3rd Grade Math Worksheets Graphs
If you're a 3rd grade teacher or a parent looking for a way to reinforce graphing skills with your child, you'll find that worksheets can be a helpful tool.
Table of Images 👆
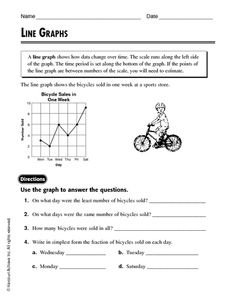
- Science Line Graph Worksheets
- Math Worksheets Printable
- Standard Form Place Value Worksheets
- Break Apart Method Multiplication Worksheets
- Line Plot Graph Worksheets 3rd Grade
- Printable Color by Number Coloring Pages
- 3rd Grade Reading Practice Tests
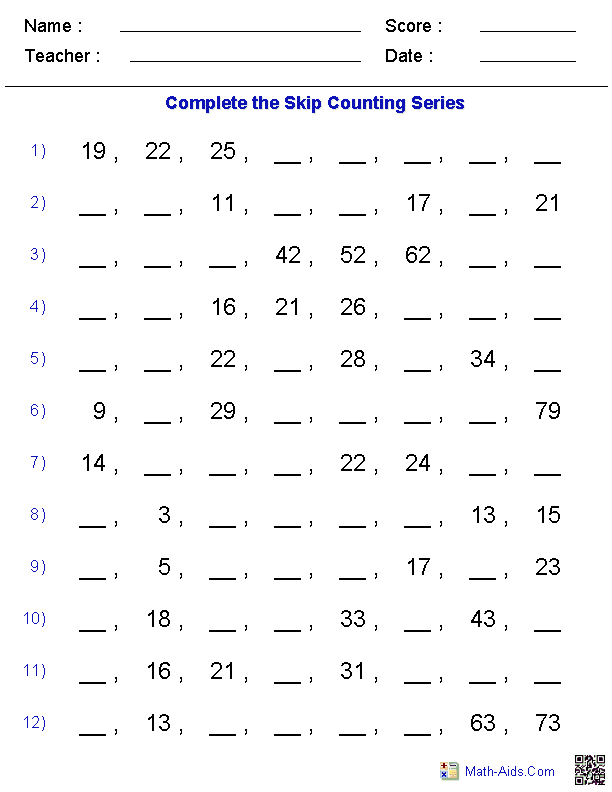
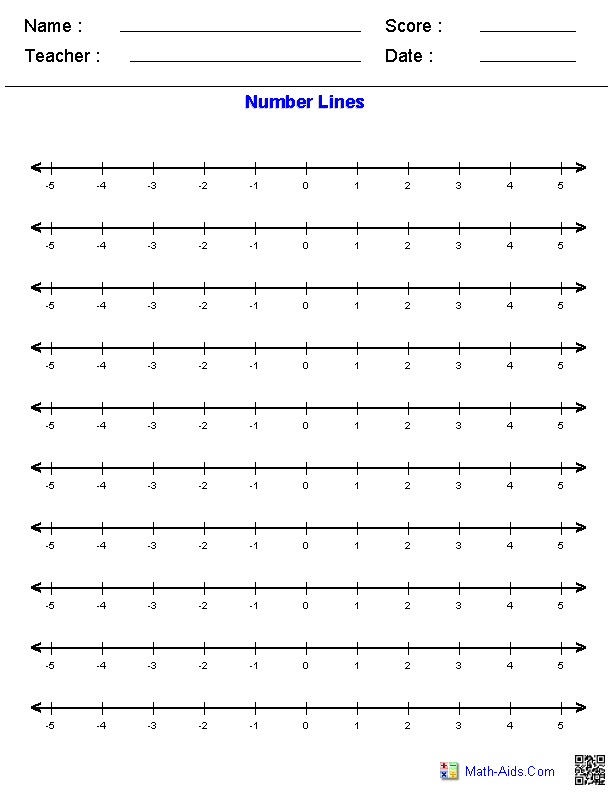
- Printable Number Line Worksheet
- PSSA 4th Grade Worksheets
- Free Printable Math Color by Number Addition Worksheets
- 3 by 2 Digit Multiplication Worksheets
- Blank Multiplication Times Table Chart
- Winter Word Searches and Crossword Puzzles
More 3rd Grade Worksheets
Telling Time Worksheets 3rd GradeTime Worksheets for 3rd Grade
3rd Grade Reading Comprehension Worksheets
Multiplication Worksheets for 3rd Grade
3rd Grade Math Division Worksheets Printable
Short Reading Comprehension Worksheets 3rd Grade
Soil Worksheets for 3rd Grade
Cursive Writing Worksheets for 3rd Grade
3rd Grade Multiplication Properties Worksheet
First Day of School Worksheets 3rd Grade
What is a graph?
A graph is a mathematical structure that represents relationships between pairs of objects. It consists of vertices, which are also called nodes or points, and edges, which are the lines or arcs connecting the vertices. Graphs are widely used in various fields such as mathematics, computer science, social sciences, and more to model complex systems, networks, and relationships.
How do you read and interpret a bar graph?
To read and interpret a bar graph, start by examining the horizontal (x-axis) and vertical (y-axis) axes to understand what data is being shown. Identify the categories or groups represented by the bars on the x-axis and the values or quantities being measured on the y-axis. Look at the length or height of each bar to compare the values or quantities they represent. Pay attention to the scale of the axes to understand the magnitude of the data being displayed. Analyze the patterns, trends, and relationships displayed by the bars to draw insights and conclusions from the bar graph.
What is the purpose of a line graph?
A line graph is used to show the relationship between two or more variables, displaying trends and patterns over time. It is effective in visualizing data points and identifying any correlations or changes in the data. Line graphs are commonly used in various fields such as economics, science, and business to illustrate patterns, trends, or comparisons in a clear and easy-to-understand manner.
How do you determine the scale or intervals on a graph?
To determine the scale or intervals on a graph, you first need to identify the range of values for the data you are plotting. Divide this range into equal segments that are easy to read and interpret, making sure to choose values that are convenient for the scale. Consider factors such as the precision of the data, the size of the graph, and the clarity of the intervals. Adjust the scale or intervals as needed to ensure that the graph accurately represents the data and is easily understood by the viewer.
What are the different types of graphs used in third grade math?
In third grade math, students typically learn about bar graphs, pictographs, and line plots. Bar graphs display data using rectangular bars of varying lengths, pictographs use pictures to represent data, and line plots show data points on a number line. These types of graphs help students organize and visually represent data in a clear and understandable way.
How do you compare data on a graph?
To compare data on a graph, first, look at the scale of the graph to understand the range and intervals for each data set. Next, visually compare the position, height, or length of the data points or bars on the graph to see which values are higher or lower. You can also use additional tools like trendlines, annotations, or color coding to emphasize and compare specific data points or trends on the graph. Additionally, consider the context of the data and any patterns or relationships that may be present to draw meaningful comparisons between different data sets.
What is the difference between a pictograph and a bar graph?
A pictograph uses pictures or symbols to represent data values, whereas a bar graph uses bars of various lengths to represent numerical data. Pictographs are more visually engaging and can help convey information in a simple and intuitive manner, while bar graphs are typically used to show comparisons between different categories or groups of data using a common scale.
How do you create a tally chart from data and vice versa?
To create a tally chart from data, you would first list the categories you want to track vertically down the left side of the chart. Then, for each data point that falls into a category, you make a vertical line next to that category heading. To convert a tally chart back to data, you count the number of tally marks for each category to determine the frequency or quantity of data points in that category.
How can you use a graph to make predictions or draw conclusions?
You can use a graph to make predictions or draw conclusions by analyzing trends, patterns, and relationships within the data displayed on the graph. By examining the direction and shape of the plotted points or lines, you can identify correlations, forecast future outcomes, or make inferences about the data. Additionally, you can compare different data sets or variables on the graph to uncover insights and relationships that may not be apparent from simply looking at the raw data. By studying the visual representation of data in a graph, you can make informed decisions and predictions based on the patterns and trends you observe.
What are some real-world examples of how graphs are used in everyday life?
Graphs are used in everyday life in a variety of ways, such as in social networks to map out connections between individuals, in transportation systems to optimize routes and schedules, in financial markets to analyze trends and make investment decisions, and in healthcare to track the spread of diseases and monitor patient data. Additionally, graphs are used in marketing to target specific demographics and measure campaign effectiveness, in internet search engines to rank websites and provide relevant results, and in computer networking to optimize data flow and troubleshoot connectivity issues.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






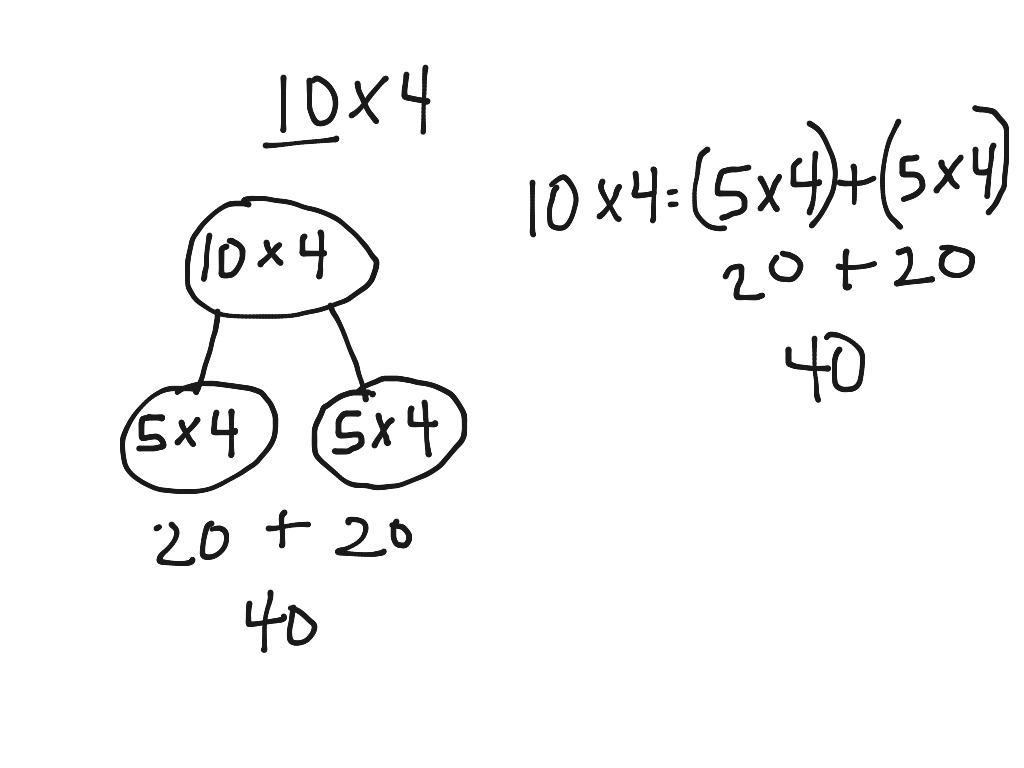


















Comments