5th Grade Science Worksheets Light
Are you searching for engaging and informative worksheets to reinforce your 5th-grade students' understanding of light in science class? Look no further! Our carefully curated collection of 5th-grade science worksheets covers a wide range of topics related to light, providing students with ample opportunities to explore and learn about this fascinating natural phenomenon.
Table of Images 👆
- Reflection Refraction Worksheet
- Sun Solar System Worksheets 3rd Grade
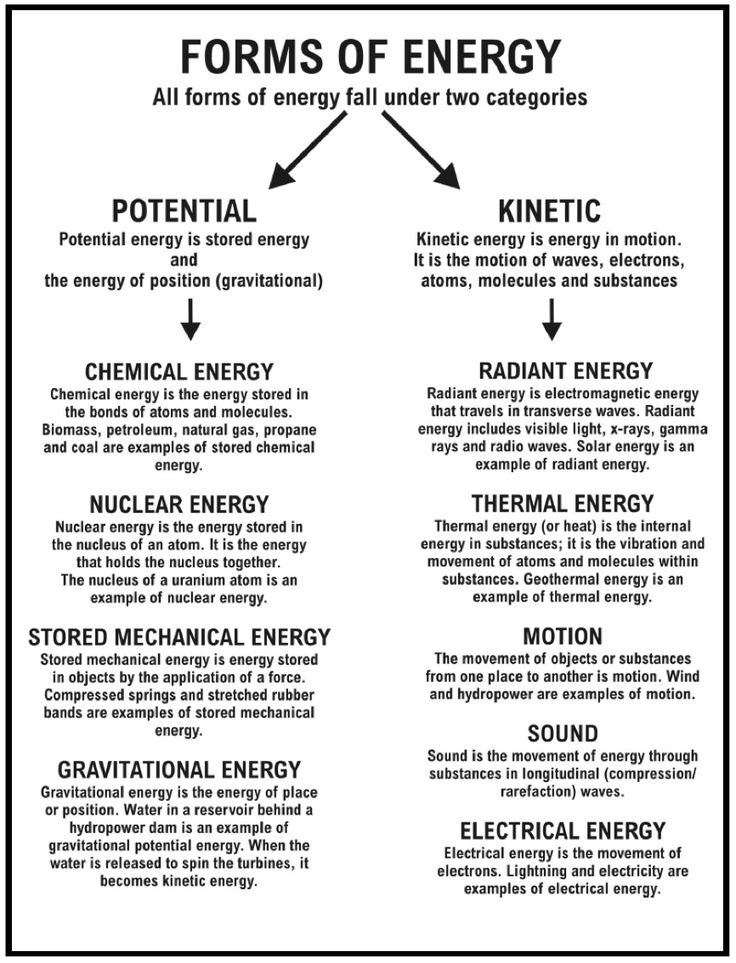
- Forms of Energy Worksheet Answers
- Science Electricity Worksheets 4th Grade
- Light and Sound Science Worksheet First Grade
- Natural Resources Worksheets 3rd Grade
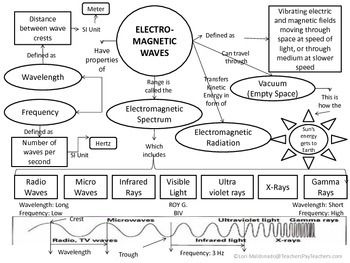
- Electromagnetic Wave Concept Map Worksheet
- Photosynthesis Comic Strip
- All About Me Activity Worksheets
- Potential Kinetic Energy Worksheet
More 5th Grade Worksheets
5th Grade Math Worksheets PrintableMultiplication Worksheets for 5th Grade
Constitution Worksheets for 5th Grade
Coordinates Worksheets 5th Grade
United States Worksheets 5th Grade
Free Division Worksheets for 5th Grade
Poetry Terms 5th Grade Worksheets
5th Grade Social Studies Printable Worksheets
What is light?
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye. It is made up of photons, which are tiny packets of energy that travel in a wave-like pattern. Light can be produced by natural sources such as the sun or by artificial sources like light bulbs, and it plays a crucial role in enabling us to see and perceive our surroundings.
How does light travel?
Light travels in the form of electromagnetic waves, which are a combination of electric and magnetic fields oscillating perpendicular to each other and to the direction of travel. These waves can travel through empty space at a speed of approximately 186,282 miles per second (299,792 kilometers per second) in a vacuum, but can also travel through transparent materials such as air, water, or glass at slightly slower speeds.
What is the speed of light?
The speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (186,282 miles per second).
How does light interact with different objects?
Light interacts with different objects through absorption, reflection, transmission, and scattering. When light hits an object, it can be absorbed, where the object captures and retains the light energy. Reflection occurs when light bounces off the surface of an object. Transmission happens when light passes through an object without being absorbed or reflected. Lastly, scattering occurs when light is deflected in different directions by irregularities or particles in the object. The interaction of light with objects depends on factors such as the object's material, texture, and surface characteristics.
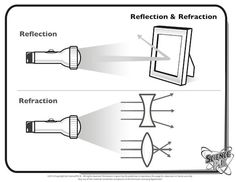
What is the difference between reflection and refraction?
Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media, such as when light bounces off a mirror. Refraction, on the other hand, is the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another, such as when light passes through a lens. In reflection, the wavefront returns into the same medium, while in refraction, the wavefront enters a new medium and changes direction.
How do we see colors?
We see colors through a process called color vision, which involves the eyes, brain, and light. The eyes contain specialized cells called cones that are able to detect different wavelengths of light. These cones then convert these light signals into electrical signals that are sent to the brain. The brain processes these signals to interpret the different wavelengths of light as different colors, allowing us to see and distinguish between the wide array of colors in our surroundings.
How does light allow us to see objects?
Light allows us to see objects through a process called vision. When light reflects off an object and enters our eyes, it is focused by the cornea and lens onto the retina at the back of the eye. The retina contains photoreceptor cells called rods and cones that convert the light into electrical signals, which are then transmitted to the brain via the optic nerve. The brain processes these signals to create the images we see, allowing us to perceive the shape, color, and texture of the objects around us.
What are the sources of light?
The primary sources of light are natural sources like the sun, stars, and fire, as well as artificial sources including light bulbs, lamps, and vehicles' headlights. Additionally, bioluminescent organisms and certain chemical reactions can also produce light.
How does light enable photosynthesis?
Light enables photosynthesis by providing the energy needed to drive the chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. Specifically, light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll in the chloroplasts of plant cells, which triggers a series of reactions that ultimately result in the conversion of light energy into chemical energy stored in the form of glucose. This process is crucial for plants to produce their own food and oxygen, which sustains life on Earth.
How does light affect our daily lives?
Light affects our daily lives in numerous ways, such as regulating our circadian rhythm and influencing our mood and energy levels. It also allows us to see and perceive the world around us, aiding in various activities like reading, working, and driving. Light is essential for plant growth and photosynthesis, which in turn sustains life on Earth. Additionally, light plays a crucial role in communication, art, and design, influencing our creativity and perception of the world.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments