9 Grade Physical Science Worksheets
Are you searching for high-quality worksheets to support your 9th grade physical science curriculum? Look no further! Our collection of worksheets is specifically designed to engage and challenge your students, covering a wide range of topics in the subject. From molecules and chemical reactions to forces and motion, these worksheets provide a valuable resource to reinforce key concepts and foster deeper understanding.
Table of Images 👆
- Force and Motion Worksheets 5th Grade
- 8th Grade Physical Science Study Guide
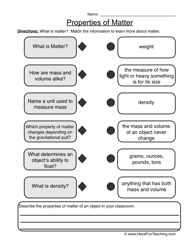
- Properties of Matter Worksheet Grade 2
- Dichotomous Key Worksheets Answers
- Analyze Text Structure Worksheets
- Root Structure and Function Worksheet
- Static Electricity Worksheet 4th Grade
- Science Landforms Worksheets
- 4th Grade Map Skills Worksheets
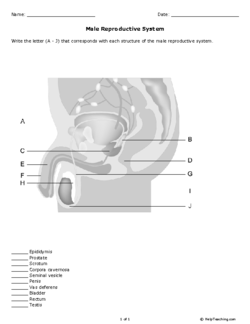
- Male Reproductive System Printable
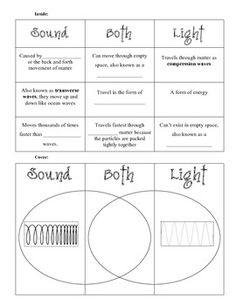
- Light and Sound Waves
- Worksheets Answer Key
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
What is the Law of Conservation of Mass?
The Law of Conservation of Mass states that in a closed system, the mass of substances remains constant over time, regardless of the physical or chemical changes that take place. This means that mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction; it can only change form or be rearranged.
How do you determine the density of a substance?
To determine the density of a substance, you would measure its mass using a balance to find its weight in grams or kilograms. Then, you would measure its volume using a graduated cylinder, beaker, or any appropriate instrument for the shape of the substance to find its volume in milliliters or cubic centimeters. By dividing the mass by the volume, you can calculate the density of the substance, typically expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3) or kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m3).
What is the difference between potential and kinetic energy?
Potential energy is the energy that an object possesses due to its position or condition, such as gravitational potential energy or elastic potential energy. Kinetic energy, on the other hand, is the energy of an object in motion. Essentially, potential energy is energy that is stored and waiting to be released, while kinetic energy is energy in motion.
What is the difference between a physical and a chemical change?
A physical change involves a change in the appearance or state of a substance without altering its chemical composition, such as melting, freezing, or dissolving. In contrast, a chemical change results in the formation of new substances with different chemical compositions, such as rusting, burning, or fermentation.
How does a simple machine make work easier?
A simple machine makes work easier by either changing the direction or magnitude of the force applied, or by increasing the distance over which the force is applied. By doing so, a simple machine reduces the amount of force or effort needed to perform a task, making it more efficient and allowing work to be done with less effort.
What are the three types of heat transfer?
The three types of heat transfer are conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction is the transfer of heat through a material by direct contact, convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids or gases, and radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves.
How does an electric circuit work?
An electric circuit works by providing a path for electric current to flow, typically along a closed loop of conductive materials like wires. The flow of electrons is driven by a voltage source (such as a battery) that creates a potential difference, causing electrons to move from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. Components like resistors, capacitors, and switches control the flow of current within the circuit. When the circuit is complete and all components are connected properly, the electrons can flow continuously, allowing electrical devices to operate.
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
Speed is a scalar quantity that refers to how fast an object is moving, while velocity is a vector quantity that includes the speed of an object as well as its direction of motion. In other words, speed only tells you how fast something is moving, while velocity provides both the speed and the direction of the motion.
How do you calculate the acceleration of an object?
You can calculate the acceleration of an object by dividing the change in velocity by the time it takes for that change to occur. This can be expressed in the formula: acceleration (a) = (final velocity - initial velocity) / time. The acceleration unit is typically in meters per second squared (m/sē) in the metric system.
What is the difference between a series and a parallel circuit?
In a series circuit, the components are connected in a single path, where the same current flows through each component one after the other. In contrast, in a parallel circuit, the components are connected in multiple paths, so that the current splits and flows through each component simultaneously. This means that in a series circuit, if one component fails, the entire circuit is interrupted, while in a parallel circuit, if one component fails, the other components can still operate independently.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments