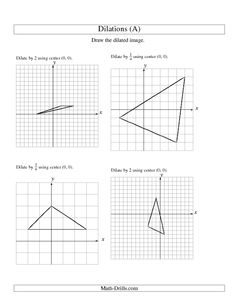
8th Grade Dilations Worksheet
Are you an 8th grade student looking for a comprehensive and engaging worksheet on dilations? Look no further! This worksheet is designed to help you understand the concept of dilations and practice applying it to different geometric figures. With clear instructions and carefully chosen examples, this worksheet will provide you with the practice you need to master dilations.
Table of Images 👆
What is the definition of a dilation?
A dilation is a transformation that changes the size of a figure without changing its shape. It involves stretching or shrinking a figure by a certain scale factor, either enlarging it if the scale factor is greater than 1, or reducing it if the scale factor is between 0 and 1.
How does the scale factor affect a dilation?
The scale factor in a dilation determines how the size of the figure is changed. If the scale factor is greater than 1, the figure will be enlarged, while if it is between 0 and 1, the figure will be reduced in size. The scale factor also determines the direction of the dilation - a negative scale factor will cause the figure to be reflected across the line of dilation. Ultimately, the scale factor affects the proportionality of the figure in relation to the original figure being dilated.
Can a scale factor be greater than 1?
Yes, a scale factor can be greater than 1. In fact, a scale factor greater than 1 would indicate an enlargement or expansion of the original object or shape in a similar proportion. This means the new object will be larger than the original in all dimensions.
Can a scale factor be between 0 and 1?
Yes, a scale factor can be between 0 and 1. A scale factor represents how much larger or smaller a figure is after a dilation, and when the scale factor is between 0 and 1, it indicates that the figure has been reduced in size or compressed.
How does a dilation affect the shape of an object?
A dilation will change the size of an object, making it larger or smaller, but it will not change its shape. The shape of the object remains the same, with all angles and proportions remaining constant, only the dimensions are altered in a uniform manner.
How does a dilation affect the size of an object?
A dilation affects the size of an object by either enlarging or shrinking it in proportion to a fixed point called the center of dilation. When the scale factor of the dilation is greater than 1, the object is enlarged, making it larger than the original. Conversely, if the scale factor is between 0 and 1, the object is shrunk, resulting in a smaller size compared to the original. The relationship between the original and dilated object is determined by the scale factor used in the dilation process.
How is a dilation different from a translation or rotation?
A dilation is a transformation that changes the size of an object while keeping its shape the same, by either shrinking or enlarging it. In contrast, a translation moves an object from one location to another without changing its size or orientation, while a rotation involves turning an object around a fixed point. So, the main difference is that a dilation alters the size of an object, while a translation changes its position and a rotation changes its orientation.
What is the center of dilation?
The center of dilation is the fixed point from which all points are expanded or contracted by a scale factor in a dilation. It is the point that remains unchanged while all other points move farther away or closer to it.
How can you determine the scale factor of a dilation?
To determine the scale factor of a dilation, compare the corresponding lengths or distances of the original figure and its dilated image. The scale factor is calculated by dividing the length of any side of the dilated image by the length of the corresponding side of the original figure. This ratio will give you the scale factor of the dilation.
How can you use dilations to find the area or perimeter of a figure?
To find the area or perimeter of a figure using dilations, you can first dilate the figure by a given scale factor. The area of the dilated figure will be the scale factor squared times the original area of the figure. Similarly, the perimeter of the dilated figure will be the scale factor times the original perimeter of the figure. By understanding the relationship between the scale factor and the area or perimeter during dilation, you can determine the new measurements of the figure and calculate its area or perimeter accordingly.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.















Comments