6th Grade Science Worksheets Solar System
Are you searching for engaging and informative resources to reinforce the concepts of the solar system for your 6th grade science class? Look to worksheets as a valuable tool to enhance understanding and promote student engagement. With a variety of topics and exercises, these worksheets serve as an excellent supplement to classroom instruction, providing an effective means for students to practice and reinforce their knowledge of the solar system.
Table of Images 👆
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
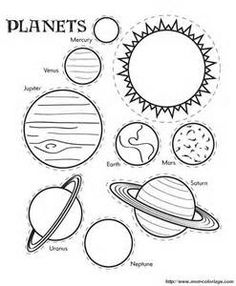
What is the Solar System?
The Solar System is a vast region in space that consists of the Sun at its center, surrounded by eight planets and their moons, as well as numerous asteroids, comets, and other objects. It also includes dwarf planets such as Pluto and Eris, as well as the Kuiper Belt and the Oort Cloud. The Solar System is bound together by gravity and has been a subject of observation and exploration for centuries.
How many planets are there in the Solar System?
There are eight planets in the Solar System: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
What is the largest planet in the Solar System?
Jupiter is the largest planet in the Solar System. It has a diameter of about 86,881 miles (139,822 kilometers) and is more than 11 times the size of Earth.
Which planet is closest to the Sun?
Mercury is the planet closest to the Sun in our solar system.
What are asteroids?
Asteroids are rocky, metallic objects that orbit the Sun and are significantly smaller than planets. They range in size from small boulders to hundreds of kilometers in diameter and are mostly found in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, as well as throughout the solar system. These remnants from the early solar system play a crucial role in studying the history and formation of our solar system.
What is a comet?
A comet is a small celestial body made up of ice, dust, and rock that orbits the sun in a highly elliptical path. As a comet gets closer to the sun, it heats up and releases dust and gas, forming a glowing coma and often a tail that points away from the sun due to solar wind.
What is the Kuiper Belt?
The Kuiper Belt is a region of our solar system beyond Neptune that is home to a vast number of small icy bodies, including dwarf planets such as Pluto. This belt is similar to the asteroid belt that lies between Mars and Jupiter but is much larger and contains predominantly icy objects. These objects are remnants from the early formation of the solar system and provide important insights into its history and composition.
How does Earth's tilt contribute to the changing seasons?
Earth's tilt plays a crucial role in the changing seasons by affecting the angle at which sunlight hits the planet. When a hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun, it receives more direct sunlight, leading to longer days, higher temperatures, and summer in that part of the world. Conversely, when a hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun, it receives less direct sunlight, resulting in shorter days, lower temperatures, and winter. As Earth orbits the Sun, the tilt causes the seasons to change as different parts of the planet receive varying amounts of sunlight throughout the year.
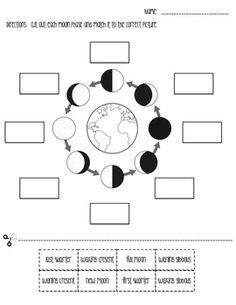
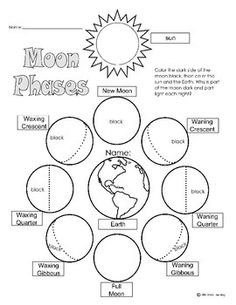
What are the phases of the Moon?
The phases of the Moon include new moon, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full moon, waning gibbous, last quarter, and waning crescent. These phases result from the changing positions of the Moon relative to the Earth and the Sun, leading to varying amounts of the Moon's illuminated side being visible from Earth.
How does gravity keep objects in orbit around the Sun?
Gravity keeps objects in orbit around the Sun by exerting a force that pulls the objects towards the Sun. This force, known as centripetal force, is balanced by the inertia of the object moving in a straight line. As a result, the object remains in a stable orbit, continuously falling towards the Sun due to gravity but also moving tangentially fast enough to stay in a circular or elliptical path around it.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments