wishes of the homeowners. The Third Amendment ensures that citizens have the right to privacy and security in their own homes, free from government intrusion or military presence without their permission.
What does the Fourth Amendment protect against?
The Fourth Amendment protects against unreasonable searches and seizures by the government, ensuring that individuals have the right to privacy and freedom from arbitrary intrusion into their homes, property, and personal belongings without a warrant based on probable cause.
What are some examples of unconstitutional searches and seizures?
Examples of unconstitutional searches and seizures include cases where law enforcement conducts searches without a warrant or probable cause, performs invasive body cavity searches without valid justification, conducts searches based on racial profiling or discriminatory motives, or seizes property without following proper legal procedures. Additionally, searching a person's home or property without consent or a warrant, or seizing property without a lawful reason, would also constitute unconstitutional searches and seizures.
What does the Fifth Amendment protect?
The Fifth Amendment of the United States Constitution protects individuals from self-incrimination, ensures the right to due process of law, guarantees the right to a fair trial by jury, and prohibits double jeopardy, which prevents a person from being tried twice for the same crime. It also requires the government to provide just compensation when private property is taken for public use.
How does the Fifth Amendment relate to due process and self-incrimination?
The Fifth Amendment of the United States Constitution plays a significant role in protecting individuals' rights to due process and against self-incrimination. It ensures that individuals cannot be deprived of life, liberty, or property without due process of law and guarantees that individuals have the right to remain silent and not incriminate themselves in a criminal case. By invoking the Fifth Amendment, individuals can refuse to answer questions that may result in self-incrimination and ensure their right to a fair legal process.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments