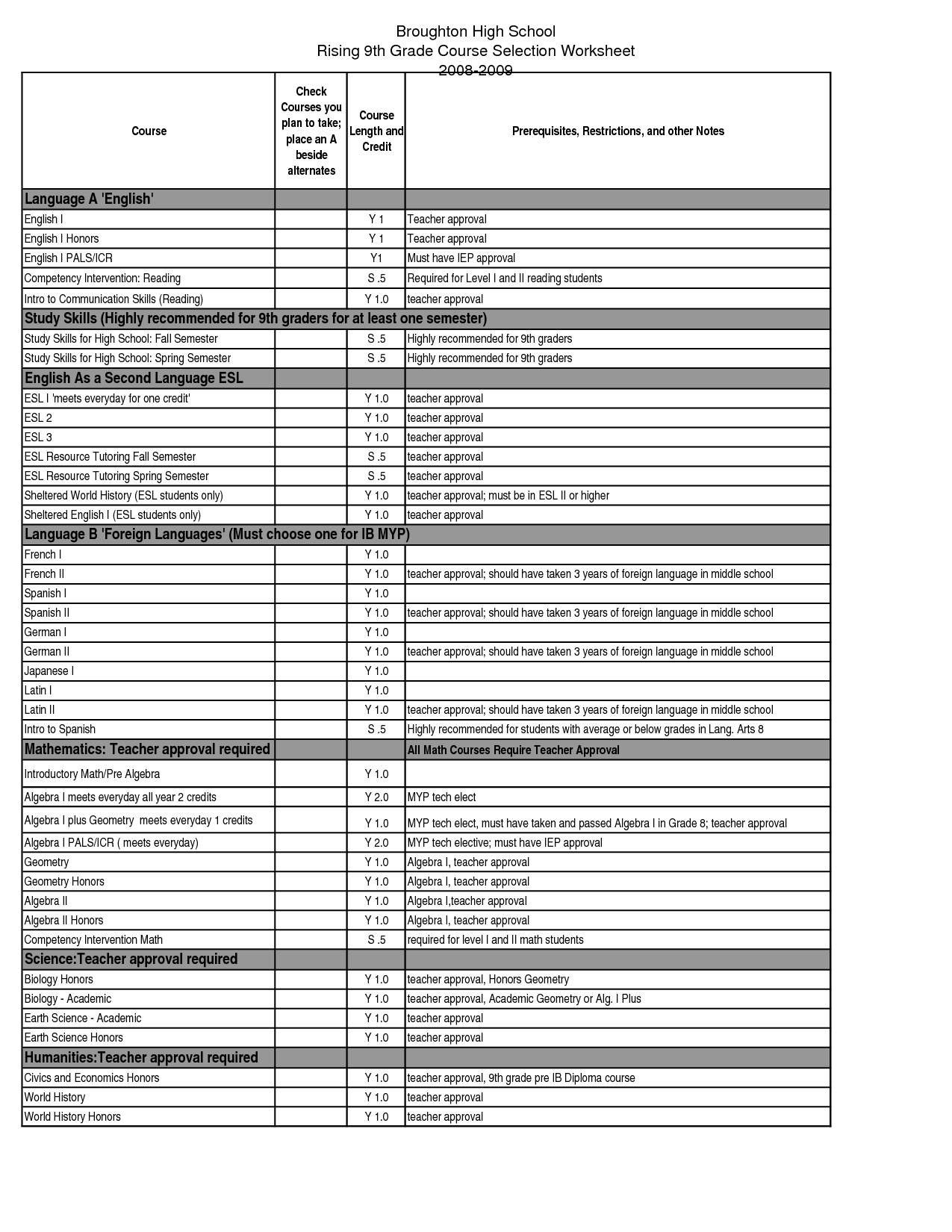
9th Grade Science Worksheets
Are you in need of additional resources to reinforce your understanding of 9th grade science concepts? Look no further, because we have a wide range of worksheets designed specifically for students like you. These worksheets cover various topics, including biology, chemistry, physics, and earth science. With carefully curated content, our worksheets serve as a valuable tool for solidifying your knowledge and enhancing your academic performance in science.
Table of Images 👆
- 9th Grade Worksheets
- Free 9th Grade Vocabulary Worksheets
- Printable Context Clues Worksheets 9th Grade
- 9th Grade Math Worksheets
- 9th Grade Vocabulary Worksheets
- 9th Grade Physical Science Worksheets
- 9th Grade Reading Comprehension Worksheets
- 9th Grade Language Arts Worksheets
- 9th Grade Printable Worksheets
- Science Vocabulary Worksheets
- 9th Grade Biology Lesson Plans
- 9th Grade School Worksheets
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
What is the Law of Conservation of Energy?
The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed but can only be converted from one form to another. This means that the total amount of energy in an isolated system remains constant over time, with energy being transferred or transformed but never lost. Energy is a fundamental concept in physics and plays a critical role in understanding the behavior of objects and systems in the universe.
