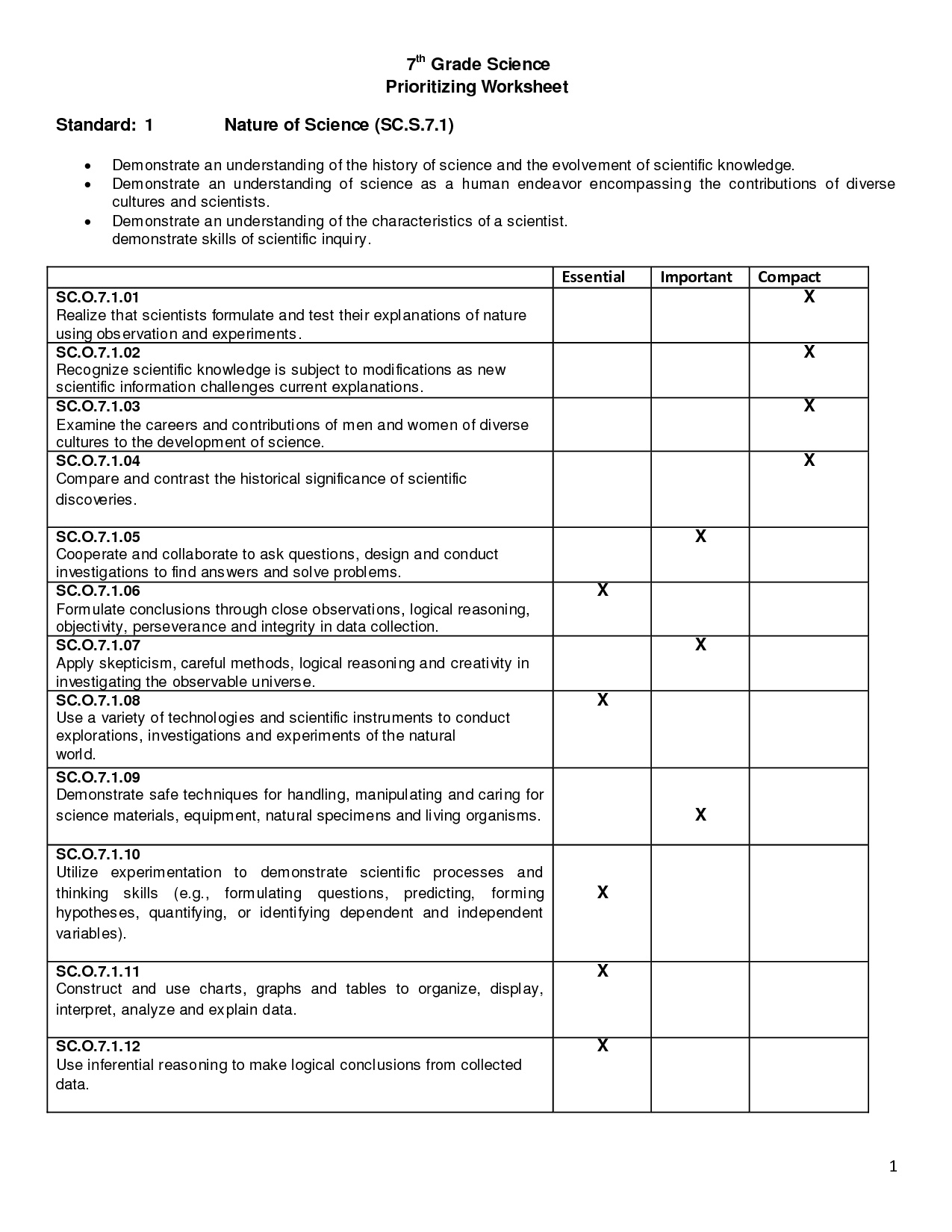
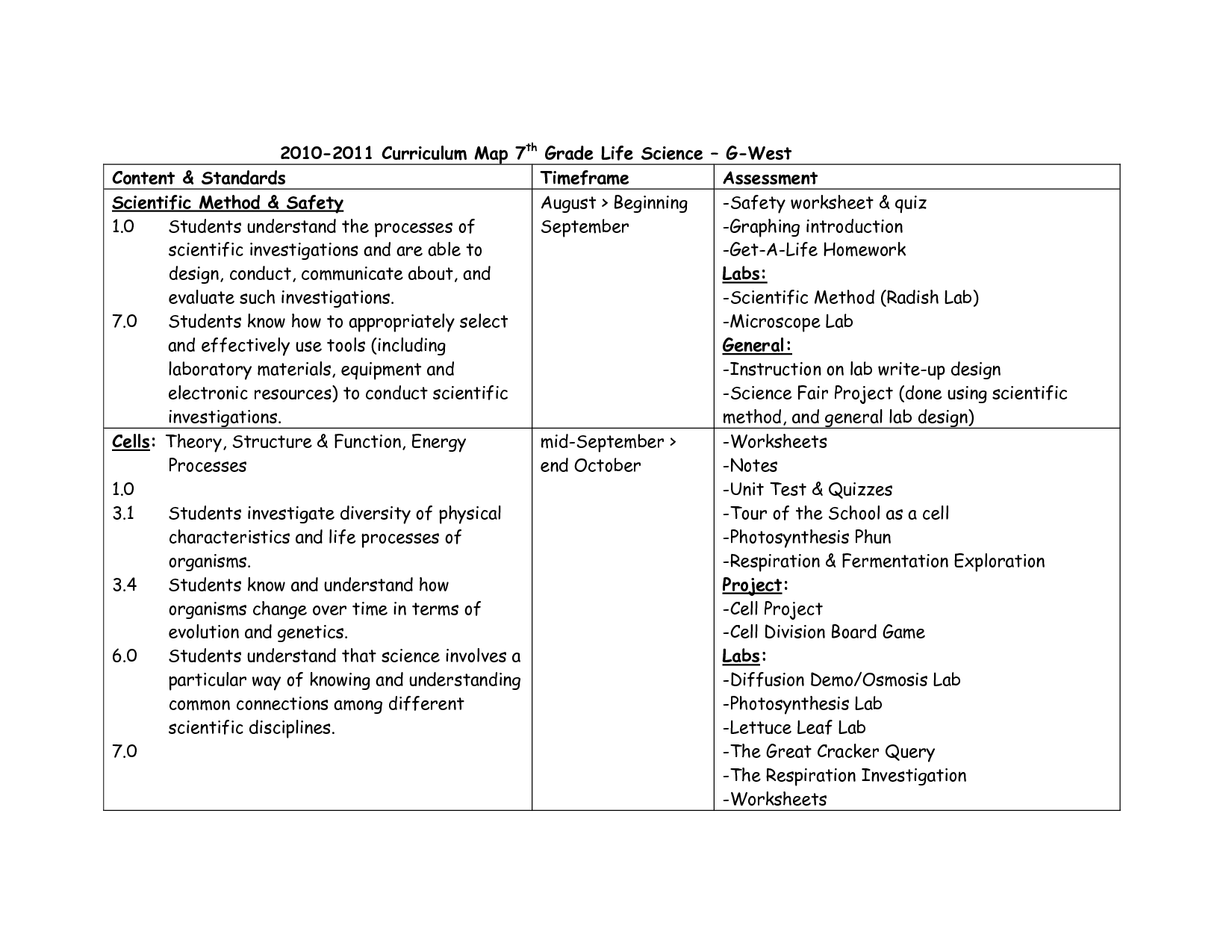
7th Grade Life Science Cells Worksheet
Are you a 7th grade life science student seeking a comprehensive worksheet on cells? Look no further! This blog post is specifically designed for students like you, who are eager to deepen their understanding of cellular structures and functions. In this worksheet, we will explore various aspects of cells, including their different parts and their roles in maintaining life processes. Get ready to dive into the fascinating world of cells and enhance your knowledge in this important area of science!
Table of Images 👆
- 7th Grade Science Worksheets
- 7th Grade Life Science Worksheets
- Photosynthesis 7th Grade Science Worksheet Answers
- Plant and Animal Cell Worksheets 7th Grade
- Living Things Worksheet 7th Grade
- 7th Grade Science Study Guide
- 7th Grade Science Practice Tests
- 7th Grade Science Vocabulary Worksheets
- 5th Grade Reading Comprehension Worksheets
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
What is the basic unit of life that makes up all living organisms?
The basic unit of life that makes up all living organisms is the cell. Cells are the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism, and they are responsible for carrying out the essential processes of life such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Cells can vary in size, shape, and function, but they all share fundamental characteristics that make them the building blocks of life.
What is the main function of the cell membrane?
The main function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell by regulating the passage of substances in and out of the cell, maintaining the cell's internal environment. It also plays a crucial role in cell recognition, cell signaling, and communication with other cells. Additionally, the cell membrane helps in maintaining cell shape and structure.
What is the function of the nucleus in a cell?
The nucleus of a cell serves as the control center, managing and regulating the activities of the cell. It contains the cell's genetic material, DNA, which directs the synthesis of proteins and other essential molecules necessary for cell function. The nucleus also plays a crucial role in cell division, ensuring accurate replication and distribution of genetic material to daughter cells.
How does a plant cell differ from an animal cell?
One key difference between a plant cell and an animal cell is that plant cells have a cell wall composed of cellulose, which provides structural support and protection. Additionally, plant cells contain chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis and containing the pigment chlorophyll. Animal cells do not have cell walls or chloroplasts, but instead have lysosomes for digestive functions and centrioles for cell division.