Describe the process of cell division in mitosis.
Mitosis is a type of cell division where a parent cell divides to produce two genetically identical daughter cells. It consists of several phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. In prophase, the genetic material condenses into chromosomes, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and spindle fibers form. During metaphase, the chromosomes align in the middle of the cell. In anaphase, the sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles, pulled by the spindle fibers. Finally, in telophase, the chromosomes decondense, nuclear envelopes reform around them, and the cell undergoes cytokinesis, splitting into two daughter cells with the same genetic material.
Explain how natural selection drives evolution.
Natural selection drives evolution by favoring individuals with traits that make them better adapted to their environment, allowing them to survive and reproduce more successfully. Over time, these advantageous traits become more common in the population while less favorable traits are selected against. This gradual process of adaptation and change leads to the evolution of new species with characteristics that are better suited to their specific ecological niches.
What is an ecosystem and how do biotic and abiotic factors interact within it?
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms, such as plants and animals, interacting with each other and their non-living environment. Biotic factors refer to living components like plants, animals, and microorganisms within the ecosystem, while abiotic factors are non-living elements such as sunlight, temperature, water, and soil. Biotic and abiotic factors interact in a complex way within an ecosystem. For example, plants (biotic) rely on sunlight (abiotic) for photosynthesis, which produces oxygen that animals (biotic) need to survive. Additionally, abiotic factors like temperature and soil pH can influence the distribution and behavior of organisms within the ecosystem. These interactions are vital for maintaining the balance and health of the ecosystem.
Describe the structure and function of DNA.
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a double-helix molecule that consists of nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base, which can be adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), or guanine (G). The sequence of these bases encodes genetic information that determines an organism's traits. DNA's function is to store and transmit genetic information, serving as the blueprint for the synthesis of proteins and the regulation of cellular processes. Additionally, DNA can replicate itself during cell division, ensuring genetic continuity through generations.
Explain the difference between potential and kinetic energy.
Potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position or condition, such as a ball at the top of a hill. Kinetic energy, on the other hand, is the energy an object possesses due to its motion, like a moving car or a spinning top. In short, potential energy is stored energy that has the potential to do work, while kinetic energy is the energy of an object in motion.
How does the water cycle work and what role does it play in Earth's climate?
The water cycle, also known as the hydrological cycle, is the continuous process of water evaporating from the Earth’s surface, condensing in the atmosphere to form clouds, and eventually falling back to the Earth as precipitation. This precipitation can take the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail. The water cycle plays a crucial role in Earth's climate by regulating the distribution of water across the planet, maintaining ecosystems, and influencing weather patterns. Evaporation from oceans, rivers, and lakes provides moisture to the atmosphere, which then falls back to the Earth as precipitation, providing fresh water for plants, animals, and humans. The water cycle also helps to moderate temperatures on Earth by transferring heat energy between the oceans and the atmosphere. Overall, the water cycle is essential for sustaining life on Earth and plays a significant role in shaping the global climate.
Describe the process of photosynthesis and its importance in the food chain.
Photosynthesis is a biological process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen. This process takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells and is facilitated by the green pigment chlorophyll. Photosynthesis is essential in the food chain as it is the primary way in which energy enters an ecosystem. Plants use the glucose produced during photosynthesis as their energy source, and it also serves as a building block for growth. Other organisms, such as herbivores, then consume these plants, transferring the energy up the food chain. This process continues as carnivores eat herbivores, forming a complex and interconnected energy flow that sustains life in ecosystems.
What are the different types of clouds and how are they formed?
There are various types of clouds, including cirrus, cumulus, stratus, and nimbus clouds. Cirrus clouds are wispy and high in the sky, formed by ice crystals at high altitudes. Cumulus clouds are fluffy and puffy with flat bases, typically seen on fair weather days. Stratus clouds are layered and cover the sky like a blanket, often bringing overcast conditions. Nimbus clouds are dark and thick, associated with rain or storms. Clouds form when warm air rises, expands, and cools, causing water vapor to condense into tiny droplets or ice crystals around particles in the air, such as dust or smoke.
How does the respiratory system work to supply oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide?
The respiratory system works by the process of breathing, where inhaling draws in oxygen-rich air through the nose and mouth into the lungs, while exhaling releases carbon dioxide-rich air. In the lungs, oxygen from the air is diffused into the bloodstream through the alveoli, tiny air sacs within the lungs, where it is then carried by red blood cells to the body's tissues. At the same time, carbon dioxide produced by the body's cells is expelled from the bloodstream into the alveoli and is then exhaled out of the body. This process of gas exchange ensures that the body has a constant supply of oxygen and can effectively remove carbon dioxide, maintaining the proper balance of gases in the blood to support cellular function and overall health.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
































Comments