What is the purpose of mitochondria in a cell?
The purpose of mitochondria in a cell is to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the primary energy source for the cell. Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell due to their role in converting nutrients into ATP through a process called cellular respiration.
What are the two types of endoplasmic reticulum present in a cell and what are their functions?
The two types of endoplasmic reticulum present in a cell are rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The RER is studded with ribosomes and is involved in protein synthesis and folding, while the SER is involved in lipid metabolism, detoxification, and calcium storage within the cell.
What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in a cell?
The Golgi apparatus in a cell plays a crucial role in processing, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids into vesicles for transportation to their designated locations within the cell or for secretion outside the cell. It modifies proteins by adding sugars and other molecules, acts as a post office by directing where these molecules should go, and ensures that the cell's internal and external environments are maintained in a coordinated manner.
How do cells obtain energy for their activities?
Cells obtain energy for their activities through a process called cellular respiration. During cellular respiration, glucose molecules are broken down in the presence of oxygen to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the energy currency of the cell. This process occurs in the mitochondria of the cell and is essential for various cellular functions such as growth, movement, and maintenance of homeostasis.
Define osmosis and explain its relevance to cell function.
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. In cell function, osmosis is crucial for maintaining the balance of water and solutes inside and outside the cell. It helps cells regulate their internal environment, prevent dehydration or overhydration, and ensure proper functioning by allowing water and essential nutrients to enter the cell while removing waste products. Failure to regulate osmosis can lead to cell damage or even cell death.
What is the process of cell division called, and what are its two main phases?
The process of cell division is called mitosis, and it consists of two main phases: the first phase is called prophase, during which the chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope breaks down; the second phase is called metaphase, where the chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell before separating into two daughter cells during anaphase and telophase.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
































Comments